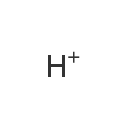
Hydrogen ion (ECMDB21225) (M2MDB001633)
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of 6- phosphogluconate to ribulose 5-phosphate and CO(2), with concomitant reduction of NADP to NADPH
- Gene Name:
- gnd
- Uniprot ID:
- P00350
- Molecular weight:
- 51481
Reactions
| 6-phospho-D-gluconate + NADP(+) = D-ribulose 5-phosphate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Two distinct, membrane-bound, FAD-containing enzymes are responsible for the catalysis of fumarate and succinate interconversion; the fumarate reductase is used in anaerobic growth, and the succinate dehydrogenase is used in aerobic growth
- Gene Name:
- frdA
- Uniprot ID:
- P00363
- Molecular weight:
- 65971
Reactions
| Succinate + acceptor = fumarate + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- L-glutamate + H(2)O + NADP(+) = 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- gdhA
- Uniprot ID:
- P00370
- Molecular weight:
- 48581
Reactions
| L-glutamate + H(2)O + NADP(+) = 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- Transfer of electrons from NADH to the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme is believed to be ubiquinone. Does not couple the redox reaction to proton translocation
- Gene Name:
- ndh
- Uniprot ID:
- P00393
- Molecular weight:
- 47358
Reactions
| NADH + acceptor = NAD(+) + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in superoxide dismutase activity
- Specific function:
- Destroys radicals which are normally produced within the cells and which are toxic to biological systems
- Gene Name:
- sodA
- Uniprot ID:
- P00448
- Molecular weight:
- 23097
Reactions
| 2 superoxide + 2 H(+) = O(2) + H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the ATP-dependent phosphorylation of L- homoserine to L-homoserine phosphate. Is also able to phosphorylate the hydroxy group on gamma-carbon of L-homoserine analogs when the functional group at the alpha-position is a carboxyl, an ester, or even a hydroxymethyl group. Neither L- threonine nor L-serine are substrates of the enzyme
- Gene Name:
- thrB
- Uniprot ID:
- P00547
- Molecular weight:
- 33623
Reactions
| ATP + L-homoserine = ADP + O-phospho-L-homoserine. |
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid binding
- Specific function:
- L-homoserine + NAD(P)(+) = L-aspartate 4- semialdehyde + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- thrA
- Uniprot ID:
- P00561
- Molecular weight:
- 89119
Reactions
| L-homoserine + NAD(P)(+) = L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde + NAD(P)H. |
| ATP + L-aspartate = ADP + 4-phospho-L-aspartate. |
- General function:
- Involved in cellular amino acid biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- L-homoserine + NAD(P)(+) = L-aspartate 4- semialdehyde + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- metL
- Uniprot ID:
- P00562
- Molecular weight:
- 88887
Reactions
| L-homoserine + NAD(P)(+) = L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde + NAD(P)H. |
| ATP + L-aspartate = ADP + 4-phospho-L-aspartate. |
- General function:
- Involved in asparaginase activity
- Specific function:
- L-asparagine + H(2)O = L-aspartate + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- ansB
- Uniprot ID:
- P00805
- Molecular weight:
- 36851
Reactions
| L-asparagine + H(2)O = L-aspartate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in cyanate hydratase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reaction of cyanate with bicarbonate to produce ammonia and carbon dioxide
- Gene Name:
- cynS
- Uniprot ID:
- P00816
- Molecular weight:
- 17049
Reactions
| Cyanate + HCO(3)(-) + 2 H(+) = NH(3) + 2 CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Meso-2,6-diaminoheptanedioate = L-lysine + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- lysA
- Uniprot ID:
- P00861
- Molecular weight:
- 46177
Reactions
| Meso-2,6-diaminoheptanedioate = L-lysine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- Through the carboxylation of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) it forms oxaloacetate, a four-carbon dicarboxylic acid source for the tricarboxylic acid cycle
- Gene Name:
- ppc
- Uniprot ID:
- P00864
- Molecular weight:
- 99062
Reactions
| Phosphate + oxaloacetate = H(2)O + phosphoenolpyruvate + HCO(3)(-). |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- 2 pyruvate = 2-acetolactate + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- ilvI
- Uniprot ID:
- P00893
- Molecular weight:
- 62984
Reactions
| 2 pyruvate = 2-acetolactate + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in acetolactate synthase activity
- Specific function:
- 2 pyruvate = 2-acetolactate + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- ilvH
- Uniprot ID:
- P00894
- Molecular weight:
- 17977
Reactions
| 2 pyruvate = 2-acetolactate + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Chorismate + L-glutamine = anthranilate + pyruvate + L-glutamate
- Gene Name:
- trpE
- Uniprot ID:
- P00895
- Molecular weight:
- 57494
Reactions
| Chorismate + L-glutamine = anthranilate + pyruvate + L-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in anthranilate phosphoribosyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Chorismate + L-glutamine = anthranilate + pyruvate + L-glutamate
- Gene Name:
- trpD
- Uniprot ID:
- P00904
- Molecular weight:
- 56869
Reactions
| Chorismate + L-glutamine = anthranilate + pyruvate + L-glutamate. |
| N-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)-anthranilate + diphosphate = anthranilate + 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Bifunctional enzyme that catalyzes two sequential steps of tryptophan biosynthetic pathway. The first reaction is catalyzed by the isomerase, coded by the trpF domain; the second reaction is catalyzed by the synthase, coded by the trpC domain
- Gene Name:
- trpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P00909
- Molecular weight:
- 49361
Reactions
| N-(5-phospho-beta-D-ribosyl)anthranilate = 1-(2-carboxyphenylamino)-1-deoxy-D-ribulose 5-phosphate. |
| 1-(2-carboxyphenylamino)-1-deoxy-D-ribulose 5-phosphate = 1-C-(3-indolyl)-glycerol 3-phosphate + CO(2) + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in D-serine ammonia-lyase activity
- Specific function:
- D-serine = pyruvate + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- dsdA
- Uniprot ID:
- P00926
- Molecular weight:
- 47900
Reactions
| D-serine = pyruvate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxal phosphate binding
- Specific function:
- O(4)-succinyl-L-homoserine + L-cysteine = L- cystathionine + succinate
- Gene Name:
- metB
- Uniprot ID:
- P00935
- Molecular weight:
- 41550
Reactions
| O(4)-succinyl-L-homoserine + L-cysteine = L-cystathionine + succinate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-tryptophan + tRNA(Trp) = AMP + diphosphate + L-tryptophyl-tRNA(Trp)
- Gene Name:
- trpS
- Uniprot ID:
- P00954
- Molecular weight:
- 37438
Reactions
| ATP + L-tryptophan + tRNA(Trp) = AMP + diphosphate + L-tryptophyl-tRNA(Trp). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the attachment of isoleucine to tRNA(Ile). As IleRS can inadvertently accommodate and process structurally similar amino acids such as valine, to avoid such errors it has two additional distinct tRNA(Ile)-dependent editing activities. One activity is designated as 'pretransfer' editing and involves the hydrolysis of activated Val-AMP. The other activity is designated 'posttransfer' editing and involves deacylation of mischarged Val-tRNA(Ile)
- Gene Name:
- ileS
- Uniprot ID:
- P00956
- Molecular weight:
- 104296
Reactions
| ATP + L-isoleucine + tRNA(Ile) = AMP + diphosphate + L-isoleucyl-tRNA(Ile). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Edits incorrectly charged Ser-tRNA(Ala) and Gly- tRNA(Ala) but not incorrectly charged Ser-tRNA(Thr)
- Gene Name:
- alaS
- Uniprot ID:
- P00957
- Molecular weight:
- 96032
Reactions
| ATP + L-alanine + tRNA(Ala) = AMP + diphosphate + L-alanyl-tRNA(Ala). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Is required not only for elongation of protein synthesis but also for the initiation of all mRNA translation through initiator tRNA(fMet) aminoacylation
- Gene Name:
- metG
- Uniprot ID:
- P00959
- Molecular weight:
- 76254
Reactions
| ATP + L-methionine + tRNA(Met) = AMP + diphosphate + L-methionyl-tRNA(Met). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + glycine + tRNA(Gly) = AMP + diphosphate + glycyl-tRNA(Gly)
- Gene Name:
- glyQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P00960
- Molecular weight:
- 34774
Reactions
| ATP + glycine + tRNA(Gly) = AMP + diphosphate + glycyl-tRNA(Gly). |
- General function:
- Involved in arginine-tRNA ligase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + glycine + tRNA(Gly) = AMP + diphosphate + glycyl-tRNA(Gly)
- Gene Name:
- glyS
- Uniprot ID:
- P00961
- Molecular weight:
- 76812
Reactions
| ATP + glycine + tRNA(Gly) = AMP + diphosphate + glycyl-tRNA(Gly). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-glutamine + tRNA(Gln) = AMP + diphosphate + L-glutaminyl-tRNA(Gln)
- Gene Name:
- glnS
- Uniprot ID:
- P00962
- Molecular weight:
- 63477
Reactions
| ATP + L-glutamine + tRNA(Gln) = AMP + diphosphate + L-glutaminyl-tRNA(Gln). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-aspartate + NH(3) = AMP + diphosphate + L-asparagine
- Gene Name:
- asnA
- Uniprot ID:
- P00963
- Molecular weight:
- 36650
Reactions
| ATP + L-aspartate + NH(3) = AMP + diphosphate + L-asparagine. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- 2 ATP + L-glutamine + HCO(3)(-) + H(2)O = 2 ADP + phosphate + L-glutamate + carbamoyl phosphate
- Gene Name:
- carB
- Uniprot ID:
- P00968
- Molecular weight:
- 117841
Reactions
| 2 ATP + L-glutamine + HCO(3)(-) + H(2)O = 2 ADP + phosphate + L-glutamate + carbamoyl phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Cell wall formation. Synthesis of cross-linked peptidoglycan from the lipid intermediates. The enzyme has a penicillin-insensitive transglycosylase N-terminal domain (formation of linear glycan strands) and a penicillin-sensitive transpeptidase C-terminal domain (cross-linking of the peptide subunits)
- Gene Name:
- mrcA
- Uniprot ID:
- P02918
- Molecular weight:
- 93636
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Cell wall formation. Synthesis of cross-linked peptidoglycan from the lipid intermediates. The enzyme has a penicillin-insensitive transglycosylase N-terminal domain (formation of linear glycan strands) and a penicillin-sensitive transpeptidase C-terminal domain (cross-linking of the peptide subunits)
- Gene Name:
- mrcB
- Uniprot ID:
- P02919
- Molecular weight:
- 94292
Reactions
| (GlcNAc-(1->4)-Mur2Ac(oyl-L-Ala-gamma-D-Glu-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala))(n)-diphosphoundecaprenol + GlcNAc-(1->4)-Mur2Ac(oyl-L-Ala-gamma-D-Glu-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala)-diphosphoundecaprenol = (GlcNAc-(1->4)-Mur2Ac(oyl-L-Ala-gamma-D-Glu-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala))(n+1)-diphosphoundecaprenol + undecaprenyl diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in potassium-transporting ATPase activity
- Specific function:
- One of the components of the high-affinity ATP-driven potassium transport (or KDP) system, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of hydrogen and potassium ions
- Gene Name:
- kdpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P03959
- Molecular weight:
- 59189
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + K(+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + K(+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- One of the components of the high-affinity ATP-driven potassium transport (or KDP) system, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of hydrogen and potassium ions
- Gene Name:
- kdpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P03960
- Molecular weight:
- 72198
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + K(+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + K(+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in potassium-transporting ATPase activity
- Specific function:
- One of the components of the high-affinity ATP-driven potassium transport (or KDP) system, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of hydrogen and potassium ions. The C subunit may be involved in assembly of the KDP complex
- Gene Name:
- kdpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P03961
- Molecular weight:
- 20267
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + K(+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + K(+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in dihydrodipicolinate reductase activity
- Specific function:
- 2,3,4,5-tetrahydrodipicolinate + NAD(P)(+) = 2,3-dihydrodipicolinate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- dapB
- Uniprot ID:
- P04036
- Molecular weight:
- 28756
Reactions
| (S)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrodipicolinate + NAD(P)(+) = (S)-2,3-dihydrodipicolinate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in GMP synthase (glutamine-hydrolyzing) activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the synthesis of GMP from XMP
- Gene Name:
- guaA
- Uniprot ID:
- P04079
- Molecular weight:
- 58679
Reactions
| ATP + xanthosine 5'-phosphate + L-glutamine + H(2)O = AMP + diphosphate + GMP + L-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in carboxyl- or carbamoyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Carbamoyl phosphate + L-ornithine = phosphate + L-citrulline
- Gene Name:
- argI
- Uniprot ID:
- P04391
- Molecular weight:
- 36907
Reactions
| Carbamoyl phosphate + L-ornithine = phosphate + L-citrulline. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + gamma-L-glutamyl-L-cysteine + glycine = ADP + phosphate + glutathione
- Gene Name:
- gshB
- Uniprot ID:
- P04425
- Molecular weight:
- 35561
Reactions
| ATP + gamma-L-glutamyl-L-cysteine + glycine = ADP + phosphate + glutathione. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the attachment of glutamate to tRNA(Glu) in a two-step reaction:glutamate is first activated by ATP to form Glu-AMP and then transferred to the acceptor end of tRNA(Glu)
- Gene Name:
- gltX
- Uniprot ID:
- P04805
- Molecular weight:
- 53815
Reactions
| ATP + L-glutamate + tRNA(Glu) = AMP + diphosphate + L-glutamyl-tRNA(Glu). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the formation of alpha-ketobutyrate from threonine in a two-step reaction. The first step is a dehydration of threonine, followed by rehydration and liberation of ammonia. Deaminates L-threonine, but also L-serine to a lesser extent
- Gene Name:
- ilvA
- Uniprot ID:
- P04968
- Molecular weight:
- 56195
Reactions
| L-threonine = 2-oxobutanoate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex RbsABCD involved in ribose import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- rbsA
- Uniprot ID:
- P04983
- Molecular weight:
- 55041
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + monosaccharide(Out) = ADP + phosphate + monosaccharide(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-dihydroorotate + H(2)O = N-carbamoyl-L- aspartate
- Gene Name:
- pyrC
- Uniprot ID:
- P05020
- Molecular weight:
- 38827
Reactions
| (S)-dihydroorotate + H(2)O = N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidation of erythronate-4-phosphate to 3- hydroxy-2-oxo-4-phosphonooxybutanoate
- Gene Name:
- pdxB
- Uniprot ID:
- P05459
- Molecular weight:
- 41367
Reactions
| 4-phospho-D-erythronate + NAD(+) = (3R)-3-hydroxy-2-oxo-4-phosphonooxybutanoate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in bis(5'-nucleosyl)-tetraphosphatase (symmetrical) activity
- Specific function:
- Hydrolyzes diadenosine 5',5'''-P1,P4-tetraphosphate to yield ADP
- Gene Name:
- apaH
- Uniprot ID:
- P05637
- Molecular weight:
- 31296
Reactions
| P(1),P(4)-bis(5'-adenosyl) tetraphosphate + H(2)O = 2 ADP. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- D-sorbitol 6-phosphate + NAD(+) = D-fructose 6-phosphate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- srlD
- Uniprot ID:
- P05707
- Molecular weight:
- 27858
Reactions
| D-sorbitol 6-phosphate + NAD(+) = D-fructose 6-phosphate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- (R)-2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate + NADP(+) = (S)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxobutanoate + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- ilvC
- Uniprot ID:
- P05793
- Molecular weight:
- 54069
Reactions
| (R)-2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate + NADP(+) = (S)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxobutanoate + NADPH. |
| (2R,3R)-2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylpentanoate + NADP(+) = (S)-2-hydroxy-2-ethyl-3-oxobutanoate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in flavin adenine dinucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- First component of the membrane-bound D-lactate oxidase, which is believed to play an important role in the energization of the active transport of a variety of sugars and amino acids
- Gene Name:
- dld
- Uniprot ID:
- P06149
- Molecular weight:
- 64612
Reactions
| (R)-lactate + NAD(+) = pyruvate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in CDP-diacylglycerol diphosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- CDP-diacylglycerol + H(2)O = CMP + phosphatidate
- Gene Name:
- cdh
- Uniprot ID:
- P06282
- Molecular weight:
- 28451
Reactions
| CDP-diacylglycerol + H(2)O = CMP + phosphatidate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex BtuCDF involved in vitamin B12 import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- btuD
- Uniprot ID:
- P06611
- Molecular weight:
- 27081
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + vitamin B12(Out) = ADP + phosphate + vitamin B12(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in biotin-[acetyl-CoA-carboxylase] ligase activity
- Specific function:
- BirA acts both as a biotin-operon repressor and as the enzyme that synthesizes the corepressor, acetyl-CoA:carbon-dioxide ligase. This protein also activates biotin to form biotinyl-5'- adenylate and transfers the biotin moiety to biotin-accepting proteins
- Gene Name:
- birA
- Uniprot ID:
- P06709
- Molecular weight:
- 35312
Reactions
| ATP + biotin + apo-[acetyl-CoA:carbon-dioxide ligase (ADP-forming)] = AMP + diphosphate + [acetyl-CoA:carbon-dioxide ligase (ADP-forming)]. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Maintains high levels of reduced glutathione in the cytosol
- Gene Name:
- gor
- Uniprot ID:
- P06715
- Molecular weight:
- 48772
Reactions
| 2 glutathione + NADP(+) = glutathione disulfide + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxal phosphate binding
- Specific function:
- L-cystathionine + H(2)O = L-homocysteine + NH(3) + pyruvate
- Gene Name:
- metC
- Uniprot ID:
- P06721
- Molecular weight:
- 43212
Reactions
| L-cystathionine + H(2)O = L-homocysteine + NH(3) + pyruvate. |
- General function:
- Involved in carboxyl- or carbamoyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Carbamoyl phosphate + L-ornithine = phosphate + L-citrulline
- Gene Name:
- argF
- Uniprot ID:
- P06960
- Molecular weight:
- 36827
Reactions
| Carbamoyl phosphate + L-ornithine = phosphate + L-citrulline. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- This enzyme is involved in nucleotide metabolism:it produces dUMP, the immediate precursor of thymidine nucleotides and it decreases the intracellular concentration of dUTP so that uracil cannot be incorporated into DNA
- Gene Name:
- dut
- Uniprot ID:
- P06968
- Molecular weight:
- 16155
Reactions
| dUTP + H(2)O = dUMP + diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the sequential NAD-dependent oxidations of L- histidinol to L-histidinaldehyde and then to L-histidine
- Gene Name:
- hisD
- Uniprot ID:
- P06988
- Molecular weight:
- 46110
Reactions
| L-histidinol + H(2)O + 2 NAD(+) = L-histidine + 2 NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphoribosyl-AMP cyclohydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- 1-(5-phosphoribosyl)-ATP + H(2)O = 1-(5- phosphoribosyl)-AMP + diphosphate
- Gene Name:
- hisI
- Uniprot ID:
- P06989
- Molecular weight:
- 22756
Reactions
| 1-(5-phosphoribosyl)-ATP + H(2)O = 1-(5-phosphoribosyl)-AMP + diphosphate. |
| 1-(5-phosphoribosyl)-AMP + H(2)O = 1-(5-phosphoribosyl)-5-((5-phosphoribosylamino)methylideneamino)imidazole-4-carboxamide. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- ATP + D-fructose 6-phosphate = ADP + D- fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
- Gene Name:
- pfkB
- Uniprot ID:
- P06999
- Molecular weight:
- 32456
Reactions
| ATP + D-fructose 6-phosphate = ADP + D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. |
- General function:
- Lipid transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- 2-lysophosphatidylcholine + H(2)O = glycerophosphocholine + a carboxylate
- Gene Name:
- pldB
- Uniprot ID:
- P07000
- Molecular weight:
- 38978
Reactions
| 2-lysophosphatidylcholine + H(2)O = glycerophosphocholine + a carboxylate. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- The transhydrogenation between NADH and NADP is coupled to respiration and ATP hydrolysis and functions as a proton pump across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- pntA
- Uniprot ID:
- P07001
- Molecular weight:
- 54623
Reactions
| NADPH + NAD(+) = NADP(+) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Pyruvate + ferricytochrome b1 + H(2)O = acetate + CO(2) + ferrocytochrome b1
- Gene Name:
- poxB
- Uniprot ID:
- P07003
- Molecular weight:
- 62011
Reactions
| Pyruvate + ubiquinone + H(2)O = acetate + CO(2) + ubiquinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NADPH dependent reduction of L-gamma- glutamyl 5-phosphate into L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde and phosphate. The product spontaneously undergoes cyclization to form 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate
- Gene Name:
- proA
- Uniprot ID:
- P07004
- Molecular weight:
- 44630
Reactions
| L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde + phosphate + NADP(+) = L-glutamyl 5-phosphate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- Chorismate = prephenate
- Gene Name:
- tyrA
- Uniprot ID:
- P07023
- Molecular weight:
- 42042
Reactions
| Chorismate = prephenate. |
| Prephenate + NAD(+) = 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate + CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Degradation of external UDP-glucose to uridine monophosphate and glucose-1-phosphate, which can then be used by the cell
- Gene Name:
- ushA
- Uniprot ID:
- P07024
- Molecular weight:
- 60824
Reactions
| UDP-sugar + H(2)O = UMP + alpha-D-aldose 1-phosphate. |
| A 5'-ribonucleotide + H(2)O = a ribonucleoside + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in acid phosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- A phosphate monoester + H(2)O = an alcohol + phosphate
- Gene Name:
- appA
- Uniprot ID:
- P07102
- Molecular weight:
- 47056
Reactions
| A phosphate monoester + H(2)O = an alcohol + phosphate. |
| Myo-inositol hexakisphosphate + H(2)O = 1D-myo-inositol 1,2,3,5,6-pentakisphosphate + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for histidine. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- hisP
- Uniprot ID:
- P07109
- Molecular weight:
- 28653
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the attachment of valine to tRNA(Val). As ValRS can inadvertently accommodate and process structurally similar amino acids such as threonine, to avoid such errors, it has a "posttransfer" editing activity that hydrolyzes mischarged Thr-tRNA(Val) in a tRNA-dependent manner
- Gene Name:
- valS
- Uniprot ID:
- P07118
- Molecular weight:
- 108192
Reactions
| ATP + L-valine + tRNA(Val) = AMP + diphosphate + L-valyl-tRNA(Val). |
- General function:
- Involved in RNA binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-phenylalanine + tRNA(Phe) = AMP + diphosphate + L-phenylalanyl-tRNA(Phe)
- Gene Name:
- pheT
- Uniprot ID:
- P07395
- Molecular weight:
- 87377
Reactions
| ATP + L-phenylalanine + tRNA(Phe) = AMP + diphosphate + L-phenylalanyl-tRNA(Phe). |
- General function:
- Involved in formate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity
- Specific function:
- Decomposes formic acid to hydrogen and carbon dioxide under anaerobic conditions in the absence of exogenous electron acceptors
- Gene Name:
- fdhF
- Uniprot ID:
- P07658
- Molecular weight:
- 79373
Reactions
| Formate + NAD(+) = CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-leucine + tRNA(Leu) = AMP + diphosphate + L-leucyl-tRNA(Leu)
- Gene Name:
- leuS
- Uniprot ID:
- P07813
- Molecular weight:
- 97233
Reactions
| ATP + L-leucine + tRNA(Leu) = AMP + diphosphate + L-leucyl-tRNA(Leu). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex fhuCDB involved in iron(3+)-hydroxamate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- fhuC
- Uniprot ID:
- P07821
- Molecular weight:
- 28886
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + iron chelate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + iron chelate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Cell wall formation
- Gene Name:
- ddlB
- Uniprot ID:
- P07862
- Molecular weight:
- 32839
Reactions
| ATP + 2 D-alanine = ADP + phosphate + D-alanyl-D-alanine. |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- L-threonine + NAD(+) = L-2-amino-3- oxobutanoate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- tdh
- Uniprot ID:
- P07913
- Molecular weight:
- 37239
Reactions
| L-threonine + NAD(+) = L-2-amino-3-oxobutanoate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- 2 pyruvate = 2-acetolactate + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- ilvB
- Uniprot ID:
- P08142
- Molecular weight:
- 60440
Reactions
| 2 pyruvate = 2-acetolactate + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + 2-(formamido)-N(1)-(5-phospho-D- ribosyl)acetamidine = ADP + phosphate + 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D- ribosyl)imidazole
- Gene Name:
- purM
- Uniprot ID:
- P08178
- Molecular weight:
- 36854
Reactions
| ATP + 2-(formamido)-N(1)-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)acetamidine = ADP + phosphate + 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydroxymethyl-, formyl- and related transferase activity
- Specific function:
- 10-formyltetrahydrofolate + N(1)-(5-phospho-D- ribosyl)glycinamide = tetrahydrofolate + N(2)-formyl-N(1)-(5- phospho-D-ribosyl)glycinamide
- Gene Name:
- purN
- Uniprot ID:
- P08179
- Molecular weight:
- 23238
Reactions
| 10-formyltetrahydrofolate + N(1)-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)glycinamide = tetrahydrofolate + N(2)-formyl-N(1)-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)glycinamide. |
- General function:
- Involved in tetrahydrofolylpolyglutamate synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Conversion of folates to polyglutamate derivatives
- Gene Name:
- folC
- Uniprot ID:
- P08192
- Molecular weight:
- 45405
Reactions
| ATP + tetrahydropteroyl-(gamma-Glu)(n) + L-glutamate = ADP + phosphate + tetrahydropteroyl-(gamma-Glu)(n+1). |
| ATP + 7,8-dihydropteroate + L-glutamate = ADP + phosphate + 7,8-dihydropteroylglutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Isocitrate + NADP(+) = 2-oxoglutarate + CO(2) + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- icd
- Uniprot ID:
- P08200
- Molecular weight:
- 45756
Reactions
| Isocitrate + NADP(+) = 2-oxoglutarate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- Ammonium hydroxide + 3 NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = nitrite + 3 NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- nirB
- Uniprot ID:
- P08201
- Molecular weight:
- 93121
Reactions
| Ammonium hydroxide + 3 NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = nitrite + 3 NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- ATP + L(or D)-ribulose = ADP + L(or D)- ribulose 5-phosphate
- Gene Name:
- araB
- Uniprot ID:
- P08204
- Molecular weight:
- 61089
Reactions
| ATP + L(or D)-ribulose = ADP + L(or D)-ribulose 5-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the decarboxylation of orotidine 5'- monophosphate (OMP) to uridine 5'-monophosphate (UMP)
- Gene Name:
- pyrF
- Uniprot ID:
- P08244
- Molecular weight:
- 26350
Reactions
| Orotidine 5'-phosphate = UMP + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-phenylalanine + tRNA(Phe) = AMP + diphosphate + L-phenylalanyl-tRNA(Phe)
- Gene Name:
- pheS
- Uniprot ID:
- P08312
- Molecular weight:
- 36832
Reactions
| ATP + L-phenylalanine + tRNA(Phe) = AMP + diphosphate + L-phenylalanyl-tRNA(Phe). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- This bifunctional enzyme catalyzes two consecutive reactions during ribonucleic acid degradation. Converts a 2',3'- cyclic nucleotide to a 3'-nucleotide and then the 3'-nucleotide to the corresponding nucleoside and phosphate
- Gene Name:
- cpdB
- Uniprot ID:
- P08331
- Molecular weight:
- 70832
Reactions
| Nucleoside 2',3'-cyclic phosphate + H(2)O = nucleoside 3'-phosphate. |
| A 3'-ribonucleotide + H(2)O = a ribonucleoside + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in flavin adenine dinucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Cell wall formation
- Gene Name:
- murB
- Uniprot ID:
- P08373
- Molecular weight:
- 37851
Reactions
| UDP-N-acetylmuramate + NADP(+) = UDP-N-acetyl-3-O-(1-carboxyvinyl)-D-glucosamine + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Acetyl-CoA + H(2)O + glyoxylate = (S)-malate + CoA
- Gene Name:
- aceB
- Uniprot ID:
- P08997
- Molecular weight:
- 60273
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + H(2)O + glyoxylate = (S)-malate + CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- Possesses an ATPase activity that is dependent on the presence of AIR (aminoimidazole ribonucleotide). The association of purK and purE produces an enzyme complex capable of converting AIR to CAIR efficiently under physiological condition
- Gene Name:
- purK
- Uniprot ID:
- P09029
- Molecular weight:
- 39461
Reactions
| ATP + 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole + HCO(3)(-) = ADP + phosphate + 5-carboxyamino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole. |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity
- Specific function:
- L-valine + pyruvate = 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate + L-alanine
- Gene Name:
- avtA
- Uniprot ID:
- P09053
- Molecular weight:
- 46711
Reactions
| L-valine + pyruvate = 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate + L-alanine. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- ATP + D-xylulose = ADP + D-xylulose 5- phosphate
- Gene Name:
- xylB
- Uniprot ID:
- P09099
- Molecular weight:
- 52618
Reactions
| ATP + D-xylulose = ADP + D-xylulose 5-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Coenzyme transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- S-adenosyl-L-methionine + uroporphyrinogen III = S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + precorrin-1
- Gene Name:
- hemX
- Uniprot ID:
- P09127
- Molecular weight:
- 42963
Reactions
| S-adenosyl-L-methionine + uroporphyrinogen III = S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + precorrin-1. |
| S-adenosyl-L-methionine + precorrin-1 = S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + precorrin-2. |
- General function:
- Involved in 2-isopropylmalate synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the condensation of the acetyl group of acetyl-CoA with 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate (2-oxoisovalerate) to form 3-carboxy-3-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoate (2-isopropylmalate)
- Gene Name:
- leuA
- Uniprot ID:
- P09151
- Molecular weight:
- 57297
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate + H(2)O = (2S)-2-isopropylmalate + CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- The nitrate reductase enzyme complex allows E.coli to use nitrate as an electron acceptor during anaerobic growth. The alpha chain is the actual site of nitrate reduction
- Gene Name:
- narG
- Uniprot ID:
- P09152
- Molecular weight:
- 140489
Reactions
| Nitrite + acceptor = nitrate + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the production of spermidine from putrescine and decarboxylated S-adenosylmethionine (dcSAM), which serves as an aminopropyl donor
- Gene Name:
- speE
- Uniprot ID:
- P09158
- Molecular weight:
- 32321
Reactions
| S-adenosylmethioninamine + putrescine = 5'-S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine + spermidine. |
- General function:
- Involved in glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase activity
- Specific function:
- Glycerophosphoryl diester phosphodiesterase hydrolyzes deacylated phospholipids to G3P and the corresponding alcohols
- Gene Name:
- glpQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P09394
- Molecular weight:
- 40843
Reactions
| A glycerophosphodiester + H(2)O = an alcohol + sn-glycerol 3-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- D-mannitol 1-phosphate + NAD(+) = D-fructose 6-phosphate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- mtlD
- Uniprot ID:
- P09424
- Molecular weight:
- 41139
Reactions
| D-mannitol 1-phosphate + NAD(+) = D-fructose 6-phosphate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Oxidizes proline to glutamate for use as a carbon and nitrogen source and also function as a transcriptional repressor of the put operon
- Gene Name:
- putA
- Uniprot ID:
- P09546
- Molecular weight:
- 143814
Reactions
| L-proline + acceptor = (S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate + reduced acceptor. |
| (S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate + NAD(P)(+) + 2 H(2)O = L-glutamate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- 2 L-glutamate + NADP(+) = L-glutamine + 2- oxoglutarate + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- gltB
- Uniprot ID:
- P09831
- Molecular weight:
- 166708
Reactions
| 2 L-glutamate + NADP(+) = L-glutamine + 2-oxoglutarate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in iron-sulfur cluster binding
- Specific function:
- 2 L-glutamate + NADP(+) = L-glutamine + 2- oxoglutarate + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- gltD
- Uniprot ID:
- P09832
- Molecular weight:
- 52015
Reactions
| 2 L-glutamate + NADP(+) = L-glutamine + 2-oxoglutarate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the removal of elemental sulfur and selenium atoms from cysteine and selenocysteine to produce alanine. Functions as a sulfur delivery protein for NAD, biotin and Fe-S cluster synthesis. Transfers sulfur on 'Cys-456' of thiI in a transpersulfidation reaction. Transfers sulfur on 'Cys-19' of tusA in a transpersulfidation reaction. Functions also as a selenium delivery protein in the pathway for the biosynthesis of selenophosphate
- Gene Name:
- iscS
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6B7
- Molecular weight:
- 45089
Reactions
| L-cysteine + acceptor = L-alanine + S-sulfanyl-acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in cellular amino acid biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Acetyl-CoA + L-glutamate = CoA + N-acetyl-L- glutamate
- Gene Name:
- argA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6C5
- Molecular weight:
- 49195
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + L-glutamate = CoA + N-acetyl-L-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- The physiological substrate is not known
- Gene Name:
- ydiB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6D5
- Molecular weight:
- 31228
Reactions
| L-quinate + NAD(P)(+) = 3-dehydroquinate + NAD(P)H. |
| Shikimate + NAD(P)(+) = 3-dehydroshikimate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in shikimate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the specific phosphorylation of the 3-hydroxyl group of shikimic acid using ATP as a cosubstrate
- Gene Name:
- aroK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6D7
- Molecular weight:
- 19538
Reactions
| ATP + shikimate = ADP + shikimate 3-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in shikimate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the specific phosphorylation of the 3-hydroxyl group of shikimic acid using ATP as a cosubstrate
- Gene Name:
- aroL
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6E1
- Molecular weight:
- 19151
Reactions
| ATP + shikimate = ADP + shikimate 3-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in argininosuccinate synthase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-citrulline + L-aspartate = AMP + diphosphate + N(omega)-(L-arginino)succinate
- Gene Name:
- argG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6E4
- Molecular weight:
- 49898
Reactions
| ATP + L-citrulline + L-aspartate = AMP + diphosphate + N(omega)-(L-arginino)succinate. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism
- Specific function:
- Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- atpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6E6
- Molecular weight:
- 15068
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + 7,8-diaminononanoate + CO(2) = ADP + phosphate + dethiobiotin
- Gene Name:
- ynfK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6E9
- Molecular weight:
- 24981
Reactions
| ATP + 7,8-diaminononanoate + CO(2) = ADP + phosphate + dethiobiotin. |
- General function:
- Involved in glutamine catabolic process
- Specific function:
- 2 ATP + L-glutamine + HCO(3)(-) + H(2)O = 2 ADP + phosphate + L-glutamate + carbamoyl phosphate
- Gene Name:
- carA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6F1
- Molecular weight:
- 41431
Reactions
| 2 ATP + L-glutamine + HCO(3)(-) + H(2)O = 2 ADP + phosphate + L-glutamate + carbamoyl phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Key enzyme in the regulation of glycerol uptake and metabolism
- Gene Name:
- glpK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6F3
- Molecular weight:
- 56230
Reactions
| ATP + glycerol = ADP + sn-glycerol 3-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in pantothenate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + (R)-pantothenate = ADP + (R)-4'- phosphopantothenate
- Gene Name:
- coaA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6I3
- Molecular weight:
- 36359
Reactions
| ATP + (R)-pantothenate = ADP + (R)-4'-phosphopantothenate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Reversibly transfers an adenylyl group from ATP to 4'- phosphopantetheine, yielding dephospho-CoA (dPCoA) and pyrophosphate
- Gene Name:
- coaD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6I6
- Molecular weight:
- 17837
Reactions
| ATP + pantetheine 4'-phosphate = diphosphate + 3'-dephospho-CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in dephospho-CoA kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of the 3'-hydroxyl group of dephosphocoenzyme A to form coenzyme A
- Gene Name:
- coaE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6I9
- Molecular weight:
- 22622
Reactions
| ATP + 3'-dephospho-CoA = ADP + CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in adenylylsulfate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the synthesis of activated sulfate
- Gene Name:
- cysC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6J1
- Molecular weight:
- 22321
Reactions
| ATP + adenylyl sulfate = ADP + 3'-phosphoadenylyl sulfate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Cell wall formation
- Gene Name:
- ddlA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6J8
- Molecular weight:
- 39315
Reactions
| ATP + 2 D-alanine = ADP + phosphate + D-alanyl-D-alanine. |
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Removes the formyl group from the N-terminal Met of newly synthesized proteins. Requires at least a dipeptide for an efficient rate of reaction. N-terminal L-methionine is a prerequisite for activity but the enzyme has broad specificity at other positions
- Gene Name:
- def
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6K3
- Molecular weight:
- 19328
Reactions
| Formyl-L-methionyl peptide + H(2)O = formate + methionyl peptide. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde + pyruvate = dihydrodipicolinate + 2 H(2)O
- Gene Name:
- dapA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6L2
- Molecular weight:
- 31270
Reactions
| L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde + pyruvate = dihydrodipicolinate + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- D-altronate + NAD(+) = D-tagaturonate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- uxaB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6L7
- Molecular weight:
- 54808
Reactions
| D-altronate + NAD(+) = D-tagaturonate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the condensation reaction of fatty acid synthesis by the addition to an acyl acceptor of two carbons from malonyl-ACP. Catalyzes the first condensation reaction which initiates fatty acid synthesis and may therefore play a role in governing the total rate of fatty acid production. Possesses both acetoacetyl-ACP synthase and acetyl transacylase activities. Has some substrate specificity for acetyl-CoA. Its substrate specificity determines the biosynthesis of straight-chain of fatty acids instead of branched-chain
- Gene Name:
- fabH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6R0
- Molecular weight:
- 33515
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + malonyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] = acetoacetyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + CoA + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- sn-glycerol 3-phosphate + NAD(P)(+) = glycerone phosphate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- gpsA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6S7
- Molecular weight:
- 36361
Reactions
| sn-glycerol 3-phosphate + NAD(P)(+) = glycerone phosphate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in galactokinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + D-galactose = ADP + alpha-D-galactose 1- phosphate
- Gene Name:
- galK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6T3
- Molecular weight:
- 41442
Reactions
| ATP + D-galactose = ADP + alpha-D-galactose 1-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in GTP cyclohydrolase I activity
- Specific function:
- GTP + H(2)O = formate + 2-amino-4-hydroxy-6- (erythro-1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl)-dihydropteridine triphosphate
- Gene Name:
- folE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6T5
- Molecular weight:
- 24830
Reactions
| GTP + H(2)O = formate + 2-amino-4-hydroxy-6-(erythro-1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl)-dihydropteridine triphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Synthesizes alpha-1,4-glucan chains using ADP-glucose
- Gene Name:
- glgA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6U8
- Molecular weight:
- 52822
Reactions
| ADP-glucose + (1,4-alpha-D-glucosyl)(n) = ADP + (1,4-alpha-D-glucosyl)(n+1). |
- General function:
- Involved in glycogen biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- ATP + alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate = diphosphate + ADP-glucose
- Gene Name:
- glgC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6V1
- Molecular weight:
- 48697
Reactions
| ATP + alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate = diphosphate + ADP-glucose. |
- General function:
- Involved in thiosulfate sulfurtransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes, although with low efficiency, the sulfur transfer reaction from thiosulfate to cyanide. The relatively low affinity of glpE for both thiosulfate and cyanide suggests that these compounds are not the physiological substrates. Thioredoxin 1 or related dithiol proteins could instead be the physiological sulfur-acceptor substrate. Possible association with the metabolism of glycerol-phosphate remains to be elucidated
- Gene Name:
- glpE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6V5
- Molecular weight:
- 12082
Reactions
| Thiosulfate + cyanide = sulfite + thiocyanate. |
- General function:
- Involved in glucokinase activity
- Specific function:
- Not highly important in E.coli as glucose is transported into the cell by the PTS system already as glucose 6-phosphate
- Gene Name:
- glk
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6V8
- Molecular weight:
- 34723
Reactions
| ATP + D-glucose = ADP + D-glucose 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in glutamate-cysteine ligase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-glutamate + L-cysteine = ADP + phosphate + gamma-L-glutamyl-L-cysteine
- Gene Name:
- gshA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6W9
- Molecular weight:
- 58269
Reactions
| ATP + L-glutamate + L-cysteine = ADP + phosphate + gamma-L-glutamyl-L-cysteine. |
- General function:
- Involved in glutamyl-tRNA reductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of glutamyl- tRNA(Glu) to glutamate 1-semialdehyde (GSA). In the absence of NADPH, exhibits substrate esterase activity, leading to the release of glutamate from tRNA
- Gene Name:
- hemA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6X1
- Molecular weight:
- 46306
Reactions
| L-glutamate 1-semialdehyde + NADP(+) + tRNA(Glu) = L-glutamyl-tRNA(Glu) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate:hydrogen symporter activity
- Specific function:
- The 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate permease transports the degraded pectin products into the bacterial cell, where they serve as carbon and energy sources. This is a hydrogen coupled transport system
- Gene Name:
- kdgT
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A712
- Molecular weight:
- 33669
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + D-ribose 5-phosphate = AMP + 5-phospho- alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate
- Gene Name:
- prs
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A717
- Molecular weight:
- 34218
Reactions
| ATP + D-ribose 5-phosphate = AMP + 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reversible adenylation of nicotinate mononucleotide (NaMN) to nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide (NaAD)
- Gene Name:
- nadD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A752
- Molecular weight:
- 24528
Reactions
| ATP + beta-nicotinate-D-ribonucleotide = diphosphate + deamido-NAD(+). |
- General function:
- Involved in carboxyl- or carbamoyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Carbamoyl phosphate + L-aspartate = phosphate + N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
- Gene Name:
- pyrB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A786
- Molecular weight:
- 34427
Reactions
| Carbamoyl phosphate + L-aspartate = phosphate + N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate. |
- General function:
- Involved in aspartate 1-decarboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the pyruvoyl-dependent decarboxylation of aspartate to produce beta-alanine
- Gene Name:
- panD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A790
- Molecular weight:
- 13834
Reactions
| L-aspartate = beta-alanine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the complicated ring closure reaction between the two acyclic compounds 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate (DXP) and 3-amino-2-oxopropyl phosphate (1-amino-acetone-3-phosphate or AAP) to form pyridoxine 5'-phosphate (PNP) and inorganic phosphate
- Gene Name:
- pdxJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A794
- Molecular weight:
- 26384
Reactions
| 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate + 3-amino-2-oxopropyl phosphate = pyridoxine 5'-phosphate + phosphate + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + D-fructose 6-phosphate = ADP + D- fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
- Gene Name:
- pfkA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A796
- Molecular weight:
- 34842
Reactions
| ATP + D-fructose 6-phosphate = ADP + D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in protein-L-isoaspartate (D-aspartate) O-methyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the methyl esterification of L-isoaspartyl residues in peptides and proteins that result from spontaneous decomposition of normal L-aspartyl and L-asparaginyl residues. It plays a role in the repair and/or degradation of damaged proteins. This enzyme does not act on D-aspartyl residues
- Gene Name:
- pcm
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A7A5
- Molecular weight:
- 23258
Reactions
| S-adenosyl-L-methionine + protein L-isoaspartate = S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + protein L-isoaspartate alpha-methyl ester. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Diphosphate + H(2)O = 2 phosphate
- Gene Name:
- ppa
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A7A9
- Molecular weight:
- 19703
Reactions
| Diphosphate + H(2)O = 2 phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in NAD+ kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of NAD to NADP. Utilizes ATP and other nucleoside triphosphates as well as inorganic polyphosphate as a source of phosphorus
- Gene Name:
- ppnK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A7B3
- Molecular weight:
- 32566
Reactions
| ATP + NAD(+) = ADP + NADP(+). |
- General function:
- Involved in adenylosuccinate synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Plays an important role in the de novo pathway of purine nucleotide biosynthesis. Catalyzes the first commited step in the biosynthesis of AMP from IMP
- Gene Name:
- purA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A7D4
- Molecular weight:
- 47345
Reactions
| GTP + IMP + L-aspartate = GDP + phosphate + N(6)-(1,2-dicarboxyethyl)-AMP. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D- ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxylate + L-aspartate = ADP + phosphate + (S)-2-(5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4- carboxamido)succinate
- Gene Name:
- purC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A7D7
- Molecular weight:
- 26995
Reactions
| ATP + 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxylate + L-aspartate = ADP + phosphate + (S)-2-(5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamido)succinate. |
- General function:
- Involved in CTP synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the ATP-dependent amination of UTP to CTP with either L-glutamine or ammonia as the source of nitrogen
- Gene Name:
- pyrG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A7E5
- Molecular weight:
- 60374
Reactions
| ATP + UTP + NH(3) = ADP + phosphate + CTP. |
- General function:
- Involved in 'de novo' pyrimidine base biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Involved in allosteric regulation of aspartate carbamoyltransferase
- Gene Name:
- pyrI
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A7F3
- Molecular weight:
- 17121
- General function:
- Involved in adenosylmethionine decarboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the decarboxylation of S-adenosylmethionine to S-adenosylmethioninamine (dcAdoMet), the propylamine donor required for the synthesis of the polyamines spermine and spermidine from the diamine putrescine
- Gene Name:
- speD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A7F6
- Molecular weight:
- 30384
Reactions
| S-adenosyl-L-methionine = (5-deoxy-5-adenosyl)(3-aminopropyl)-methylsulfonium salt + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in GTP cyclohydrolase II activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the conversion of GTP to 2,5-diamino-6- ribosylamino-4(3H)-pyrimidinone 5'-phosphate (DARP), formate and pyrophosphate
- Gene Name:
- ribA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A7I7
- Molecular weight:
- 21836
Reactions
| GTP + 3 H(2)O = formate + 2,5-diamino-6-hydroxy-4-(5-phospho-D-ribosylamino)pyrimidine + diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in 3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone-4-phosphate synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the conversion of D-ribulose 5-phosphate to formate and 3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone 4-phosphate
- Gene Name:
- ribB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A7J0
- Molecular weight:
- 23353
Reactions
| D-ribulose 5-phosphate = formate + L-3,4-dihydroxybutan-2-one 4-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Converts seryl-tRNA(Sec) to selenocysteinyl-tRNA(Sec) required for selenoprotein biosynthesis. Requires selenophosphate as the selenium-donor molecule
- Gene Name:
- selA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A821
- Molecular weight:
- 50607
Reactions
| L-seryl-tRNA(Sec) + selenophosphate = L-selenocysteinyl-tRNA(Sec) + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Interconversion of serine and glycine
- Gene Name:
- glyA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A825
- Molecular weight:
- 45316
Reactions
| 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + glycine + H(2)O = tetrahydrofolate + L-serine. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Nucleotidase with a broad substrate specificity as it can dephosphorylate various ribo- and deoxyribonucleoside 5'- monophosphates and ribonucleoside 3'-monophosphates with highest affinity to 3'-AMP. Also hydrolyzes polyphosphate (exopolyphosphatase activity) with the preference for short-chain- length substrates (P20-25). Might be involved in the regulation of dNTP and NTP pools, and in the turnover of 3'-mononucleotides produced by numerous intracellular RNases (T1, T2, and F) during the degradation of various RNAs. Also plays a significant physiological role in stress-response and is required for the survival of E.coli in stationary growth phase
- Gene Name:
- surE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A840
- Molecular weight:
- 26900
Reactions
| A 5'-ribonucleotide + H(2)O = a ribonucleoside + phosphate. |
| A 3'-ribonucleotide + H(2)O = a ribonucleoside + phosphate. |
| (Polyphosphate)(n) + H(2)O = (polyphosphate)(n-1) + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in lyase activity
- Specific function:
- L-tryptophan + H(2)O = indole + pyruvate + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- tnaA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A853
- Molecular weight:
- 52773
Reactions
| L-tryptophan + H(2)O = indole + pyruvate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + uridine = ADP + UMP
- Gene Name:
- udk
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A8F4
- Molecular weight:
- 24353
Reactions
| ATP + uridine = ADP + UMP. |
| ATP + cytidine = ADP + CMP. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphatidylserine decarboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- Phosphatidyl-L-serine = phosphatidylethanolamine + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- psd
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A8K1
- Molecular weight:
- 35934
Reactions
| Phosphatidyl-L-serine = phosphatidylethanolamine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the attachment of serine to tRNA(Ser). Is also able to aminoacylate tRNA(Sec) with serine, to form the misacylated tRNA L-seryl-tRNA(Sec), which will be further converted into selenocysteinyl-tRNA(Sec)
- Gene Name:
- serS
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A8L1
- Molecular weight:
- 48414
Reactions
| ATP + L-serine + tRNA(Ser) = AMP + diphosphate + L-seryl-tRNA(Ser). |
| ATP + L-serine + tRNA(Sec) = AMP + diphosphate + L-seryl-tRNA(Sec). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-asparagine + tRNA(Asn) = AMP + diphosphate + L-asparaginyl-tRNA(Asn)
- Gene Name:
- asnS
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A8M0
- Molecular weight:
- 52570
Reactions
| ATP + L-asparagine + tRNA(Asn) = AMP + diphosphate + L-asparaginyl-tRNA(Asn). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Also can synthesize a number of adenyl dinucleotides (in particular AppppA). These dinucleotides have been proposed to act as modulators of the heat-shock response and stress response
- Gene Name:
- lysU
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A8N5
- Molecular weight:
- 57826
Reactions
| ATP + L-lysine + tRNA(Lys) = AMP + diphosphate + L-lysyl-tRNA(Lys). |
- General function:
- Energy production and conversion
- Specific function:
- Seems to be involved in the anchoring of the catalytic components of the fumarate reductase complex to the cytoplasmic membrane
- Gene Name:
- frdC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A8Q0
- Molecular weight:
- 15015
- General function:
- Involved in fumarate metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Seems to be involved in the anchoring of the catalytic components of the fumarate reductase complex to the cytoplasmic membrane
- Gene Name:
- frdD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A8Q3
- Molecular weight:
- 13107
- General function:
- Involved in phospholipase activity
- Specific function:
- Has broad substrate specificity including hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine with phospholipase A2 (EC 3.1.1.4) and phospholipase A1 (EC 3.1.1.32) activities. Strong expression leads to outer membrane breakdown and cell death; is dormant in normal growing cells. Required for efficient secretion of bacteriocins
- Gene Name:
- pldA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A921
- Molecular weight:
- 33163
Reactions
| Phosphatidylcholine + H(2)O = 2-acylglycerophosphocholine + a carboxylate. |
| Phosphatidylcholine + H(2)O = 1-acylglycerophosphocholine + a carboxylate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Hydrolyzes phosphatidylglycerophosphate, phosphatidic acid, and lysophosphatidic acid; the pattern of activities varies according to subcellular location
- Gene Name:
- pgpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A924
- Molecular weight:
- 29021
Reactions
| Phosphatidylglycerophosphate + H(2)O = phosphatidylglycerol + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in N-acetyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Regulates polyamine concentration by their degradation. Acts on spermidine, forming N(1)- and N(8)-acetylspermidine
- Gene Name:
- speG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A951
- Molecular weight:
- 21887
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + an alkane-alpha,omega-diamine = CoA + an N-acetyldiamine. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the condensation reaction of fatty acid synthesis by the addition to an acyl acceptor of two carbons from malonyl-ACP. Specific for elongation from C-10 to unsaturated C-16 and C-18 fatty acids
- Gene Name:
- fabB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A953
- Molecular weight:
- 42613
Reactions
| Acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + malonyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] = 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + CO(2) + [acyl-carrier-protein]. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- 4-hydroxy-2-oxoglutarate = pyruvate + glyoxylate
- Gene Name:
- eda
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A955
- Molecular weight:
- 22284
Reactions
| 4-hydroxy-2-oxoglutarate = pyruvate + glyoxylate. |
| 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-gluconate 6-phosphate = pyruvate + D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in asparaginase activity
- Specific function:
- L-asparagine + H(2)O = L-aspartate + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- ansA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A962
- Molecular weight:
- 37127
Reactions
| L-asparagine + H(2)O = L-aspartate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the aldehyde or oxo group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
- Specific function:
- D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + phosphate + NAD(+) = 3-phospho-D-glyceroyl phosphate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- gapA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9B2
- Molecular weight:
- 35532
Reactions
| D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + phosphate + NAD(+) = 3-phospho-D-glyceroyl phosphate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in erythrose-4-phosphate dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NAD-dependent conversion of D-erythrose 4- phosphate to 4-phosphoerythronate
- Gene Name:
- epd
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9B6
- Molecular weight:
- 37299
Reactions
| D-erythrose 4-phosphate + NAD(+) + H(2)O = 4-phosphoerythronate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in glutamate-ammonia ligase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-glutamate + NH(3) = ADP + phosphate + L-glutamine
- Gene Name:
- glnA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9C5
- Molecular weight:
- 51903
Reactions
| ATP + L-glutamate + NH(3) = ADP + phosphate + L-glutamine. |
- General function:
- Involved in protein binding
- Specific function:
- Conjugation of reduced glutathione to a wide number of exogenous and endogenous hydrophobic electrophiles
- Gene Name:
- gst
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9D2
- Molecular weight:
- 22868
Reactions
| RX + glutathione = HX + R-S-glutathione. |
- General function:
- Involved in carboxy-lyase activity
- Specific function:
- Appears to play a role in pH homeostasis by consuming protons and neutralizing the acidic by-products of carbohydrate fermentation
- Gene Name:
- cadA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9H3
- Molecular weight:
- 81260
Reactions
| L-lysine = cadaverine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Required for both de novo synthesis of the corrin ring for the assimilation of exogenous corrinoids. Participates in the adenosylation of a variety of incomplete and complete corrinoids
- Gene Name:
- btuR
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9H5
- Molecular weight:
- 21999
Reactions
| ATP + cob(I)yrinic acid a,c-diamide = triphosphate + adenosylcob(III)yrinic acid a,c-diamide. |
| ATP + cobinamide = triphosphate + adenosylcobinamide. |
- General function:
- Involved in lipid biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Transfers a methylene group from S-adenosyl-L-methionine to the cis double bond of an unsaturated fatty acid chain resulting in the replacement of the double bond with a methylene bridge
- Gene Name:
- cfa
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9H7
- Molecular weight:
- 43909
Reactions
| S-adenosyl-L-methionine + phospholipid olefinic fatty acid = S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + phospholipid cyclopropane fatty acid. |
- General function:
- Involved in nitrite reductase [NAD(P)H] activity
- Specific function:
- Required for activity of the reductase
- Gene Name:
- nirD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9I8
- Molecular weight:
- 12284
Reactions
| Ammonium hydroxide + 3 NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = nitrite + 3 NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of ketopantoate into pantoic acid
- Gene Name:
- panE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9J4
- Molecular weight:
- 33871
Reactions
| (R)-pantoate + NADP(+) = 2-dehydropantoate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- ATP + D-ribose = ADP + D-ribose 5-phosphate
- Gene Name:
- rbsK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9J6
- Molecular weight:
- 32290
Reactions
| ATP + D-ribose = ADP + D-ribose 5-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in chorismate mutase activity
- Specific function:
- Chorismate = prephenate
- Gene Name:
- pheA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9J8
- Molecular weight:
- 43111
Reactions
| Chorismate = prephenate. |
| Prephenate = phenylpyruvate + H(2)O + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- L-proline + NAD(P)(+) = 1-pyrroline-5- carboxylate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- proC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9L8
- Molecular weight:
- 28145
Reactions
| L-proline + NAD(P)(+) = 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in [formate-C-acetyltransferase]-activating enzyme activity
- Specific function:
- Activation of anaerobic ribonucleoside-triphosphate reductase under anaerobic conditions by generation of an organic free radical, using S-adenosylmethionine and reduced flavodoxin as cosubstrates to produce 5'-deoxy-adenosine
- Gene Name:
- nrdG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9N8
- Molecular weight:
- 17446
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Lipoamide dehydrogenase is a component of the glycine cleavage system as well as of the alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complexes
- Gene Name:
- lpdA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9P0
- Molecular weight:
- 50688
Reactions
| Protein N(6)-(dihydrolipoyl)lysine + NAD(+) = protein N(6)-(lipoyl)lysine + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- Thioredoxin + NADP(+) = thioredoxin disulfide + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- trxB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9P4
- Molecular weight:
- 34623
Reactions
| Thioredoxin + NADP(+) = thioredoxin disulfide + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes a reversible reduction of 5-ketoglutanate to form D-gluconate. Dependent on NADP, almost inactive with NAD
- Gene Name:
- idnO
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9P9
- Molecular weight:
- 27563
Reactions
| D-gluconate + NAD(P)(+) = 5-dehydro-D-gluconate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- Controls translation of mRNA for both itself and the alpha-subunit (accA) by binding to a probable hairpin in the 5' of the mRNA. Binding to mRNA inhibits translation; this is partially relieved by acetyl-CoA. Increasing amounts of mRNA also inhibit enzyme activity
- Gene Name:
- accD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9Q5
- Molecular weight:
- 33322
Reactions
| ATP + acetyl-CoA + HCO(3)(-) = ADP + phosphate + malonyl-CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- This enzyme has three activities:ADH, ACDH, and PFL- deactivase. In aerobic conditions it acts as a hydrogen peroxide scavenger. The PFL deactivase activity catalyzes the quenching of the pyruvate-formate-lyase catalyst in an iron, NAD, and CoA dependent reaction
- Gene Name:
- adhE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9Q7
- Molecular weight:
- 96126
Reactions
| An alcohol + NAD(+) = an aldehyde or ketone + NADH. |
| Acetaldehyde + CoA + NAD(+) = acetyl-CoA + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde + phosphate + NADP(+) = L-4-aspartyl phosphate + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- asd
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9Q9
- Molecular weight:
- 40018
Reactions
| L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde + phosphate + NADP(+) = L-4-aspartyl phosphate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- (R)-propane-1,2-diol + NAD(+) = (R)- lactaldehyde + NADH
- Gene Name:
- fucO
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9S1
- Molecular weight:
- 40644
Reactions
| (R)-propane-1,2-diol + NAD(+) = (R)-lactaldehyde + NADH. |
| (S)-propane-1,2-diol + NAD(+) = (S)-lactaldehyde + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Converts galactitol 1-phosphate to tagatose 6-phosphate
- Gene Name:
- gatD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9S3
- Molecular weight:
- 37390
Reactions
| Galactitol-1-phosphate + NAD(+) = L-tagatose 6-phosphate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NAD-dependent oxidation of glycerol to dihydroxyacetone (glycerone). Allows microorganisms to utilize glycerol as a source of carbon under anaerobic conditions. In E.coli, an important role of gldA is also likely to regulate the intracellular level of dihydroxyacetone by catalyzing the reverse reaction, i.e. the conversion of dihydroxyacetone into glycerol. Possesses a broad substrate specificity, since it is also able to oxidize 1,2-propanediol and to reduce glycolaldehyde, methylglyoxal and hydroxyacetone into ethylene glycol, lactaldehyde and 1,2-propanediol, respectively
- Gene Name:
- gldA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9S5
- Molecular weight:
- 38712
Reactions
| Glycerol + NAD(+) = glycerone + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid binding
- Specific function:
- 3-phospho-D-glycerate + NAD(+) = 3- phosphonooxypyruvate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- serA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9T0
- Molecular weight:
- 44175
Reactions
| 3-phospho-D-glycerate + NAD(+) = 3-phosphonooxypyruvate + NADH. |
| 2-hydroxyglutarate + NAD(+) = 2-oxoglutarate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in enzyme regulator activity
- Specific function:
- UTP + alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate = diphosphate + UDP-glucose
- Gene Name:
- galF
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAB6
- Molecular weight:
- 32829
Reactions
| UTP + alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate = diphosphate + UDP-glucose. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex AraFGH involved in arabinose import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- araG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAF3
- Molecular weight:
- 55018
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + monosaccharide(Out) = ADP + phosphate + monosaccharide(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex MglABC involved in galactose/methyl galactoside import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- mglA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAG8
- Molecular weight:
- 56415
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + monosaccharide(Out) = ADP + phosphate + monosaccharide(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex pstSACB involved in phosphate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- pstB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAH0
- Molecular weight:
- 29027
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + phosphate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + phosphate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring acyl groups other than amino-acyl groups
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the condensation reaction of fatty acid synthesis by the addition to an acyl acceptor of two carbons from malonyl-ACP. Has a preference for short chain acid substrates and may function to supply the octanoic substrates for lipoic acid biosynthesis
- Gene Name:
- fabF
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAI5
- Molecular weight:
- 43045
Reactions
| (Z)-hexadec-11-enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + malonyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] = (Z)-3-oxooctadec-13-enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + CO(2) + [acyl-carrier-protein]. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Electron transfer subunit of the terminal reductase during anaerobic growth on various sulfoxide and N-oxide compounds
- Gene Name:
- ynfG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAJ1
- Molecular weight:
- 22752
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Formate dehydrogenase allows E.coli to use formate as major electron donor during anaerobic respiration, when nitrate is used as electron acceptor. The beta chain is an electron transfer unit containing 4 cysteine clusters involved in the formation of iron-sulfur centers. Electrons are transferred from the gamma chain to the molybdenum cofactor of the alpha subunit
- Gene Name:
- fdnH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAJ3
- Molecular weight:
- 32239
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Allows to use formate as major electron donor during aerobic respiration. The beta chain is an electron transfer unit containing 4 cysteine clusters involved in the formation of iron- sulfur centers. Electrons are transferred from the gamma chain to the molybdenum cofactor of the alpha subunit
- Gene Name:
- fdoH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAJ5
- Molecular weight:
- 33100
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Probable electron transfer protein for hydrogenase 3
- Gene Name:
- hycB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAK1
- Molecular weight:
- 21873
- General function:
- Involved in acylphosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- An acylphosphate + H(2)O = a carboxylate + phosphate
- Gene Name:
- yccX
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AB65
- Molecular weight:
- 10300
Reactions
| An acylphosphate + H(2)O = a carboxylate + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in NAD(P)+ transhydrogenase (AB-specific) activity
- Specific function:
- The transhydrogenation between NADH and NADP is coupled to respiration and ATP hydrolysis and functions as a proton pump across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- pntB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AB67
- Molecular weight:
- 48723
Reactions
| NADPH + NAD(+) = NADP(+) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Key component of the proton channel; it plays a direct role in the translocation of protons across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- atpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AB98
- Molecular weight:
- 30303
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the F(0) channel, it forms part of the peripheral stalk, linking F(1) to F(0)
- Gene Name:
- atpF
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABA0
- Molecular weight:
- 17264
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism
- Specific function:
- This protein is part of the stalk that links CF(0) to CF(1). It either transmits conformational changes from CF(0) to CF(1) or is implicated in proton conduction
- Gene Name:
- atpH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABA4
- Molecular weight:
- 19332
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism
- Specific function:
- Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane. The gamma chain is believed to be important in regulating ATPase activity and the flow of protons through the CF(0) complex
- Gene Name:
- atpG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABA6
- Molecular weight:
- 31577
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane. The alpha chain is a regulatory subunit
- Gene Name:
- atpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABB0
- Molecular weight:
- 55222
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + H(+)(In) = ADP + phosphate + H(+)(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane. The catalytic sites are hosted primarily by the beta subunits
- Gene Name:
- atpD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABB4
- Molecular weight:
- 50325
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + H(+)(In) = ADP + phosphate + H(+)(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, catalyzing transmembrane movement of substances
- Specific function:
- Mediates magnesium influx to the cytosol
- Gene Name:
- mgtA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABB8
- Molecular weight:
- 99466
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Mg(2+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + Mg(2+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase (ACC) complex. First, biotin carboxylase catalyzes the carboxylation of biotin on its carrier protein (BCCP) and then the CO(2) group is transferred by the carboxyltransferase to acetyl-CoA to form malonyl-CoA
- Gene Name:
- accA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABD5
- Molecular weight:
- 35241
Reactions
| ATP + acetyl-CoA + HCO(3)(-) = ADP + phosphate + malonyl-CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of the acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase complex; first, biotin carboxylase catalyzes the carboxylation of the carrier protein and then the transcarboxylase transfers the carboxyl group to form malonyl-CoA
- Gene Name:
- accB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABD8
- Molecular weight:
- 16687
- General function:
- Involved in carbonate dehydratase activity
- Specific function:
- Reversible hydration of carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide formed in the bicarbonate-dependent decomposition of cyanate by cyanase (cynS) diffuses out of the cell faster than it would be hydrated to bicarbonate, so the apparent function of this enzyme is to catalyze the hydration of carbon dioxide and thus prevent depletion of cellular bicarbonate
- Gene Name:
- cynT
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABE9
- Molecular weight:
- 23764
Reactions
| H(2)CO(3) = CO(2) + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- This enzyme scavenge exogenous and endogenous cytidine and 2'-deoxycytidine for UMP synthesis
- Gene Name:
- cdd
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABF6
- Molecular weight:
- 31539
Reactions
| Cytidine + H(2)O = uridine + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, for other substituted phosphate groups
- Specific function:
- This protein catalyzes the committed step to the synthesis of the acidic phospholipids
- Gene Name:
- pgsA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABF8
- Molecular weight:
- 20700
Reactions
| CDP-diacylglycerol + sn-glycerol 3-phosphate = CMP + 3(3-sn-phosphatidyl)-sn-glycerol 1-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups
- Specific function:
- CTP + phosphatidate = diphosphate + CDP- diacylglycerol
- Gene Name:
- cdsA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABG1
- Molecular weight:
- 31453
Reactions
| CTP + phosphatidate = diphosphate + CDP-diacylglycerol. |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring acyl groups, acyl groups converted into alkyl on transfer
- Specific function:
- Acetyl-CoA + H(2)O + oxaloacetate = citrate + CoA
- Gene Name:
- gltA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABH7
- Molecular weight:
- 48015
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + H(2)O + oxaloacetate = citrate + CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in cysteine biosynthetic process from serine
- Specific function:
- O(3)-acetyl-L-serine + H(2)S = L-cysteine + acetate
- Gene Name:
- cysK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABK5
- Molecular weight:
- 34489
Reactions
| O(3)-acetyl-L-serine + H(2)S = L-cysteine + acetate. |
| 3-chloro-L-alanine + thioglycolate = S-carboxymethyl-L-cysteine + chloride. |
- General function:
- Involved in nitrogen compound metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Plays a role in nitrite reduction
- Gene Name:
- nrfA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABK9
- Molecular weight:
- 53703
Reactions
| NH(3) + 2 H(2)O + 6 ferricytochrome c = nitrite + 6 ferrocytochrome c + 7 H(+). |
- General function:
- Involved in diacylglycerol kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Recycling of diacylglycerol produced during the turnover of membrane phospholipid
- Gene Name:
- dgkA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABN1
- Molecular weight:
- 13245
Reactions
| ATP + 1,2-diacylglycerol = ADP + 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in purine-nucleoside phosphorylase activity
- Specific function:
- Cleavage of guanosine or inosine to respective bases and sugar-1-phosphate molecules
- Gene Name:
- deoD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABP8
- Molecular weight:
- 25950
Reactions
| Purine nucleoside + phosphate = purine + alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphopantothenate--cysteine ligase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes two steps in the biosynthesis of coenzyme A. In the first step cysteine is conjugated to 4'-phosphopantothenate to form 4-phosphopantothenoylcysteine, in the latter compound is decarboxylated to form 4'-phosphopantotheine
- Gene Name:
- coaBC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABQ0
- Molecular weight:
- 43438
Reactions
| N-((R)-4'-phosphopantothenoyl)-L-cysteine = pantotheine 4'-phosphate + CO(2). |
| CTP + (R)-4'-phosphopantothenate + L-cysteine = CMP + diphosphate + N-((R)-4'-phosphopantothenoyl)-L-cysteine. |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- (R)-glycerate + NAD(P)(+) = 2-hydroxy-3- oxopropanoate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- garR
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABQ2
- Molecular weight:
- 30427
Reactions
| D-glycerate + NAD(P)(+) = 2-hydroxy-3-oxopropanoate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in dihydrofolate reductase activity
- Specific function:
- Key enzyme in folate metabolism. Catalyzes an essential reaction for de novo glycine and purine synthesis, and for DNA precursor synthesis
- Gene Name:
- folA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABQ4
- Molecular weight:
- 17999
Reactions
| 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate + NADP(+) = 7,8-dihydrofolate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the multicomponent 3-phenylpropionate dioxygenase. Converts 3-phenylpropionic acid (PP) and cinnamic acid (CI) into 3-phenylpropionate-dihydrodiol (PP-dihydrodiol) and cinnamic acid-dihydrodiol (CI-dihydrodiol), respectively
- Gene Name:
- hcaE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABR5
- Molecular weight:
- 51109
Reactions
| 3-phenylpropanoate + NADH + O(2) = 3-(cis-5,6-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,3-dien-1-yl)propanoate + NAD(+). |
| (2E)-3-phenylprop-2-enoate + NADH + O(2) = (2E)-3-(2,3-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate + NAD(+). |
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the non-heme iron(II)-dependent oxidative cleavage of 2,3-dihydroxyphenylpropionic acid and 2,3- dihydroxicinnamic acid into 2-hydroxy-6-ketononadienedioate and 2- hydroxy-6-ketononatrienedioate, respectively
- Gene Name:
- mhpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABR9
- Molecular weight:
- 34196
Reactions
| 3-(2,3-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoate + O(2) = 2-hydroxy-6-oxonona-2,4-diene-1,9-dioate. |
| (2E)-3-(2,3-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate + O(2) = 2-hydroxy-6-oxonona-2,4,7-triene-1,9-dioate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Converts o-succinylbenzoyl-CoA (OSB-CoA) to 1,4- dihydroxy-2-naphthoyl-CoA (DHNA-CoA)
- Gene Name:
- menB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABU0
- Molecular weight:
- 31633
Reactions
| 4-(2-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxobutanoyl-CoA = 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoyl-CoA + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the multicomponent 3-phenylpropionate dioxygenase, that converts 3-phenylpropionic acid (PP) and cinnamic acid (CI) into 3-phenylpropionate-dihydrodiol (PP- dihydrodiol) and cinnamic acid-dihydrodiol (CI-dihydrodiol), respectively. This protein seems to be a 2Fe-2S ferredoxin
- Gene Name:
- hcaC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABW0
- Molecular weight:
- 11329
- General function:
- Involved in aspartate ammonia-lyase activity
- Specific function:
- L-aspartate = fumarate + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- aspA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AC38
- Molecular weight:
- 52356
Reactions
| L-aspartate = fumarate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Two distinct, membrane-bound, FAD-containing enzymes are responsible for the catalysis of fumarate and succinate interconversion; the fumarate reductase is used in anaerobic growth, and the succinate dehydrogenase is used in aerobic growth
- Gene Name:
- frdB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AC47
- Molecular weight:
- 27123
Reactions
| Succinate + acceptor = fumarate + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- D-glucose 6-phosphate + NADP(+) = D-glucono- 1,5-lactone 6-phosphate + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- zwf
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AC53
- Molecular weight:
- 55704
Reactions
| D-glucose 6-phosphate + NADP(+) = 6-phospho-D-glucono-1,5-lactone + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Essential step in lipopolysaccharides biosynthesis. Acts at transfer of 3-deoxy-D-mono octulonic acid (KDO) from CMP-KDO to a tetraacyldisaccharide 1,4'-bisphosphate precursor of lipid A (lipid IVA). Transfers two molecules of KDO to lipid IVA. Degraded by FtsH; therefore FtsH regulates the addition of the sugar moiety of the LPS and thus the maturation of the LPS precursor
- Gene Name:
- waaA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AC75
- Molecular weight:
- 47291
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Thiolesterase that catalyzes the hydrolysis of S-D- lactoyl-glutathione to form glutathione and D-lactic acid
- Gene Name:
- gloB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AC84
- Molecular weight:
- 28434
Reactions
| S-(2-hydroxyacyl)glutathione + H(2)O = glutathione + a 2-hydroxy carboxylate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes an early step in the biosynthesis of tetrapyrroles. Binds two molecules of 5-aminolevulinate per subunit, each at a distinct site, and catalyzes their condensation to form porphobilinogen
- Gene Name:
- hemB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ACB2
- Molecular weight:
- 35624
Reactions
| 2 5-aminolevulinate = porphobilinogen + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the last two sequential reactions in the de novo biosynthetic pathway for UDP-GlcNAc. Responsible for the acetylation of Glc-N-1-P to give GlcNAc-1-P and for the uridyl transfer from UTP to GlcNAc-1-P which produces UDP-GlcNAc
- Gene Name:
- glmU
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ACC7
- Molecular weight:
- 49190
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + alpha-D-glucosamine 1-phosphate = CoA + N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine 1-phosphate. |
| UTP + N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine 1-phosphate = diphosphate + UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine. |
- General function:
- Involved in nickel cation binding
- Specific function:
- This is one of three E.coli hydrogenases synthesized in response to different physiological conditions. HYD1 is believed to have a role in hydrogen cycling during fermentative growth
- Gene Name:
- hyaB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ACD8
- Molecular weight:
- 66253
Reactions
| H(2) + A = AH(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in nickel cation binding
- Specific function:
- This is one of three E.coli hydrogenases synthesized in response to different physiological conditions. HYD2 is involved in hydrogen uptake
- Gene Name:
- hybC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ACE0
- Molecular weight:
- 62491
Reactions
| H(2) + A = AH(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + pyruvate = ADP + phosphoenolpyruvate
- Gene Name:
- pykF
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AD61
- Molecular weight:
- 50729
Reactions
| ATP + pyruvate = ADP + phosphoenolpyruvate. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Hydrolyzes only long chain acyl thioesters (C12-C18). Specificity similar to chymotrypsin
- Gene Name:
- tesA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ADA1
- Molecular weight:
- 23622
Reactions
| 2-lysophosphatidylcholine + H(2)O = glycerophosphocholine + a carboxylate. |
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid binding
- Specific function:
- 2 pyruvate = 2-acetolactate + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- ilvN
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ADF8
- Molecular weight:
- 11106
Reactions
| 2 pyruvate = 2-acetolactate + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in acetolactate synthase activity
- Specific function:
- 2 pyruvate = 2-acetolactate + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- ilvM
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ADG1
- Molecular weight:
- 9703
Reactions
| 2 pyruvate = 2-acetolactate + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Inosine 5'-phosphate + NAD(+) + H(2)O = xanthosine 5'-phosphate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- guaB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ADG7
- Molecular weight:
- 52022
Reactions
| Inosine 5'-phosphate + NAD(+) + H(2)O = xanthosine 5'-phosphate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in isochorismatase activity
- Specific function:
- Required for production of 2,3-DHB. Also serves as an aryl carrier protein and plays a role in enterobactin assembly
- Gene Name:
- entB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ADI4
- Molecular weight:
- 32554
Reactions
| Isochorismate + H(2)O = 2,3-dihydroxy-2,3-dihydrobenzoate + pyruvate. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Can oxidize menadiol to menadione
- Gene Name:
- ygiN
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ADU2
- Molecular weight:
- 11532
- General function:
- Involved in arginine N-succinyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the transfer of succinyl-CoA to arginine to produce N(2)-succinylarginine
- Gene Name:
- astA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE37
- Molecular weight:
- 38456
Reactions
| Succinyl-CoA + L-arginine = CoA + N(2)-succinyl-L-arginine. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- ATP-dependent phosphorylation of adenosylcobinamide and adds GMP to adenosylcobinamide phosphate
- Gene Name:
- cobU
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE76
- Molecular weight:
- 20164
Reactions
| ATP or GTP + adenosylcobinamide = adenosylcobinamide phosphate + ADP or GDP. |
| GTP + adenosylcobinamide phosphate = diphosphate + adenosylcobinamide-GDP. |
- General function:
- Involved in methyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Multifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the SAM-dependent methylation of uroporphyrinogen III at position C-2 and C-7 to form precorrin-2 and then position C-12 or C-18 to form trimethylpyrrocorphin 2. It also catalyzes the conversion of precorrin-2 into siroheme. This reaction consists of the NAD- dependent oxidation of precorrin-2 into sirohydrochlorin and its subsequent ferrochelation into siroheme
- Gene Name:
- cysG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEA8
- Molecular weight:
- 49951
Reactions
| S-adenosyl-L-methionine + uroporphyrinogen III = S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + precorrin-1. |
| S-adenosyl-L-methionine + precorrin-1 = S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + precorrin-2. |
| Precorrin-2 + NAD(+) = sirohydrochlorin + NADH. |
| Siroheme + 2 H(+) = sirohydrochlorin + Fe(2+). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the hydrolysis of 4-amino-2-methyl-5- hydroxymethylpyrimidine pyrophosphate (HMP-PP) to 4-amino-2- methyl-5-hydroxymethylpyrimidine phosphate (HMP-P), and hydrolysis of thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) to thiamine monophosphate (TMP). Can hydrolyze other substrates such as MeO-HMP-PP, CF(3)-HMP-PP and MeO-TPP. Is also a non-specific nucleoside tri- and diphosphatase that releases inorganic orthophosphate
- Gene Name:
- nudJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEI6
- Molecular weight:
- 17433
- General function:
- Involved in 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADPH) activity
- Specific function:
- (3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NADP(+) = 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- fabG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEK2
- Molecular weight:
- 25560
Reactions
| (3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NADP(+) = 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADH) activity
- Specific function:
- Acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NAD(+) = trans- 2,3-dehydroacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NADH
- Gene Name:
- fabI
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEK4
- Molecular weight:
- 27864
Reactions
| Acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NAD(+) = trans-2,3-dehydroacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in respiratory electron transport chain
- Specific function:
- Formate dehydrogenase allows E.coli to use formate as major electron donor during anaerobic respiration, when nitrate is used as electron acceptor. Subunit gamma is the cytochrome b556(FDN) component of the formate dehydrogenase
- Gene Name:
- fdnI
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEK7
- Molecular weight:
- 25368
- General function:
- Involved in respiratory electron transport chain
- Specific function:
- Allows to use formate as major electron donor during aerobic respiration. Subunit gamma is probably the cytochrome b556(FDO) component of the formate dehydrogenase
- Gene Name:
- fdoI
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEL0
- Molecular weight:
- 24606
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reduction of soluble flavins by reduced pyridine nucleotides. Seems to reduces the complexed Fe(3+) iron of siderophores to Fe(2+), thus releasing it from the chelator
- Gene Name:
- fre
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEN1
- Molecular weight:
- 26242
Reactions
| Reduced riboflavin + NAD(P)(+) = riboflavin + NAD(P)H. |
| 2 cob(II)alamin + NAD(+) = 2 aquacob(III)alamin + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in UTP:glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- May play a role in stationary phase survival
- Gene Name:
- galU
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEP3
- Molecular weight:
- 32942
Reactions
| UTP + alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate = diphosphate + UDP-glucose. |
- General function:
- Involved in tartronate-semialdehyde synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the condensation of two molecules of glyoxylate to give 2-hydroxy-3-oxopropanoate (also termed tartronate semialdehyde)
- Gene Name:
- gcl
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEP7
- Molecular weight:
- 64731
Reactions
| 2 glyoxylate = tartronate semialdehyde + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Amino acid transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the formation of an amide bond between glutathione and spermidine coupled with hydrolysis of ATP; also catalyzes the hydrolysis of glutathionylspermidine to glutathione and spermidine
- Gene Name:
- gsp
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AES0
- Molecular weight:
- 70531
Reactions
| Glutathione + spermidine + ATP = glutathionylspermidine + ADP + phosphate. |
| Glutathionylspermidine + H(2)O = glutathione + spermidine. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- ATP + inosine = ADP + IMP
- Gene Name:
- gsk
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEW6
- Molecular weight:
- 48448
Reactions
| ATP + inosine = ADP + IMP. |
- General function:
- Involved in 1-phosphofructokinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + D-fructose 1-phosphate = ADP + D- fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
- Gene Name:
- fruK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEW9
- Molecular weight:
- 33755
Reactions
| ATP + D-fructose 1-phosphate = ADP + D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleoside-triphosphate diphosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- mazG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEY3
- Molecular weight:
- 30412
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O = AMP + diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (NADPH) activity
- Specific function:
- 5-methyltetrahydrofolate + NAD(P)(+) = 5,10- methylenetetrahydrofolate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- metF
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEZ1
- Molecular weight:
- 33102
Reactions
| 5-methyltetrahydrofolate + NAD(P)(+) = 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in nitrate reductase activity
- Specific function:
- This is a second nitrate reductase enzyme which can substitute for the NRA enzyme and allows E.coli to use nitrate as an electron acceptor during anaerobic growth. The gamma chain is a membrane-embedded heme-iron unit resembling cytochrome b, which transfers electrons from quinones to the beta subunit
- Gene Name:
- narV
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AF32
- Molecular weight:
- 26018
Reactions
| Nitrite + acceptor = nitrate + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in dATP pyrophosphohydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the hydrolysis of dihydroneopterin triphosphate to dihydroneopterin monophosphate and pyrophosphate. Required for efficient folate biosynthesis. Can also hydrolyze nucleoside triphosphates with a preference for dATP
- Gene Name:
- nudB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFC0
- Molecular weight:
- 17306
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on NADH or NADPH
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFC3
- Molecular weight:
- 16457
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFC7
- Molecular weight:
- 25056
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFD1
- Molecular weight:
- 18590
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient. This subunit may bind ubiquinone
- Gene Name:
- nuoH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFD4
- Molecular weight:
- 36219
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoI
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFD6
- Molecular weight:
- 20538
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFE0
- Molecular weight:
- 19874
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on NADH or NADPH
- Specific function:
- There are 2 NADH dehydrogenases in E.coli, however only this complex is able to use dNADH (reduced nicotinamide hypoxanthine dinucleotide, deamino-NADH) and dNADH-DB (dimethoxy- 5-methyl-6-decyl-1,4-benzoquinone) as substrates
- Gene Name:
- nuoK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFE4
- Molecular weight:
- 10845
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoM
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFE8
- Molecular weight:
- 56524
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoN
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFF0
- Molecular weight:
- 52044
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (succinyl-transferring) activity
- Specific function:
- The 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of 2-oxoglutarate to succinyl-CoA and CO(2). It contains multiple copies of three enzymatic components:2- oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (E1), dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase (E2) and lipoamide dehydrogenase (E3)
- Gene Name:
- sucA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFG3
- Molecular weight:
- 105061
Reactions
| 2-oxoglutarate + [dihydrolipoyllysine-residue succinyltransferase] lipoyllysine = [dihydrolipoyllysine-residue succinyltransferase] S-succinyldihydrolipoyllysine + CO(2). |
261. Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue succinyltransferase component of 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring acyl groups
- Specific function:
- The 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of 2-oxoglutarate to succinyl-CoA and CO(2). It contains multiple copies of three enzymatic components:2- oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (E1), dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase (E2) and lipoamide dehydrogenase (E3)
- Gene Name:
- sucB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFG6
- Molecular weight:
- 44011
Reactions
| Succinyl-CoA + enzyme N(6)-(dihydrolipoyl)lysine = CoA + enzyme N(6)-(S-succinyldihydrolipoyl)lysine. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA and CO(2). It contains multiple copies of three enzymatic components:pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1), dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase (E2) and lipoamide dehydrogenase (E3)
- Gene Name:
- aceE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFG8
- Molecular weight:
- 99668
Reactions
| Pyruvate + [dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase] lipoyllysine = [dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase] S-acetyldihydrolipoyllysine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxalyl-CoA decarboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- Oxalyl-CoA = formyl-CoA + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- oxc
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFI0
- Molecular weight:
- 60581
Reactions
| Oxalyl-CoA = formyl-CoA + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Degradation of inorganic polyphosphates. Orthophosphate is released progressively from the ends of polyphosphate of circa 500 residues long, while chains of circa 15 residues compete poorly with polyphosphate as substrate
- Gene Name:
- ppx
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFL6
- Molecular weight:
- 58136
Reactions
| (Polyphosphate)(n) + H(2)O = (polyphosphate)(n-1) + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reduction of dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate
- Gene Name:
- folM
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFS3
- Molecular weight:
- 26348
Reactions
| 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate + NADP(+) = 7,8-dihydrofolate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in riboflavin synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Riboflavin synthase is a bifunctional enzyme complex catalyzing the formation of riboflavin from 5-amino-6-(1'-D)- ribityl-amino-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione and L-3,4-dihydrohy-2- butanone-4-phosphate via 6,7-dimethyl-8-lumazine. The alpha subunit catalyzes the dismutation of 6,7-dimethyl-8-lumazine to riboflavin and 5-amino-6-(1'-D)-ribityl-amino-2,4(1H,3H)- pyrimidinedione
- Gene Name:
- ribE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFU8
- Molecular weight:
- 23445
Reactions
| 2 6,7-dimethyl-8-(1-D-ribityl)lumazine = riboflavin + 4-(1-D-ribitylamino)-5-amino-2,6-dihydroxypyrimidine. |
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid binding
- Specific function:
- In eubacteria ppGpp (guanosine 3'-diphosphate 5-' diphosphate) is a mediator of the stringent response that coordinates a variety of cellular activities in response to changes in nutritional abundance. This enzyme catalyzes the formation of pppGpp which is then hydrolyzed to form ppGpp
- Gene Name:
- relA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG20
- Molecular weight:
- 83875
Reactions
| ATP + GTP = AMP + guanosine 3'-diphosphate 5'-triphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- In eubacteria ppGpp (guanosine 3'-diphosphate 5-' diphosphate) is a mediator of the stringent response that coordinates a variety of cellular activities in response to changes in nutritional abundance. This enzyme catalyzes both the synthesis and degradation of ppGpp. The second messengers ppGpp and c-di-GMP together control biofilm formation in response to translational stress; ppGpp represses biofilm formation while c- di-GMP induces it
- Gene Name:
- spoT
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG24
- Molecular weight:
- 79342
Reactions
| ATP + GTP = AMP + guanosine 3'-diphosphate 5'-triphosphate. |
| Guanosine 3',5'-bis(diphosphate) + H(2)O = guanosine 5'-diphosphate + diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in FMN adenylyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + riboflavin = ADP + FMN
- Gene Name:
- ribF
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG40
- Molecular weight:
- 34734
Reactions
| ATP + riboflavin = ADP + FMN. |
| ATP + FMN = diphosphate + FAD. |
- General function:
- Involved in superoxide metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Destroys radicals which are normally produced within the cells and which are toxic to biological systems
- Gene Name:
- sodC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGD1
- Molecular weight:
- 17681
Reactions
| 2 superoxide + 2 H(+) = O(2) + H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in superoxide dismutase activity
- Specific function:
- Destroys radicals which are normally produced within the cells and which are toxic to biological systems
- Gene Name:
- sodB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGD3
- Molecular weight:
- 21266
Reactions
| 2 superoxide + 2 H(+) = O(2) + H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Acts on both serine and threonine, and properly considered as a hydroxy amino acid deaminase
- Gene Name:
- tdcB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGF6
- Molecular weight:
- 35232
Reactions
| L-threonine = 2-oxobutanoate + NH(3). |
| L-serine = pyruvate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Efficient electron donor for the essential enzyme ribonucleotide reductase. Is also able to reduce the interchain disulfide bridges of insulin
- Gene Name:
- trxC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGG4
- Molecular weight:
- 15555
Reactions
| Protein dithiol + NAD(P)(+) = protein disulfide + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the attachment of tyrosine to tRNA(Tyr) in a two-step reaction:tyrosine is first activated by ATP to form Tyr- AMP and then transferred to the acceptor end of tRNA(Tyr)
- Gene Name:
- tyrS
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGJ9
- Molecular weight:
- 47527
Reactions
| ATP + L-tyrosine + tRNA(Tyr) = AMP + diphosphate + L-tyrosyl-tRNA(Tyr). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the tagatose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase gatYZ that is required for full activity and stability of the Y subunit. Could have a chaperone-like function for the proper and stable folding of gatY. When expressed alone, gatZ does not show any aldolase activity. Is involved in the catabolism of galactitol
- Gene Name:
- gatZ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0C8J8
- Molecular weight:
- 47108
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the tagatose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase kbaYZ that is required for full activity and stability of the Y subunit. Could have a chaperone-like function for the proper and stable folding of kbaY. When expressed alone, kbaZ does not show any aldolase activity
- Gene Name:
- kbaZ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0C8K0
- Molecular weight:
- 47192
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Activates the carboxylate group of 2,3-dihydroxy- benzoate (2,3-DHB), via ATP-dependent PPi exchange reactions, to the acyladenylate. Then, catalyzes the acylation of holo-entB with 2,3-DHB adenylate, preparing that molecule for amide bond formation with L-serine
- Gene Name:
- entE
- Uniprot ID:
- P10378
- Molecular weight:
- 59112
Reactions
| ATP + 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate = diphosphate + (2,3-dihydroxybenzoyl)adenylate. |
| (2,3-dihydroxybenzoyl)adenylate + holo-entB = adenosine 5'-monophosphate + acyl-holo-entB. |
- General function:
- Involved in lipid-A-disaccharide synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Condensation of UDP-2,3-diacylglucosamine and 2,3- diacylglucosamine-1-phosphate to form lipid A disaccharide, a precursor of lipid A, a phosphorylated glycolipid that anchors the lipopolysaccharide to the outer membrane of the cell
- Gene Name:
- lpxB
- Uniprot ID:
- P10441
- Molecular weight:
- 42382
Reactions
| UDP-2,3-bis(3-hydroxytetradecanoyl)glucosamine + 2,3-bis(3-hydroxytetradecanoyl)-beta-D-glucosaminyl 1-phosphate = UDP + 2,3-bis(3-hydroxytetradecanoyl)-D-glucosaminyl-1,6-beta-D-2,3-bis(3-hydroxytetradecanoyl)-beta-D-glucosaminyl 1-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidation of L-aspartate to iminoaspartate
- Gene Name:
- nadB
- Uniprot ID:
- P10902
- Molecular weight:
- 60337
Reactions
| L-aspartate + O(2) = iminosuccinate + H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex UgpABCE involved in sn-glycerol-3-phosphate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable). Can also transport glycerophosphoryl diesters
- Gene Name:
- ugpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P10907
- Molecular weight:
- 39524
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + glycerol-3-phosphate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + glycerol-3-phosphate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase activity
- Specific function:
- Glycerophosphoryl diester phosphodiesterase hydrolyzes deacylated phospholipids to G3P and the corresponding alcohols
- Gene Name:
- ugpQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P10908
- Molecular weight:
- 27409
Reactions
| A glycerophosphodiester + H(2)O = an alcohol + sn-glycerol 3-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in iron-sulfur cluster binding
- Specific function:
- The nitrate reductase enzyme complex allows E.coli to use nitrate as an electron acceptor during anaerobic growth. The beta chain is an electron transfer unit containing four cysteine clusters involved in the formation of iron-sulfur centers. Electrons are transferred from the gamma chain to the molybdenum cofactor of the alpha subunit
- Gene Name:
- narH
- Uniprot ID:
- P11349
- Molecular weight:
- 58066
Reactions
| Nitrite + acceptor = nitrate + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in nitrate reductase activity
- Specific function:
- The nitrate reductase enzyme complex allows E.coli to use nitrate as an electron acceptor during anaerobic growth. The gamma chain is a membrane-embedded heme-iron unit resembling cytochrome b, which transfers electrons from quinones to the beta subunit
- Gene Name:
- narI
- Uniprot ID:
- P11350
- Molecular weight:
- 25497
Reactions
| Nitrite + acceptor = nitrate + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in N-acetyl-gamma-glutamyl-phosphate reductase activity
- Specific function:
- N-acetyl-L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde + NADP(+) + phosphate = N-acetyl-5-glutamyl phosphate + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- argC
- Uniprot ID:
- P11446
- Molecular weight:
- 35952
Reactions
| N-acetyl-L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde + NADP(+) + phosphate = N-acetyl-5-glutamyl phosphate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in ligase activity
- Specific function:
- Activates the carboxylate group of L-serine via ATP- dependent PPi exchange reactions to the aminoacyladenylate, preparing that molecule for the final stages of enterobactin synthesis. Holo-entF acts as the catalyst for the formation of the three amide and three ester bonds present in the cyclic (2,3- dihydroxybenzoyl)serine trimer enterobactin, using seryladenylate and acyl-holo-entB (acylated with 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate by entE)
- Gene Name:
- entF
- Uniprot ID:
- P11454
- Molecular weight:
- 141990
Reactions
| ATP + L-serine = diphosphate + L-serine-adenylate. |
- General function:
- Involved in carbohydrate transport
- Specific function:
- Mediates the uptake of L-fucose across the boundary membrane with the concomitant transport of protons into the cell (symport system). Can also transport L-galactose and D-arabinose, but at reduced rates compared with L-fucose. Is not able to transport L-rhamnose and L-arabinose
- Gene Name:
- fucP
- Uniprot ID:
- P11551
- Molecular weight:
- 47544
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-fuculose = ADP + L-fuculose 1- phosphate
- Gene Name:
- fucK
- Uniprot ID:
- P11553
- Molecular weight:
- 53235
Reactions
| ATP + L-fuculose = ADP + L-fuculose 1-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-arginine + tRNA(Arg) = AMP + diphosphate + L-arginyl-tRNA(Arg)
- Gene Name:
- argS
- Uniprot ID:
- P11875
- Molecular weight:
- 64682
Reactions
| ATP + L-arginine + tRNA(Arg) = AMP + diphosphate + L-arginyl-tRNA(Arg). |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in cell wall formation. Catalyzes the final step in the synthesis of UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-pentapeptide, the precursor of murein
- Gene Name:
- murF
- Uniprot ID:
- P11880
- Molecular weight:
- 47447
Reactions
| ATP + UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-gamma-D-glutamyl-L-lysine + D-alanyl-D-alanine = ADP + phosphate + UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-gamma-D-glutamyl-L-lysyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the conversion of dethiobiotin (DTB) to biotin by the insertion of a sulfur atom into dethiobiotin via a radical- based mechanism
- Gene Name:
- bioB
- Uniprot ID:
- P12996
- Molecular weight:
- 38648
Reactions
| Dethiobiotin + sulfur + 2 S-adenosyl-L-methionine = biotin + 2 L-methionine + 2 5'-deoxyadenosine. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + 7,8-diaminononanoate + CO(2) = ADP + phosphate + dethiobiotin
- Gene Name:
- bioD
- Uniprot ID:
- P13000
- Molecular weight:
- 24139
Reactions
| ATP + 7,8-diaminononanoate + CO(2) = ADP + phosphate + dethiobiotin. |
- General function:
- Involved in biotin biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Shows carboxylesterase activity with a preference for short chain fatty acid esters (acyl chain length of up to 6 carbons). Also displays a weak thioesterase activity. Can form a complex with CoA, and may be involved in the condensation of CoA and pimelic acid into pimeloyl-CoA, a precursor in biotin biosynthesis
- Gene Name:
- bioH
- Uniprot ID:
- P13001
- Molecular weight:
- 28505
Reactions
| Pimelyl-[acyl-carrier protein] methyl ester + H(2)O = pimelyl-[acyl-carrier protein] + methanol. |
- General function:
- Involved in methionine synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group from methyl- cobalamin to homocysteine, yielding enzyme-bound cob(I)alamin and methionine. Subsequently, remethylates the cofactor using methyltetrahydrofolate
- Gene Name:
- metH
- Uniprot ID:
- P13009
- Molecular weight:
- 135996
Reactions
| 5-methyltetrahydrofolate + L-homocysteine = tetrahydrofolate + L-methionine. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalase activity
- Specific function:
- Bifunctional enzyme with both catalase and broad- spectrum peroxidase activity. Displays also NADH oxidase, INH lyase and isonicotinoyl-NAD synthase activity
- Gene Name:
- katG
- Uniprot ID:
- P13029
- Molecular weight:
- 80023
Reactions
| Donor + H(2)O(2) = oxidized donor + 2 H(2)O. |
| 2 H(2)O(2) = O(2) + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Upon internalization, ferric enterobactin is processed via an exquisitely specific pathway that is dependent on FES activity, making iron available for metabolic use
- Gene Name:
- fes
- Uniprot ID:
- P13039
- Molecular weight:
- 42569
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in a multicomponent binding-protein-dependent transport system for glycine betaine/L-proline
- Gene Name:
- proV
- Uniprot ID:
- P14175
- Molecular weight:
- 44162
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Cell wall formation. Catalyzes the addition of glutamate to the nucleotide precursor UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine (UMA)
- Gene Name:
- murD
- Uniprot ID:
- P14900
- Molecular weight:
- 46973
Reactions
| ATP + UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine + glutamate = ADP + phosphate + UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for citrate-dependent Fe(3+). Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- fecE
- Uniprot ID:
- P15031
- Molecular weight:
- 28191
- General function:
- Involved in DNA ligase (NAD+) activity
- Specific function:
- DNA ligase that catalyzes the formation of phosphodiester linkages between 5'-phosphoryl and 3'-hydroxyl groups in double-stranded DNA using NAD as a coenzyme and as the energy source for the reaction. It is essential for DNA replication and repair of damaged DNA
- Gene Name:
- ligA
- Uniprot ID:
- P15042
- Molecular weight:
- 73605
Reactions
| NAD(+) + (deoxyribonucleotide)(n) + (deoxyribonucleotide)(m) = AMP + beta-nicotinamide D-ribonucleotide + (deoxyribonucleotide)(n+m). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- 2,3-dihydro-2,3-dihydroxybenzoate + NAD(+) = 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- entA
- Uniprot ID:
- P15047
- Molecular weight:
- 26250
Reactions
| 2,3-dihydro-2,3-dihydroxybenzoate + NAD(+) = 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + N(2)-formyl-N(1)-(5-phospho-D- ribosyl)glycinamide + L-glutamine + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate + 2- (formamido)-N(1)-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)acetamidine + L-glutamate
- Gene Name:
- purL
- Uniprot ID:
- P15254
- Molecular weight:
- 141402
Reactions
| ATP + N(2)-formyl-N(1)-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)glycinamide + L-glutamine + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate + 2-(formamido)-N(1)-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)acetamidine + L-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + 5-phospho-D-ribosylamine + glycine = ADP + phosphate + N(1)-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)glycinamide
- Gene Name:
- purD
- Uniprot ID:
- P15640
- Molecular weight:
- 45940
Reactions
| ATP + 5-phospho-D-ribosylamine + glycine = ADP + phosphate + N(1)-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)glycinamide. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Shikimate + NADP(+) = 3-dehydroshikimate + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- aroE
- Uniprot ID:
- P15770
- Molecular weight:
- 29413
Reactions
| Shikimate + NADP(+) = 3-dehydroshikimate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on CH-OH group of donors
- Specific function:
- GDH is probably involved in energy conservation rather than in sugar metabolism
- Gene Name:
- gcd
- Uniprot ID:
- P15877
- Molecular weight:
- 86747
Reactions
| D-glucose + ubiquinone = D-glucono-1,5-lactone + ubiquinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in L-serine ammonia-lyase activity
- Specific function:
- Deaminates also threonine, particularly when it is present in high concentration
- Gene Name:
- sdaA
- Uniprot ID:
- P16095
- Molecular weight:
- 48906
Reactions
| L-serine = pyruvate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on NADH or NADPH
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- hycE
- Uniprot ID:
- P16431
- Molecular weight:
- 64980
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Probable electron transfer protein for hydrogenase 3
- Gene Name:
- hycF
- Uniprot ID:
- P16432
- Molecular weight:
- 20309
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- hycG
- Uniprot ID:
- P16433
- Molecular weight:
- 27999
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the attachment of proline to tRNA(Pro) in a two-step reaction:proline is first activated by ATP to form Pro- AMP and then transferred to the acceptor end of tRNA(Pro). As ProRS can inadvertently accommodate and process non-cognate amino acids such as alanine and cysteine, to avoid such errors it has two additional distinct editing activities against alanine. One activity is designated as 'pretransfer' editing and involves the tRNA(Pro)-independent hydrolysis of activated Ala-AMP. The other activity is designated 'posttransfer' editing and involves deacylation of mischarged Ala-tRNA(Pro). Misacylated Cys-tRNA(Pro) is not edited by ProRS, but instead may be edited in trans by ybaK
- Gene Name:
- proS
- Uniprot ID:
- P16659
- Molecular weight:
- 63692
Reactions
| ATP + L-proline + tRNA(Pro) = AMP + diphosphate + L-prolyl-tRNA(Pro). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- cysA
- Uniprot ID:
- P16676
- Molecular weight:
- 41059
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + sulfate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + sulfate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in cysteine biosynthetic process from serine
- Specific function:
- Two cysteine synthase enzymes are found. Both catalyze the same reaction. Cysteine synthase B can also use thiosulfate in place of sulfide to give cysteine thiosulfonate as a product
- Gene Name:
- cysM
- Uniprot ID:
- P16703
- Molecular weight:
- 32664
Reactions
| O(3)-acetyl-L-serine + H(2)S = L-cysteine + acetate. |
- General function:
- Involved in thiamine pyrophosphate binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the thiamine diphosphate-dependent decarboxylation of 2-oxoglutarate and the subsequent addition of the resulting succinic semialdehyde-thiamine pyrophosphate anion to isochorismate to yield 2-succinyl-5-enolpyruvyl-6-hydroxy-3- cyclohexene-1-carboxylate (SEPHCHC)
- Gene Name:
- menD
- Uniprot ID:
- P17109
- Molecular weight:
- 61367
Reactions
| Isochorismate + 2-oxoglutarate = 5-enolpyruvoyl-6-hydroxy-2-succinyl-cyclohex-3-ene-1-carboxylate + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in undecaprenyldiphospho-muramoylpentapeptide beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Cell wall formation. Catalyzes the transfer of a GlcNAc subunit on undecaprenyl-pyrophosphoryl-MurNAc-pentapeptide (lipid intermediate I) to form undecaprenyl-pyrophosphoryl-MurNAc- (pentapeptide)GlcNAc (lipid intermediate II)
- Gene Name:
- murG
- Uniprot ID:
- P17443
- Molecular weight:
- 37815
Reactions
| UDP-N-acetylglucosamine + Mur2Ac(oyl-L-Ala-gamma-D-Glu-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala)-diphosphoundecaprenol = UDP + GlcNAc-(1->4)-Mur2Ac(oyl-L-Ala-gamma-D-Glu-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala)-diphosphoundecaprenol. |
- General function:
- Involved in choline dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Can catalyze the oxidation of choline to betaine aldehyde and betaine aldehyde to glycine betaine at the same rate
- Gene Name:
- betA
- Uniprot ID:
- P17444
- Molecular weight:
- 61877
Reactions
| Choline + acceptor = betaine aldehyde + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Betaine aldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O = betaine + NADH
- Gene Name:
- betB
- Uniprot ID:
- P17445
- Molecular weight:
- 52911
Reactions
| Betaine aldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O = betaine + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in sulfite reductase (NADPH) activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the sulfite reductase complex that catalyzes the 6-electron reduction of sulfite to sulfide. This is one of several activities required for the biosynthesis of L- cysteine from sulfate
- Gene Name:
- cysI
- Uniprot ID:
- P17846
- Molecular weight:
- 63998
Reactions
| H(2)S + 3 NADP(+) + 3 H(2)O = sulfite + 3 NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphoadenylyl-sulfate reductase (thioredoxin) activity
- Specific function:
- Reduction of activated sulfate into sulfite
- Gene Name:
- cysH
- Uniprot ID:
- P17854
- Molecular weight:
- 27976
Reactions
| Adenosine 3',5'-bisphosphate + sulfite + thioredoxin disulfide = 3'-phosphoadenylyl sulfate + thioredoxin. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Cell wall formation
- Gene Name:
- murC
- Uniprot ID:
- P17952
- Molecular weight:
- 53626
Reactions
| ATP + UDP-N-acetylmuramate + L-alanine = ADP + phosphate + UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine. |
- General function:
- Involved in 2-polyprenyl-6-methoxy-1,4-benzoquinone methyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- S-adenosyl-L-methionine + 3- demethylubiquinone-9 = S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + ubiquinone-9
- Gene Name:
- ubiG
- Uniprot ID:
- P17993
- Molecular weight:
- 26555
Reactions
| S-adenosyl-L-methionine + 3-demethylubiquinone-n = S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + ubiquinone-n. |
| S-adenosyl-L-methionine + 3-(all-trans-polyprenyl)benzene-1,2-diol = S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + 2-methoxy-6-(all-trans-polyprenyl)phenol. |
- General function:
- Involved in nicotinate phosphoribosyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Nicotinate D-ribonucleotide + diphosphate = nicotinate + 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate
- Gene Name:
- pncB
- Uniprot ID:
- P18133
- Molecular weight:
- 45897
Reactions
| Beta-nicotinate D-ribonucleotide + diphosphate = nicotinate + 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphatidylglycerophosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- One of the three phospholipid phosphatases, specifically hydrolyzes phosphatidylglycerophosphate
- Gene Name:
- pgpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P18200
- Molecular weight:
- 19418
Reactions
| Phosphatidylglycerophosphate + H(2)O = phosphatidylglycerol + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in dimethyl sulfoxide reductase activity
- Specific function:
- Terminal reductase during anaerobic growth on various sulfoxide and N-oxide compounds. Allows E.coli to grow anaerobically on Me(2)SO as respiratory oxidant
- Gene Name:
- dmsA
- Uniprot ID:
- P18775
- Molecular weight:
- 90398
Reactions
| Dimethylsulfide + menaquinone + H(2)O = dimethylsulfoxide + menaquinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Electron transfer subunit of the terminal reductase during anaerobic growth on various sulfoxide and N-oxide compounds
- Gene Name:
- dmsB
- Uniprot ID:
- P18776
- Molecular weight:
- 22869
- General function:
- Involved in NAD+ synthase (glutamine-hydrolyzing) activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes a key step in NAD biosynthesis, transforming deamido-NAD into NAD by a two-step reaction
- Gene Name:
- nadE
- Uniprot ID:
- P18843
- Molecular weight:
- 30637
Reactions
| ATP + deamido-NAD(+) + NH(3) = AMP + diphosphate + NAD(+). |
- General function:
- Involved in unfolded protein binding
- Specific function:
- Chaperone required for proper molybdenum cofactor insertion and final assembly of the membrane-bound respiratory nitrate reductase 2
- Gene Name:
- narW
- Uniprot ID:
- P19317
- Molecular weight:
- 26160
- General function:
- Involved in iron-sulfur cluster binding
- Specific function:
- This is a second nitrate reductase enzyme which can substitute for the NRA enzyme and allows E.coli to use nitrate as an electron acceptor during anaerobic growth. The beta chain is an electron transfer unit containing four cysteine clusters involved in the formation of iron-sulfur centers. Electrons are transferred from the gamma chain to the molybdenum cofactor of the alpha subunit
- Gene Name:
- narY
- Uniprot ID:
- P19318
- Molecular weight:
- 58557
Reactions
| Nitrite + acceptor = nitrate + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- The alpha chain is the actual site of nitrate reduction
- Gene Name:
- narZ
- Uniprot ID:
- P19319
- Molecular weight:
- 140226
Reactions
| Nitrite + acceptor = nitrate + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in 4-hydroxythreonine-4-phosphate dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NAD(P)-dependent oxidation of 4- (phosphohydroxy)-L-threonine (HTP) into 2-amino-3-oxo-4- (phosphohydroxy)butyric acid which spontaneously decarboxylates to form 3-amino-2-oxopropyl phosphate (AHAP)
- Gene Name:
- pdxA
- Uniprot ID:
- P19624
- Molecular weight:
- 35114
Reactions
| 4-(phosphonooxy)-L-threonine + NAD(+) = (2S)-2-amino-3-oxo-4-phosphonooxybutanoate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the transfer of the 4'-phosphopantetheine moiety from coenzyme A to apo-domains of both entB (an ArCP domain) and entF (a PCP domain). Plays an essential role in the assembly of the enterobactin
- Gene Name:
- entD
- Uniprot ID:
- P19925
- Molecular weight:
- 23604
Reactions
| CoA + apo-EntB/F = adenosine 3',5'-bisphosphate + holo-EntB/F. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- This enzyme may serve as a scavenger, allowing the cell to utilize biotin sulfoxide as a biotin source. It reduces a spontaneous oxidation product of biotin, D-biotin D-sulfoxide (BSO or BDS), back to biotin
- Gene Name:
- bisC
- Uniprot ID:
- P20099
- Molecular weight:
- 85850
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + sulfate = diphosphate + adenylyl sulfate
- Gene Name:
- cysD
- Uniprot ID:
- P21156
- Molecular weight:
- 35188
Reactions
| ATP + sulfate = diphosphate + adenylyl sulfate. |
- General function:
- Involved in carboxy-lyase activity
- Specific function:
- L-ornithine = putrescine + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- speC
- Uniprot ID:
- P21169
- Molecular weight:
- 79416
Reactions
| L-ornithine = putrescine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the biosynthesis of agmatine from arginine
- Gene Name:
- speA
- Uniprot ID:
- P21170
- Molecular weight:
- 73898
Reactions
| L-arginine = agmatine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the formation of an hydroxyacyl-CoA by addition of water on enoyl-CoA. Also exhibits 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA epimerase and 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase activities. Involved in the aerobic and anaerobic degradation of long-chain fatty acids
- Gene Name:
- fadB
- Uniprot ID:
- P21177
- Molecular weight:
- 79593
Reactions
| (S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA + NAD(+) = 3-oxoacyl-CoA + NADH. |
| (3S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA = trans-2(or 3)-enoyl-CoA + H(2)O. |
| (S)-3-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA = (R)-3-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA. |
| (3Z)-dodec-3-enoyl-CoA = (2E)-dodec-2-enoyl-CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalase activity
- Specific function:
- Decomposes hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen; serves to protect cells from the toxic effects of hydrogen peroxide
- Gene Name:
- katE
- Uniprot ID:
- P21179
- Molecular weight:
- 84162
Reactions
| 2 H(2)O(2) = O(2) + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Nicotinamide + H(2)O = nicotinate + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- pncA
- Uniprot ID:
- P21369
- Molecular weight:
- 23362
Reactions
| Nicotinamide + H(2)O = nicotinate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in two-component response regulator activity
- Specific function:
- Hydrolyzes c-di-GMP (cyclic bis(3'-5') dimeric GMP) to 5'-pGpG, known as PDE-A activity. PDE-B activity, that is hydrolysis of 5'-pGpG to GMP, proceeds only very slowly
- Gene Name:
- yahA
- Uniprot ID:
- P21514
- Molecular weight:
- 40725
- General function:
- Involved in [acyl-carrier-protein] phosphodiesterase activity
- Specific function:
- Converts holo-ACP to apo-ACP by hydrolytic cleavage of the phosphopantetheine prosthetic group from ACP
- Gene Name:
- acpH
- Uniprot ID:
- P21515
- Molecular weight:
- 22961
Reactions
| Holo-[acyl-carrier-protein] + H(2)O = 4'-phosphopantetheine + apo-[acyl-carrier-protein]. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + pyruvate = ADP + phosphoenolpyruvate
- Gene Name:
- pykA
- Uniprot ID:
- P21599
- Molecular weight:
- 51357
Reactions
| ATP + pyruvate = ADP + phosphoenolpyruvate. |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity
- Specific function:
- UDP-3-O-(3-hydroxytetradecanoyl)glucosamine + (R)-3-hydroxytetradecanoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] = UDP-2,3-bis(3- hydroxytetradecanoyl)glucosamine + [acyl-carrier-protein]
- Gene Name:
- lpxD
- Uniprot ID:
- P21645
- Molecular weight:
- 36038
Reactions
| (3R)-3-hydroxymyristoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + UDP-3-O-((3R)-hydroxymyristoyl)-alpha-D-glucosamine = UDP-2,3-bis(O-(3R)-3-hydroxymyristoyl)-alpha-D-glucosamine + a holo-[acyl-carrier-protein]. |
- General function:
- Involved in cysteine-tRNA ligase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-cysteine + tRNA(Cys) = AMP + diphosphate + L-cysteinyl-tRNA(Cys)
- Gene Name:
- cysS
- Uniprot ID:
- P21888
- Molecular weight:
- 52202
Reactions
| ATP + L-cysteine + tRNA(Cys) = AMP + diphosphate + L-cysteinyl-tRNA(Cys). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-aspartate + tRNA(Asp) = AMP + diphosphate + L-aspartyl-tRNA(Asp)
- Gene Name:
- aspS
- Uniprot ID:
- P21889
- Molecular weight:
- 65913
Reactions
| ATP + L-aspartate + tRNA(Asp) = AMP + diphosphate + L-aspartyl-tRNA(Asp). |
- General function:
- Involved in asparagine synthase (glutamine-hydrolyzing) activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-aspartate + L-glutamine + H(2)O = AMP + diphosphate + L-asparagine + L-glutamate
- Gene Name:
- asnB
- Uniprot ID:
- P22106
- Molecular weight:
- 62659
Reactions
| ATP + L-aspartate + L-glutamine + H(2)O = AMP + diphosphate + L-asparagine + L-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the addition of meso-diaminopimelic acid to the nucleotide precursor UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamate (UMAG) in the biosynthesis of bacterial cell-wall peptidoglycan. Is also able to use many meso-diaminopimelate analogs as substrates, although much less efficiently, but not L-lysine
- Gene Name:
- murE
- Uniprot ID:
- P22188
- Molecular weight:
- 53343
Reactions
| ATP + UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamate + meso-2,6-diaminoheptanedioate = ADP + phosphate + UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-gamma-glutamyl-meso-2,6-diamino-heptanedioate. |
- General function:
- Involved in deaminase activity
- Specific function:
- Adenosine + H(2)O = inosine + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- add
- Uniprot ID:
- P22333
- Molecular weight:
- 36397
Reactions
| Adenosine + H(2)O = inosine + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity
- Specific function:
- Acts as a beta-cystathionase and as a repressor of the maltose regulon
- Gene Name:
- malY
- Uniprot ID:
- P23256
- Molecular weight:
- 43641
Reactions
| L-cystathionine + H(2)O = L-homocysteine + NH(3) + pyruvate. |
- General function:
- Involved in thymidine kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Phosphorylates both thymidine and deoxyuridine
- Gene Name:
- tdk
- Uniprot ID:
- P23331
- Molecular weight:
- 23456
Reactions
| ATP + thymidine = ADP + thymidine 5'-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in glycerate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + (R)-glycerate = ADP + 3-phospho-(R)- glycerate
- Gene Name:
- garK
- Uniprot ID:
- P23524
- Molecular weight:
- 39104
Reactions
| ATP + (R)-glycerate = ADP + 3-phospho-(R)-glycerate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of pyruvate to phosphoenolpyruvate
- Gene Name:
- ppsA
- Uniprot ID:
- P23538
- Molecular weight:
- 87434
Reactions
| ATP + pyruvate + H(2)O = AMP + phosphoenolpyruvate + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in GTPase activity
- Specific function:
- May be the GTPase, regulating ATP sulfurylase activity
- Gene Name:
- cysN
- Uniprot ID:
- P23845
- Molecular weight:
- 52558
Reactions
| ATP + sulfate = diphosphate + adenylyl sulfate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ferrochelatase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the ferrous insertion into protoporphyrin IX
- Gene Name:
- hemH
- Uniprot ID:
- P23871
- Molecular weight:
- 35884
Reactions
| Protoheme + 2 H(+) = protoporphyrin + Fe(2+). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ferric enterobactin. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- fepC
- Uniprot ID:
- P23878
- Molecular weight:
- 29784
- General function:
- Involved in methionyl-tRNA formyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Modifies the free amino group of the aminoacyl moiety of methionyl-tRNA(fMet). The formyl group appears to play a dual role in the initiator identity of N-formylmethionyl-tRNA by:(I) promoting its recognition by IF2 and (II) impairing its binding to EFTu-GTP
- Gene Name:
- fmt
- Uniprot ID:
- P23882
- Molecular weight:
- 34168
Reactions
| 10-formyltetrahydrofolate + L-methionyl-tRNA(fMet) + H(2)O = tetrahydrofolate + N-formylmethionyl-tRNA(fMet). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the breakdown of putrescine. Was previously shown to have a weak but measurable ALDH enzyme activity that prefers NADP over NAD as coenzyme
- Gene Name:
- puuC
- Uniprot ID:
- P23883
- Molecular weight:
- 53418
Reactions
| Gamma-glutamyl-gamma-aminobutyraldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O = gamma-glutamyl-gamma-aminobutyrate + NADH. |
| An aldehyde + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = a carboxylate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Transcription
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of fructose to fructose-6- P. Has also low level glucokinase activity in vitro. Is not able to phosphorylate D-ribose, D-mannitol, D-sorbitol, inositol, and L-threonine
- Gene Name:
- mak
- Uniprot ID:
- P23917
- Molecular weight:
- 32500
Reactions
| ATP + D-fructose = ADP + D-fructose 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in carboxy-lyase activity
- Specific function:
- L-ornithine = putrescine + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- speF
- Uniprot ID:
- P24169
- Molecular weight:
- 82415
Reactions
| L-ornithine = putrescine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotidyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the biosynthesis of the capsular polysaccharide colanic acid
- Gene Name:
- manC
- Uniprot ID:
- P24174
- Molecular weight:
- 53016
Reactions
| GTP + alpha-D-mannose 1-phosphate = diphosphate + GDP-mannose. |
- General function:
- Involved in ligase activity
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of the acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase complex; first, biotin carboxylase catalyzes the carboxylation of the carrier protein and then the transcarboxylase transfers the carboxyl group to form malonyl-CoA
- Gene Name:
- accC
- Uniprot ID:
- P24182
- Molecular weight:
- 49320
Reactions
| ATP + biotin-[carboxyl-carrier-protein] + CO(2) = ADP + phosphate + carboxy-biotin-[carboxyl-carrier-protein]. |
| ATP + acetyl-CoA + HCO(3)(-) = ADP + phosphate + malonyl-CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in formate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity
- Specific function:
- Formate dehydrogenase allows E.coli to use formate as major electron donor during anaerobic respiration, when nitrate is used as electron acceptor. The alpha subunit forms the active site
- Gene Name:
- fdnG
- Uniprot ID:
- P24183
- Molecular weight:
- 112963
Reactions
| Formate + NAD(+) = CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidation of 5,10- methylenetetrahydrofolate to 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate and then the hydrolysis of 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate to 10- formyltetrahydrofolate. This enzyme is specific for NADP
- Gene Name:
- folD
- Uniprot ID:
- P24186
- Molecular weight:
- 31044
Reactions
| 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + NADP(+) = 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate + NADPH. |
| 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate + H(2)O = 10-formyltetrahydrofolate. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Transfers the 4'-phosphopantetheine moiety from coenzyme A to the 'Ser-36' of acyl-carrier-protein
- Gene Name:
- acpS
- Uniprot ID:
- P24224
- Molecular weight:
- 14052
Reactions
| CoA-(4'-phosphopantetheine) + apo-[acyl-carrier-protein] = adenosine 3',5'-bisphosphate + holo-[acyl-carrier-protein]. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Various electron acceptors are also reduced by HMP in vitro, including dihydropterine, ferrisiderophores, ferric citrate, cytochrome c, nitrite, S-nitrosoglutathione, and alkylhydroperoxides. However, it is unknown if these reactions are of any biological significance in vivo
- Gene Name:
- hmp
- Uniprot ID:
- P24232
- Molecular weight:
- 43867
Reactions
| 2 NO + 2 O(2) + NAD(P)H = 2 NO(3)(-) + NAD(P)(+). |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Has high formaldehyde dehydrogenase activity in the presence of glutathione and catalyzes the oxidation of normal alcohols in a reaction that is not GSH-dependent. In addition, hemithiolacetals other than those formed from GSH, including omega-thiol fatty acids, also are substrates
- Gene Name:
- frmA
- Uniprot ID:
- P25437
- Molecular weight:
- 39359
Reactions
| S-(hydroxymethyl)glutathione + NAD(P)(+) = S-formylglutathione + NAD(P)H. |
| An alcohol + NAD(+) = an aldehyde or ketone + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, acting on carbon-nitrogen (but not peptide) bonds
- Specific function:
- Cytosine + H(2)O = uracil + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- codA
- Uniprot ID:
- P25524
- Molecular weight:
- 47591
Reactions
| Cytosine + H(2)O = uracil + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Succinate semialdehyde + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = succinate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- gabD
- Uniprot ID:
- P25526
- Molecular weight:
- 51720
Reactions
| Succinate semialdehyde + NADP(+) + H(2)O = succinate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Converts 2,5-diamino-6-(ribosylamino)-4(3h)-pyrimidinone 5'-phosphate into 5-amino-6-(ribosylamino)-2,4(1h,3h)- pyrimidinedione 5'-phosphate
- Gene Name:
- ribD
- Uniprot ID:
- P25539
- Molecular weight:
- 40338
Reactions
| 2,5-diamino-6-hydroxy-4-(5-phosphoribosylamino)pyrimidine + H(2)O = 5-amino-6-(5-phosphoribosylamino)uracil + NH(3). |
| 5-amino-6-(5-phospho-D-ribitylamino)uracil + NADP(+) = 5-amino-6-(5-phospho-D-ribosylamino)uracil + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in guanosine-5'-triphosphate,3'-diphosphate diphosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- Conversion of pppGpp to ppGpp. Guanosine pentaphosphate (pppGpp) is a cytoplasmic signaling molecule which together with ppGpp controls the "stringent response", an adaptive process that allows bacteria to respond to amino acid starvation, resulting in the coordinated regulation of numerous cellular activities
- Gene Name:
- gppA
- Uniprot ID:
- P25552
- Molecular weight:
- 54871
Reactions
| Guanosine 5'-triphosphate,3'-diphosphate + H(2)O = guanosine 3',5'-bis(diphosphate) + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Acts on lactaldehyde as well as other aldehydes
- Gene Name:
- aldA
- Uniprot ID:
- P25553
- Molecular weight:
- 52272
Reactions
| (S)-lactaldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O = (S)-lactate + NADH. |
| Glycolaldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O = glycolate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in 5-methyltetrahydropteroyltriglutamate-homocysteine S-methyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group from 5- methyltetrahydrofolate to homocysteine resulting in methionine formation
- Gene Name:
- metE
- Uniprot ID:
- P25665
- Molecular weight:
- 84673
Reactions
| 5-methyltetrahydropteroyltri-L-glutamate + L-homocysteine = tetrahydropteroyltri-L-glutamate + L-methionine. |
- General function:
- Involved in 2-amino-4-hydroxy-6-hydroxymethyldihydropteridine diphosphokinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + 2-amino-4-hydroxy-6-hydroxymethyl-7,8- dihydropteridine = AMP + (2-amino-4-hydroxy-7,8-dihydropteridin-6- yl)methyl diphosphate
- Gene Name:
- folK
- Uniprot ID:
- P26281
- Molecular weight:
- 18079
Reactions
| ATP + 2-amino-4-hydroxy-6-hydroxymethyl-7,8-dihydropteridine = AMP + (2-amino-4-hydroxy-7,8-dihydropteridin-6-yl)methyl diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-malate + NAD(+) = pyruvate + CO(2) + NADH
- Gene Name:
- sfcA
- Uniprot ID:
- P26616
- Molecular weight:
- 63197
Reactions
| (S)-malate + NAD(+) = pyruvate + CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring glycosyl groups
- Specific function:
- UDP-glucose + lipopolysaccharide = UDP + D- glucosyl-lipopolysaccharide
- Gene Name:
- rfaJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P27129
- Molecular weight:
- 39040
Reactions
| UDP-glucose + lipopolysaccharide = UDP + D-glucosyl-lipopolysaccharide. |
- General function:
- Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis
- Specific function:
- Adds the O-antigen on the glucose group of LPS
- Gene Name:
- rfaL
- Uniprot ID:
- P27243
- Molecular weight:
- 46877
- General function:
- Involved in aminomethyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- The glycine cleavage system catalyzes the degradation of glycine
- Gene Name:
- gcvT
- Uniprot ID:
- P27248
- Molecular weight:
- 40146
Reactions
| [Protein]-S(8)-aminomethyldihydrolipoyllysine + tetrahydrofolate = [protein]-dihydrolipoyllysine + 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
- Specific function:
- NadR is bifunctional; it interacts with pnuC at low internal NAD levels, permitting transport of NMN intact into the cell. As NAD levels increase within the cell, the affinity of nadR for the operator regions of nadA, nadB, and pncB increases, repressing the transcription of these genes
- Gene Name:
- nadR
- Uniprot ID:
- P27278
- Molecular weight:
- 47346
Reactions
| ATP + nicotinamide ribonucleotide = diphosphate + NAD(+). |
| ATP + N-ribosylnicotinamide = ADP + nicotinamide ribonucleotide. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Transfers the gamma-phosphate of ATP to the 4'-position of a tetraacyldisaccharide 1-phosphate intermediate (termed DS-1- P) to form tetraacyldisaccharide 1,4'-bis-phosphate (lipid IVA)
- Gene Name:
- lpxK
- Uniprot ID:
- P27300
- Molecular weight:
- 35589
Reactions
| ATP + (2-N,3-O-bis(3-hydroxytetradecanoyl)-beta-D-glucosaminyl)-(1->6)-(2-N,3-O-bis(3-hydroxytetradecanoyl)-beta-D-glucosaminyl phosphate) = ADP + (2-N,3-O-bis(3-hydroxytetradecanoyl)-4-O-phosphono-beta-D-glucosaminyl)-(1->6)-(2-N,3-O-bis(3-hydroxytetradecanoyl)-beta-D-glucosaminyl phosphate). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the four-electron oxidation of UDP-N-acetyl-D- mannosamine (UDP-ManNAc), reducing NAD(+) and releasing UDP-N- acetylmannosaminuronic acid (UDP-ManNAcA)
- Gene Name:
- wecC
- Uniprot ID:
- P27829
- Molecular weight:
- 45838
Reactions
| UDP-N-acetyl-D-mannosamine + 2 NAD(+) + H(2)O = UDP-N-acetyl-D-mannosaminuronate + 2 NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in dCTP deaminase activity
- Specific function:
- dCTP + H(2)O = dUTP + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- dcd
- Uniprot ID:
- P28248
- Molecular weight:
- 21249
Reactions
| dCTP + H(2)O = dUTP + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate lyase activity
- Specific function:
- Converts 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate into 4-aminobenzoate (PABA) and pyruvate
- Gene Name:
- pabC
- Uniprot ID:
- P28305
- Molecular weight:
- 29715
Reactions
| 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate = 4-aminobenzoate + pyruvate. |
- General function:
- Involved in carboxy-lyase activity
- Specific function:
- ADC can be found in two forms:biodegradative and biosynthetic. The biodegradative form may play a role in regulating pH by consuming proteins
- Gene Name:
- adiA
- Uniprot ID:
- P28629
- Molecular weight:
- 84425
Reactions
| L-arginine = agmatine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Transports electrons between flavodoxin or ferredoxin and NADPH. Involved in the reductive activation of cobalamin- independent methionine synthase, pyruvate formate lyase and anaerobic ribonucleotide reductase. Also protects against superoxide radicals due to methyl viologen in the presence of oxygen
- Gene Name:
- fpr
- Uniprot ID:
- P28861
- Molecular weight:
- 27751
Reactions
| 2 reduced ferredoxin + NADP(+) + H(+) = 2 oxidized ferredoxin + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- 2'-deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate + thioredoxin disulfide + H(2)O = ribonucleoside triphosphate + thioredoxin
- Gene Name:
- nrdD
- Uniprot ID:
- P28903
- Molecular weight:
- 80022
Reactions
| 2'-deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate + thioredoxin disulfide + H(2)O = ribonucleoside triphosphate + thioredoxin. |
- General function:
- Involved in uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the decarboxylation of four acetate groups of uroporphyrinogen-III to yield coproporphyrinogen-III
- Gene Name:
- hemE
- Uniprot ID:
- P29680
- Molecular weight:
- 39248
Reactions
| Uroporphyrinogen III = coproporphyrinogen + 4 CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the catabolism of quinolinic acid (QA)
- Gene Name:
- nadC
- Uniprot ID:
- P30011
- Molecular weight:
- 32762
Reactions
| Beta-nicotinate D-ribonucleotide + diphosphate + CO(2) = pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylate + 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidation of 3-carboxy-2-hydroxy-4- methylpentanoate (3-isopropylmalate) to 3-carboxy-4-methyl-2- oxopentanoate. The product decarboxylates to 4-methyl-2 oxopentanoate
- Gene Name:
- leuB
- Uniprot ID:
- P30125
- Molecular weight:
- 39517
Reactions
| (2R,3S)-3-isopropylmalate + NAD(+) = 4-methyl-2-oxopentanoate + CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Condenses 4-methyl-5-(beta-hydroxyethyl)thiazole monophosphate (THZ-P) and 2-methyl-4-amino-5-hydroxymethyl pyrimidine pyrophosphate (HMP-PP) to form thiamine monophosphate (TMP)
- Gene Name:
- thiE
- Uniprot ID:
- P30137
- Molecular weight:
- 23015
Reactions
| 2-methyl-4-amino-5-hydroxymethylpyrimidine diphosphate + 4-methyl-5-(2-phosphono-oxyethyl)thiazole = diphosphate + thiamine phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in L-serine ammonia-lyase activity
- Specific function:
- Deaminates also threonine, particularly when it is present in high concentration
- Gene Name:
- sdaB
- Uniprot ID:
- P30744
- Molecular weight:
- 48753
Reactions
| L-serine = pyruvate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in Mo-molybdopterin cofactor biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Involved in sulfur transfer in the conversion of molybdopterin precursor Z to molybdopterin
- Gene Name:
- moaD
- Uniprot ID:
- P30748
- Molecular weight:
- 8758
- General function:
- Involved in Mo-molybdopterin cofactor biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Converts molybdopterin precursor Z to molybdopterin. This requires the incorporation of two sulfur atoms into precursor Z to generate a dithiolene group. The sulfur is provided by moaD
- Gene Name:
- moaE
- Uniprot ID:
- P30749
- Molecular weight:
- 16981
Reactions
| Cyclic pyranopterin monophosphate + 2 [molybdopterin-synthase sulfur-carrier protein]-Gly-NH-CH(2)-C(O)SH + H(2)O = molybdopterin + 2 [molybdopterin-synthase sulfur-carrier protein]. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reduction of 2,5-diketo-D-gluconic acid (25DKG) to 2-keto-L-gulonic acid (2KLG)
- Gene Name:
- dkgB
- Uniprot ID:
- P30863
- Molecular weight:
- 29437
Reactions
| 2-dehydro-D-gluconate + NADP(+) = 2,5-didehydro-D-gluconate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in thiosulfate sulfurtransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Transfers a sulfur ion to cyanide or to other thiol compounds. Also has weak rhodanese activity (130-fold lower). Its participation in detoxification of cyanide may be small. May be involved in the enhancement of serine sensitivity
- Gene Name:
- sseA
- Uniprot ID:
- P31142
- Molecular weight:
- 30812
Reactions
| 3-mercaptopyruvate + cyanide = pyruvate + thiocyanate. |
- General function:
- Involved in adenine deaminase activity
- Specific function:
- Adenine + H(2)O = hypoxanthine + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- ade
- Uniprot ID:
- P31441
- Molecular weight:
- 63739
Reactions
| Adenine + H(2)O = hypoxanthine + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- ATP + 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-galactonate = ADP + 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-galactonate 6-phosphate
- Gene Name:
- dgoK
- Uniprot ID:
- P31459
- Molecular weight:
- 31373
Reactions
| ATP + 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-galactonate = ADP + 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-galactonate 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for D-methionine and the toxic methionine analog alpha-methyl- methionine. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- metI
- Uniprot ID:
- P31547
- Molecular weight:
- 23256
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring acyl groups, acyl groups converted into alkyl on transfer
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the synthesis of 2-methylcitrate from propionyl-CoA and oxaloacetate. Also catalyzes the condensation of oxaloacetate with acetyl-CoA but with a lower specificity
- Gene Name:
- prpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P31660
- Molecular weight:
- 43102
Reactions
| Propanoyl-CoA + H(2)O + oxaloacetate = (2R,3S)-2-hydroxybutane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate + CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the condensation of pantoate with beta-alanine in an ATP-dependent reaction via a pantoyl-adenylate intermediate
- Gene Name:
- panC
- Uniprot ID:
- P31663
- Molecular weight:
- 31597
Reactions
| ATP + (R)-pantoate + beta-alanine = AMP + diphosphate + (R)-pantothenate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the transfer of glucose from UDP-glucose to glucose-6-phosphate to form alpha,alpha-1,1 trehalose-6-phosphate. Acts with retention of the anomeric configuration of the UDP-sugar donor. Essential for viability of the cells at low temperatures and at elevated osmotic strength
- Gene Name:
- otsA
- Uniprot ID:
- P31677
- Molecular weight:
- 53611
Reactions
| UDP-glucose + D-glucose 6-phosphate = UDP + alpha,alpha-trehalose 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoF
- Uniprot ID:
- P31979
- Molecular weight:
- 49292
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Two step NADP-dependent conversion of GDP-4-dehydro-6- deoxy-D-mannose to GDP-fucose, involving an epimerase and a reductase reaction
- Gene Name:
- fcl
- Uniprot ID:
- P32055
- Molecular weight:
- 36141
Reactions
| GDP-L-fucose + NADP(+) = GDP-4-dehydro-6-deoxy-D-mannose + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, in phosphorus-containing anhydrides
- Specific function:
- Could participate in the regulation of cell wall biosynthesis by influencing the concentration of GDP-mannose or GDP-glucose in the cell. May be involved in the degradation of GDP-mannose and GDP-glucose, diverting the GDP to the synthesis of GDP-fucose as required. Might also be involved in the biosynthesis of the slime polysaccharide colanic acid
- Gene Name:
- nudD
- Uniprot ID:
- P32056
- Molecular weight:
- 18273
Reactions
| GDP-D-mannose + H(2)O = GDP + D-mannose. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes both the ATP-dependent activation of exogenously supplied lipoate to lipoyl-AMP and the transfer of the activated lipoyl onto the lipoyl domains of lipoate-dependent enzymes. Is also able to catalyze very poorly the transfer of lipoyl and octanoyl moiety from their acyl carrier protein
- Gene Name:
- lplA
- Uniprot ID:
- P32099
- Molecular weight:
- 37926
Reactions
| ATP + lipoate = diphosphate + lipoyl-AMP. |
| Lipoyl-AMP + protein = protein N(6)-(lipoyl)lysine + AMP. |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity
- Specific function:
- Conversion of 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoate (DHNA) to dimethylmenaquinone (DMK). Attaches octaprenylpyrophosphate, a membrane-bound 40-carbon side chain to DHNA. The conversion of DHNA to DMK proceeds in three stages:the removal of the carboxyl group of DHNA as CO(2), the attachment of the isoprenoid side chain, and a quinol-to-quinone oxidation, which is thought to be spontaneous
- Gene Name:
- menA
- Uniprot ID:
- P32166
- Molecular weight:
- 33594
Reactions
| An all-trans-polyprenyl diphosphate + 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoate = a demethylmenaquinol + diphosphate + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-rhamnulose = ADP + L-rhamnulose 1- phosphate
- Gene Name:
- rhaB
- Uniprot ID:
- P32171
- Molecular weight:
- 54069
Reactions
| ATP + L-rhamnulose = ADP + L-rhamnulose 1-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in formate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity
- Specific function:
- Allows to use formate as major electron donor during aerobic respiration. Subunit alpha possibly forms the active site
- Gene Name:
- fdoG
- Uniprot ID:
- P32176
- Molecular weight:
- 112549
Reactions
| Formate + NAD(+) = CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- NAD(+) + H(2)O = AMP + NMN
- Gene Name:
- nudC
- Uniprot ID:
- P32664
- Molecular weight:
- 29689
Reactions
| NAD(+) + H(2)O = AMP + NMN. |
- General function:
- Transcription
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of D-allose to D-allose 6- P. Has also low level glucokinase activity in vitro
- Gene Name:
- alsK
- Uniprot ID:
- P32718
- Molecular weight:
- 33821
Reactions
| ATP + D-allose = ADP + D-allose 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex AlsBAC involved in D-allose import. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- alsA
- Uniprot ID:
- P32721
- Molecular weight:
- 56744
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + monosaccharide(Out) = ADP + phosphate + monosaccharide(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in carboxylesterase activity
- Specific function:
- Serine hydrolase involved in the detoxification of formaldehyde. Hydrolyzes S-formylglutathione to glutathione and formate. Shows also esterase activity against alpha-naphthyl acetate, lactoylglutathione, palmitoyl-CoA and several pNP-esters of short chain fatty acids
- Gene Name:
- yeiG
- Uniprot ID:
- P33018
- Molecular weight:
- 31259
Reactions
| S-formylglutathione + H(2)O = glutathione + formate. |
- General function:
- Involved in glycine dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) activity
- Specific function:
- The glycine cleavage system catalyzes the degradation of glycine. The P protein binds the alpha-amino group of glycine through its pyridoxal phosphate cofactor; CO(2) is released and the remaining methylamine moiety is then transferred to the lipoamide cofactor of the H protein
- Gene Name:
- gcvP
- Uniprot ID:
- P33195
- Molecular weight:
- 104376
Reactions
| Glycine + H-protein-lipoyllysine = H-protein-S-aminomethyldihydrolipoyllysine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes two reactions:the first one is the production of beta-formyl glycinamide ribonucleotide (GAR) from formate, ATP and beta GAR; the second, a side reaction, is the production of acetyl phosphate and ADP from acetate and ATP
- Gene Name:
- purT
- Uniprot ID:
- P33221
- Molecular weight:
- 42433
Reactions
| Formate + ATP + 5'-phospho-ribosylglycinamide = 5'-phosphoribosyl-N-formylglycinamide + ADP + diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-lactate + 2 ferricytochrome c = pyruvate + 2 ferrocytochrome c + 2 H(+)
- Gene Name:
- lldD
- Uniprot ID:
- P33232
- Molecular weight:
- 42728
Reactions
| (S)-lactate + 2 ferricytochrome c = pyruvate + 2 ferrocytochrome c + 2 H(+). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on NADH or NADPH
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoC
- Uniprot ID:
- P33599
- Molecular weight:
- 68236
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoG
- Uniprot ID:
- P33602
- Molecular weight:
- 100298
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoL
- Uniprot ID:
- P33607
- Molecular weight:
- 66438
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex CcmAB involved in the biogenesis of c-type cytochromes; once thought to export heme, this seems not to be the case, but its exact role is uncertain. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- ccmA
- Uniprot ID:
- P33931
- Molecular weight:
- 23053
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + heme(In) = ADP + phosphate + heme(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalytic subunit of the periplasmic nitrate reductase (NAP). Only expressed at high levels during aerobic growth. NapAB complex receives electrons from the membrane-anchored tetraheme protein napC, thus allowing electron flow between membrane and periplasm. Essential function for nitrate assimilation and may have a role in anaerobic metabolism
- Gene Name:
- napA
- Uniprot ID:
- P33937
- Molecular weight:
- 93041
Reactions
| Nitrite + acceptor = nitrate + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in coproporphyrinogen oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Key enzyme in heme biosynthesis. Catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of propionic acid side chains of rings A and B of coproporphyrinogen III
- Gene Name:
- hemF
- Uniprot ID:
- P36553
- Molecular weight:
- 34322
Reactions
| Coproporphyrinogen-III + O(2) + 2 H(+) = protoporphyrinogen-IX + 2 CO(2) + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in cobalamin 5'-phosphate synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Joins Ado-cobinamide-GDP and alpha-ribazole to generate adenosylcobalamin (Ado-cobalamin)
- Gene Name:
- cobS
- Uniprot ID:
- P36561
- Molecular weight:
- 26385
Reactions
| GDP-cobinamide + alpha-ribazole = cobalamin + GMP. |
- General function:
- Involved in nicotinate-nucleotide-dimethylbenzimidazole phosphoribosyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the synthesis of alpha-ribazole-5'-phosphate from nicotinate mononucleotide (NAMN) and 5,6- dimethylbenzimidazole (DMB)
- Gene Name:
- cobT
- Uniprot ID:
- P36562
- Molecular weight:
- 36987
Reactions
| Beta-nicotinate D-ribonucleotide + 5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole = nicotinate + alpha-ribazole 5'-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Probably involved in periplasmic detoxification of copper by oxidizing Cu(+) to Cu(2+) and thus preventing its uptake into the cytoplasm. Possesses phenoloxidase and ferroxidase activities and might be involved in the production of polyphenolic compounds and the prevention of oxidative damage in the periplasm
- Gene Name:
- cueO
- Uniprot ID:
- P36649
- Molecular weight:
- 56556
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid binding
- Specific function:
- Produces formate from formyl-tetrahydrofolate. Provides the major source of formate for the purT-dependent synthesis of 5'-phosphoribosyl-N-formylglycinamide (FGAR) during aerobic growth. Has a role in regulating the one-carbon pool
- Gene Name:
- purU
- Uniprot ID:
- P37051
- Molecular weight:
- 31934
Reactions
| 10-formyltetrahydrofolate + H(2)O = formate + tetrahydrofolate. |
- General function:
- Involved in cellular amino acid biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- ATP + NH(3) + CO(2) = ADP + carbamoyl phosphate
- Gene Name:
- arcC
- Uniprot ID:
- P37306
- Molecular weight:
- 31644
Reactions
| ATP + NH(3) + CO(2) = ADP + carbamoyl phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Accounts for almost the entire malate-synthesizing activity in cells metabolizing glyoxylate
- Gene Name:
- glcB
- Uniprot ID:
- P37330
- Molecular weight:
- 80488
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + H(2)O + glyoxylate = (S)-malate + CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex XylFGH involved in xylose import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable). The XylFGH system can also transport ribose in absence of xylose
- Gene Name:
- xylG
- Uniprot ID:
- P37388
- Molecular weight:
- 56470
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + monosaccharide(Out) = ADP + phosphate + monosaccharide(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the conversion of taurine and alpha ketoglutarate to sulfite, aminoacetaldehyde and succinate. Required for the utilization of taurine (2-aminoethanesulfonic acid) as an alternative sulfur source. Pentane-sulfonic acid, 3- (N-morpholino)propanesulfonic acid and 1,3-dioxo-2- isoindolineethanesulfonic acid are also substrates for this enzyme
- Gene Name:
- tauD
- Uniprot ID:
- P37610
- Molecular weight:
- 32409
Reactions
| Taurine + 2-oxoglutarate + O(2) = sulfite + aminoacetaldehyde + succinate + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in export of lead, cadmium, zinc and mercury
- Gene Name:
- zntA
- Uniprot ID:
- P37617
- Molecular weight:
- 76839
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Cd(2+)(In) = ADP + phosphate + Cd(2+)(Out). |
| ATP + H(2)O + Zn(2+)(In) = ADP + phosphate + Zn(2+)(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- ATP + 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-gluconate = ADP + 6- phospho-2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-gluconate
- Gene Name:
- kdgK
- Uniprot ID:
- P37647
- Molecular weight:
- 33962
Reactions
| ATP + 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-gluconate = ADP + 6-phospho-2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-gluconate. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of glyoxylate and hydroxypyruvate into glycolate and glycerate, respectively. Can also reduce 2,5-diketo-D-gluconate (25DKG) to 5-keto-D- gluconate (5KDG), 2-keto-D-gluconate (2KDG) to D-gluconate, and 2- keto-L-gulonate (2KLG) to L-idonate (IA), but it is not its physiological function. Inactive towards 2-oxoglutarate, oxaloacetate, pyruvate, 5-keto-D-gluconate, D-fructose and L- sorbose. Activity with NAD is very low
- Gene Name:
- ghrB
- Uniprot ID:
- P37666
- Molecular weight:
- 35395
Reactions
| Glycolate + NADP(+) = glyoxylate + NADPH. |
| D-glycerate + NAD(P)(+) = hydroxypyruvate + NAD(P)H. |
| D-gluconate + NADP(+) = 2-dehydro-D-gluconate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reduction of 2,3-diketo-L-gulonate in the presence of NADH, to form 3-keto-L-gulonate
- Gene Name:
- dlgD
- Uniprot ID:
- P37672
- Molecular weight:
- 36572
Reactions
| 3-dehydro-L-gulonate + NAD(P)(+) = (4R,5S)-4,5,6-trihydroxy-2,3-dioxohexanoate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of L-xylulose and 3-keto- L-gulonate. Is involved in L-lyxose utilization via xylulose, and may also be involved in the utilization of 2,3-diketo-L-gulonate
- Gene Name:
- lyx
- Uniprot ID:
- P37677
- Molecular weight:
- 55155
Reactions
| ATP + L-xylulose = ADP + L-xylulose 5-phosphate. |
| ATP + 3-dehydro-L-gulonate = ADP + 3-dehydro-L-gulonate 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the decarboxylation of 3-keto-L-gulonate-6-P into L-xylulose-5-P. May be involved in the utilization of 2,3- diketo-L-gulonate
- Gene Name:
- sgbH
- Uniprot ID:
- P37678
- Molecular weight:
- 23445
Reactions
| 3-dehydro-L-gulonate 6-phosphate = L-xylulose 5-phosphate + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NADP-dependent oxidation of diverse aldehydes such as chloroacetaldehyde, acetaldehyde, propionaldehyde, benzaldehyde, mafosfamide, 4- hydroperoxycyclophosphamide. Its preferred substrates are acetaldehyde and chloroacetaldehyde
- Gene Name:
- aldB
- Uniprot ID:
- P37685
- Molecular weight:
- 56306
- General function:
- Involved in glucose-1-phosphate thymidylyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the formation of dTDP-glucose, from dTTP and glucose 1-phosphate, as well as its pyrophosphorolysis
- Gene Name:
- rmlA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P37744
- Molecular weight:
- 32693
Reactions
| dTTP + alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate = diphosphate + dTDP-glucose. |
- General function:
- Involved in lipopolysaccharide biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- May link the O-antigen tetrasaccharide units into long chains, giving rise to typical smooth LPS
- Gene Name:
- rfc
- Uniprot ID:
- P37748
- Molecular weight:
- 44744
- General function:
- Involved in dTDP-4-dehydrorhamnose reductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reduction of dTDP-6-deoxy-L-lyxo-4- hexulose to yield dTDP-L-rhamnose. RmlD uses NADH and NADPH nearly equally well
- Gene Name:
- rfbD
- Uniprot ID:
- P37760
- Molecular weight:
- 32694
Reactions
| dTDP-6-deoxy-L-mannose + NADP(+) = dTDP-4-dehydro-6-deoxy-L-mannose + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in 2-deoxy-D-gluconate 3-dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reduction of 2,5-diketo-3-deoxygluconate (DKII or 4,6-dihydroxy-2,5-dioxohexanoate) into 2-keto-3- deoxygluconate (KDG or 2-dehydro-3-deoxygluconate) with a concomitant oxidation of NADH
- Gene Name:
- kduD
- Uniprot ID:
- P37769
- Molecular weight:
- 27070
Reactions
| 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-gluconate + NAD(+) = (4S)-4,6-dihydroxy-2,5-dioxohexanoate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the breakdown of putrescine via the oxidation of L-glutamylputrescine
- Gene Name:
- puuB
- Uniprot ID:
- P37906
- Molecular weight:
- 47169
Reactions
| Gamma-glutamylputrescine + H(2)O + O(2) = Gamma-glutamyl-gamma-aminobutyraldehyde + NH(3) + H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in sulfite reductase (NADPH) activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the sulfite reductase complex that catalyzes the 6-electron reduction of sulfite to sulfide. This is one of several activities required for the biosynthesis of L- cysteine from sulfate. The flavoprotein component catalyzes the electron flow from NADPH -> FAD -> FMN to the hemoprotein component
- Gene Name:
- cysJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P38038
- Molecular weight:
- 66269
Reactions
| H(2)S + 3 NADP(+) + 3 H(2)O = sulfite + 3 NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Reduction of a variety of nitroaromatic compounds using NADH (and to lesser extent NADPH) as source of reducing equivalents; two electrons are transferred. Capable of reducing nitrofurazone, quinones and the anti-tumor agent CB1954 (5- (aziridin-1-yl)-2,4-dinitrobenzamide). The reduction of CB1954 results in the generation of cytotoxic species
- Gene Name:
- nfnB
- Uniprot ID:
- P38489
- Molecular weight:
- 23905
Reactions
| A 5,6,7,8-tetrahydropteridine + NAD(P)(+) = a 6,7-dihydropteridine + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- D-mannonate + NAD(+) = D-fructuronate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- uxuB
- Uniprot ID:
- P39160
- Molecular weight:
- 53580
Reactions
| D-mannonate + NAD(+) = D-fructuronate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleic acid binding
- Specific function:
- S-adenosyl-L-methionine + DNA adenine = S- adenosyl-L-homocysteine + DNA 6-methylaminopurine
- Gene Name:
- yfcB
- Uniprot ID:
- P39199
- Molecular weight:
- 35001
Reactions
| S-adenosyl-L-methionine + glutamine in ribosomal protein L3 = S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + N5-methylglutamine in ribosomal protein L3. |
- General function:
- Involved in shikimate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + D-gluconate = ADP + 6-phospho-D- gluconate
- Gene Name:
- idnK
- Uniprot ID:
- P39208
- Molecular weight:
- 21004
Reactions
| ATP + D-gluconate = ADP + 6-phospho-D-gluconate. |
- General function:
- Involved in GTPase activity
- Specific function:
- May play a role in 30S ribosomal subunit biogenesis. Unusual circulary permuted GTPase that catalyzes rapid hydrolysis of GTP with a slow catalytic turnover. Dispensible for viability, but important for overall fitness. The intrinsic GTPase activity is stimulated by the presence of 30S (160-fold increase in kcat) or 70S (96 fold increase in kcat) ribosomes (PubMed:14973029). The GTPase is inhibited by aminoglycoside antibiotics such as neomycin and paromycin (PubMed:15466596) streptomycin and spectinomycin (PubMed:15828870). This inhibition is not due to competition for binding sites on the 30S or 70S ribosome (PubMed:15828870)
- Gene Name:
- rsgA
- Uniprot ID:
- P39286
- Molecular weight:
- 39193
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the decarboxylation of 3-keto-L-gulonate-6-P into L-xylulose-5-P. Is involved in the anaerobic L-ascorbate utilization
- Gene Name:
- ulaD
- Uniprot ID:
- P39304
- Molecular weight:
- 23578
Reactions
| 3-dehydro-L-gulonate 6-phosphate = L-xylulose 5-phosphate + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NADH/NADPH-dependent oxidation of L- idonate to 5-ketogluconate (5KG)
- Gene Name:
- idnD
- Uniprot ID:
- P39346
- Molecular weight:
- 37146
Reactions
| L-idonate + NAD(P)(+) = 5-dehydrogluconate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- yjhH
- Uniprot ID:
- P39359
- Molecular weight:
- 32721
- General function:
- Involved in 2 iron, 2 sulfur cluster binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in the reduction of ferric iron in cytoplasmic ferrioxamine B
- Gene Name:
- fhuF
- Uniprot ID:
- P39405
- Molecular weight:
- 30113
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Preferred specificity is towards 1-propanol
- Gene Name:
- adhP
- Uniprot ID:
- P39451
- Molecular weight:
- 35379
Reactions
| An alcohol + NAD(+) = an aldehyde or ketone + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxal kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Phosphorylates B6 vitamers; functions in a salvage pathway. Uses pyridoxal, pyridoxine, and pyridoxamine as substrates
- Gene Name:
- pdxK
- Uniprot ID:
- P40191
- Molecular weight:
- 30847
Reactions
| ATP + pyridoxal = ADP + pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NADP-dependent reduction of 2,4-dienoyl- CoA to yield trans-2- enoyl-CoA
- Gene Name:
- fadH
- Uniprot ID:
- P42593
- Molecular weight:
- 72678
Reactions
| Trans-2,3-didehydroacyl-CoA + NADP(+) = trans,trans-2,3,4,5-tetradehydroacyl-CoA + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the hydrolysis of the pyrophosphate bond of UDP-2,3-diacylglucosamine to yield 2,3-diacylglucosamine 1- phosphate (lipid X) and UMP
- Gene Name:
- lpxH
- Uniprot ID:
- P43341
- Molecular weight:
- 26894
Reactions
| UDP-2,3-bis((3R)-3-hydroxymyristoyl)-alpha-D-glucosamine + H(2)O = 2,3-bis((3R)-3-hydroxymyristoyl)-beta-D-glucosaminyl 1-phosphate + UMP. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc) to ManNAc-6-P. Has also low level glucokinase activity in vitro
- Gene Name:
- nanK
- Uniprot ID:
- P45425
- Molecular weight:
- 29644
Reactions
| ATP + N-acyl-D-mannosamine = ADP + N-acyl-D-mannosamine 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Phosphorylates fructoselysine to yield fructoselysine 6- phosphate
- Gene Name:
- frlD
- Uniprot ID:
- P45543
- Molecular weight:
- 28332
Reactions
| ATP + fructoselysine = ADP + fructoselysine 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NADP-dependent rearrangement and reduction of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate (DXP) to 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP)
- Gene Name:
- dxr
- Uniprot ID:
- P45568
- Molecular weight:
- 43388
Reactions
| 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate + NADP(+) = 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in shikimate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + D-gluconate = ADP + 6-phospho-D- gluconate
- Gene Name:
- gntK
- Uniprot ID:
- P46859
- Molecular weight:
- 19543
Reactions
| ATP + D-gluconate = ADP + 6-phospho-D-gluconate. |
- General function:
- Involved in copper ion binding
- Specific function:
- The enzyme prefers aromatic over aliphatic amines
- Gene Name:
- tynA
- Uniprot ID:
- P46883
- Molecular weight:
- 84378
Reactions
| RCH(2)NH(2) + H(2)O + O(2) = RCHO + NH(3) + H(2)O(2). |
| 2-phenylethylamine + H(2)O + O(2) = phenylacetaldehyde + NH(3) + H(2)O(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the hydrolysis of 4-amino-2-methyl-5- hydroxymethylpyrimidine pyrophosphate (HMP-PP) to 4-amino-2- methyl-5-hydroxymethylpyrimidine phosphate (HMP-P). Can also hydrolyze other substrates such as MeO-HMP-PP and CF(3)-HMP-PP
- Gene Name:
- cof
- Uniprot ID:
- P46891
- Molecular weight:
- 30371
- General function:
- Involved in carboxylesterase activity
- Specific function:
- Serine hydrolase involved in the detoxification of formaldehyde. Hydrolyzes S-formylglutathione to glutathione and formate. Shows also esterase activity against two pNP-esters (pNP- acetate and pNP-propionate), alpha-naphthyl acetate and lactoylglutathione
- Gene Name:
- frmB
- Uniprot ID:
- P51025
- Molecular weight:
- 31424
Reactions
| S-formylglutathione + H(2)O = glutathione + formate. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, in phosphorus-containing anhydrides
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the hydrolysis of nucleoside triphosphates, with a preference for pyrimidine deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dUTP, dTTP and dCTP)
- Gene Name:
- nudI
- Uniprot ID:
- P52006
- Molecular weight:
- 16371
Reactions
| Nucleoside triphosphate + H(2)O = nucleoside monophosphate + diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-methylmalonyl-CoA = propanoyl-CoA + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- mmcD
- Uniprot ID:
- P52045
- Molecular weight:
- 29172
Reactions
| (S)-methylmalonyl-CoA = propanoyl-CoA + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Hydrolyzes O6 atom-containing purine bases deoxyinosine triphosphate (dITP) and xanthosine triphosphate (XTP) as well as 2'-deoxy-N-6-hydroxylaminopurine triposphate (dHAPTP) to nucleotide monophosphate and pyrophosphate. Probably excludes non- standard purines from DNA precursor pool, preventing thus incorporation into DNA and avoiding chromosomal lesions
- Gene Name:
- rdgB
- Uniprot ID:
- P52061
- Molecular weight:
- 21039
Reactions
| A nucleoside triphosphate + H(2)O = a nucleotide + diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in carboxy-lyase activity
- Specific function:
- LDC is constitutively but weakly expressed under various conditions
- Gene Name:
- ldcC
- Uniprot ID:
- P52095
- Molecular weight:
- 80590
Reactions
| L-lysine = cadaverine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Fermentative lactate dehydrogenase
- Gene Name:
- ldhA
- Uniprot ID:
- P52643
- Molecular weight:
- 36535
Reactions
| (R)-lactate + NAD(+) = pyruvate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Oxidoreductase required for the transfer of electrons from pyruvate to flavodoxin (Potential)
- Gene Name:
- ydbK
- Uniprot ID:
- P52647
- Molecular weight:
- 128823
Reactions
| Pyruvate + CoA + oxidized flavodoxin = acetyl-CoA + CO(2) + reduced flavodoxin. |
- General function:
- Involved in 6-phosphogluconolactonase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the hydrolysis of 6-phosphogluconolactone to 6-phosphogluconate
- Gene Name:
- pgl
- Uniprot ID:
- P52697
- Molecular weight:
- 36308
Reactions
| 6-phospho-D-glucono-1,5-lactone + H(2)O = 6-phospho-D-gluconate. |
- General function:
- Involved in fucosyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the synthesis of Und-PP-GlcNAc-ManNAcA-Fuc4NAc (Lipid III), the third lipid-linked intermediate involved in ECA synthesis
- Gene Name:
- wecF
- Uniprot ID:
- P56258
- Molecular weight:
- 40639
Reactions
| TDP-Fuc4NAc + Und-PP-GlcNAc-ManNAcA = TDP + Und-PP-GlcNAc-ManNAcA-Fuc4NAc. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the irreversible NADPH-dependent deamination of GMP to IMP. It functions in the conversion of nucleobase, nucleoside and nucleotide derivatives of G to A nucleotides, and in maintaining the intracellular balance of A and G nucleotides
- Gene Name:
- guaC
- Uniprot ID:
- P60560
- Molecular weight:
- 37383
Reactions
| Inosine 5'-phosphate + NH(3) + NADP(+) = guanosine 5'-phosphate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the radical-mediated insertion of two sulfur atoms into the C-6 and C-8 positions of the octanoyl moiety bound to the lipoyl domains of lipoate-dependent enzymes, thereby converting the octanoylated domains into lipoylated derivatives. Free octanoate is not a substrate for lipA
- Gene Name:
- lipA
- Uniprot ID:
- P60716
- Molecular weight:
- 36071
Reactions
| Protein N(6)-(octanoyl)lysine + 2 sulfur + 2 S-adenosyl-L-methionine = protein N(6)-(lipoyl)lysine + 2 L-methionine + 2 5'-deoxyadenosine. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP phosphoribosyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the condensation of ATP and 5-phosphoribose 1- diphosphate to form N'-(5'-phosphoribosyl)-ATP (PR-ATP). Has a crucial role in the pathway because the rate of histidine biosynthesis seems to be controlled primarily by regulation of hisG enzymatic activity
- Gene Name:
- hisG
- Uniprot ID:
- P60757
- Molecular weight:
- 33366
Reactions
| 1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)-ATP + diphosphate = ATP + 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-histidine + tRNA(His) = AMP + diphosphate + L-histidyl-tRNA(His)
- Gene Name:
- hisS
- Uniprot ID:
- P60906
- Molecular weight:
- 47029
Reactions
| ATP + L-histidine + tRNA(His) = AMP + diphosphate + L-histidyl-tRNA(His). |
- General function:
- Involved in undecaprenyl-diphosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the dephosphorylation of undecaprenyl diphosphate (UPP). Confers resistance to bacitracin
- Gene Name:
- uppP
- Uniprot ID:
- P60932
- Molecular weight:
- 29758
Reactions
| Undecaprenyl diphosphate + H(2)O = undecaprenyl phosphate + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in carbonate dehydratase activity
- Specific function:
- H(2)CO(3) = CO(2) + H(2)O
- Gene Name:
- can
- Uniprot ID:
- P61517
- Molecular weight:
- 25097
Reactions
| H(2)CO(3) = CO(2) + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in glucose-1-phosphate thymidylyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the formation of dTDP-glucose, from dTTP and glucose 1-phosphate, as well as its pyrophosphorolysis
- Gene Name:
- rmlA2
- Uniprot ID:
- P61887
- Molecular weight:
- 32734
Reactions
| dTTP + alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate = diphosphate + dTDP-glucose. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reversible oxidation of malate to oxaloacetate
- Gene Name:
- mdh
- Uniprot ID:
- P61889
- Molecular weight:
- 32337
Reactions
| (S)-malate + NAD(+) = oxaloacetate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of the position 2 hydroxy group of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-D-erythritol. Phosphorylates isopentenyl phosphate at low rates. Also acts on isopentenol, and, much less efficiently, dimethylallyl alcohol. Dimethylallyl monophosphate does not serve as a substrate
- Gene Name:
- ispE
- Uniprot ID:
- P62615
- Molecular weight:
- 30925
Reactions
| ATP + 4-(cytidine 5'-diphospho)-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol = ADP + 2-phospho-4-(cytidine 5'-diphospho)-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Converts 2C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate (ME-2,4cPP) into 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate
- Gene Name:
- ispG
- Uniprot ID:
- P62620
- Molecular weight:
- 40683
Reactions
| (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate + H(2)O + 2 oxidized ferredoxin = 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate + 2 reduced ferredoxin. |
- General function:
- Involved in isopentenyl diphosphate biosynthetic process, mevalonate-independent pathway
- Specific function:
- Converts 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate into isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP). Is also involved in penicillin tolerance and control of the stringent response. Seems to directly or indirectly interact with relA to maintain it in an inactive form during normal growth
- Gene Name:
- ispH
- Uniprot ID:
- P62623
- Molecular weight:
- 34774
Reactions
| Isopentenyl diphosphate + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate + NAD(P)H. |
| Dimethylallyl diphosphate + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Converts CNB12 to ADOB12
- Gene Name:
- eutT
- Uniprot ID:
- P65643
- Molecular weight:
- 30171
Reactions
| ATP + cob(I)yrinic acid a,c-diamide = triphosphate + adenosylcob(III)yrinic acid a,c-diamide. |
| ATP + cobinamide = triphosphate + adenosylcobinamide. |
- General function:
- Coenzyme transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the conversion of 7,8-dihydroneopterin triphosphate (H2NTP) to 6-carboxy-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropterin (CPH4) and acetaldehyde. Can also convert 6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin (PPH4) and sepiapterin to CPH4; these 2 compounds are probably intermediates in the reaction from H2NTP
- Gene Name:
- queD
- Uniprot ID:
- P65870
- Molecular weight:
- 13773
Reactions
| 7,8-dihydroneopterin 3'-triphosphate + H(2)O = 6-carboxy-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropterin + acetaldehyde + triphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex MalEFGK involved in maltose/maltodextrin import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- malK
- Uniprot ID:
- P68187
- Molecular weight:
- 40990
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + maltose(Out) = ADP + phosphate + maltose(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Key component of the F(0) channel; it plays a direct role in translocation across the membrane. A homomeric c-ring of 10 subunits forms the central stalk rotor element with the F(1) delta and epsilon subunits
- Gene Name:
- atpE
- Uniprot ID:
- P68699
- Molecular weight:
- 8256
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reversible transfer of the terminal phosphate group between ATP and AMP. This small ubiquitous enzyme involved in the energy metabolism and nucleotide synthesis, is essential for maintenance and cell growth
- Gene Name:
- adk
- Uniprot ID:
- P69441
- Molecular weight:
- 23586
Reactions
| ATP + AMP = 2 ADP. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the esterification, concomitant with transport, of exogenous long-chain fatty acids into metabolically active CoA thioesters for subsequent degradation or incorporation into phospholipids
- Gene Name:
- fadD
- Uniprot ID:
- P69451
- Molecular weight:
- 62332
Reactions
| ATP + a long-chain fatty acid + CoA = AMP + diphosphate + an acyl-CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- This is one of three E.coli hydrogenases synthesized in response to different physiological conditions. HYD1 is believed to have a role in hydrogen cycling during fermentative growth
- Gene Name:
- hyaA
- Uniprot ID:
- P69739
- Molecular weight:
- 40681
Reactions
| H(2) + A = AH(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- This is one of three E.coli hydrogenases synthesized in response to different physiological conditions. HYD2 is involved in hydrogen uptake
- Gene Name:
- hybO
- Uniprot ID:
- P69741
- Molecular weight:
- 39652
Reactions
| H(2) + A = AH(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex PotABCD involved in spermidine/putrescine import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- potA
- Uniprot ID:
- P69874
- Molecular weight:
- 43028
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + polyamine(Out) = ADP + phosphate + polyamine(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in glutamate decarboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- Converts glutamate to gamma-aminobutyrate (GABA), consuming one intracellular proton in the reaction. The gad system helps to maintain a near-neutral intracellular pH when cells are exposed to extremely acidic conditions. The ability to survive transit through the acidic conditions of the stomach is essential for successful colonization of the mammalian host by commensal and pathogenic bacteria
- Gene Name:
- gadA
- Uniprot ID:
- P69908
- Molecular weight:
- 52685
Reactions
| L-glutamate = 4-aminobutanoate + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in glutamate decarboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- Converts glutamate to gamma-aminobutyrate (GABA), consuming one intracellular proton in the reaction. The gad system helps to maintain a near-neutral intracellular pH when cells are exposed to extremely acidic conditions. The ability to survive transit through the acidic conditions of the stomach is essential for successful colonization of the mammalian host by commensal and pathogenic bacteria
- Gene Name:
- gadB
- Uniprot ID:
- P69910
- Molecular weight:
- 52668
Reactions
| L-glutamate = 4-aminobutanoate + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Unknown Function
- Gene Name:
- yagE
- Uniprot ID:
- P75682
- Molecular weight:
- 33316
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Oxygenase that introduces the hydroxyl group at carbon five of 2-octaprenyl-3-methyl-6-methoxy-1,4-benzoquinol resulting in the formation of 2-octaprenyl-3-methyl-5-hydroxy-6-methoxy-1,4- benzoquinol
- Gene Name:
- ubiF
- Uniprot ID:
- P75728
- Molecular weight:
- 42953
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Overexpression leads to increased undecaprenyl diphosphatase activity and to increased resistance to bacitracin. May have a preferred substrate other than undecaprenyl diphosphate in vivo
- Gene Name:
- ybjG
- Uniprot ID:
- P75806
- Molecular weight:
- 22398
Reactions
| Undecaprenyl diphosphate + H(2)O = undecaprenyl phosphate + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on other nitrogenous compounds as donors
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reduction of hydroxylamine to form NH(3) and H(2)O. Is also able to reduce hydroxylamine analogs such as methylhydroxylamine and hydroxyquinone. Might have a role as a scavenger of potentially toxic by-products of nitrate metabolism
- Gene Name:
- hcp
- Uniprot ID:
- P75825
- Molecular weight:
- 60063
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of glyoxylate and hydroxypyruvate into glycolate and glycerate, respectively. Inactive towards 2-oxo-D-gluconate, 2-oxoglutarate, oxaloacetate and pyruvate. Only D- and L-glycerate are involved in the oxidative activity with NADP. Activity with NAD is very low
- Gene Name:
- ghrA
- Uniprot ID:
- P75913
- Molecular weight:
- 35343
Reactions
| Glycolate + NADP(+) = glyoxylate + NADPH. |
| D-glycerate + NAD(P)(+) = hydroxypyruvate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of thiamine to thiamine phosphate
- Gene Name:
- thiK
- Uniprot ID:
- P75948
- Molecular weight:
- 32397
Reactions
| ATP + thiamine = ADP + thiamine phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in N-acetylglucosamine kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc) derived from cell-wall degradation, yielding GlcNAc-6-P. Has also low level glucokinase activity in vitro
- Gene Name:
- nagK
- Uniprot ID:
- P75959
- Molecular weight:
- 33042
Reactions
| ATP + N-acetyl-D-glucosamine = ADP + N-acetyl-D-glucosamine 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of a multicomponent oxygenase involved in phenylacetyl-CoA hydroxylation
- Gene Name:
- paaE
- Uniprot ID:
- P76081
- Molecular weight:
- 39320
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Could possibly oxidize fatty acids using specific components
- Gene Name:
- paaF
- Uniprot ID:
- P76082
- Molecular weight:
- 27237
Reactions
| (3S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA = trans-2(or 3)-enoyl-CoA + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-3-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA + NADP(+) = 3- acetoacetyl-CoA + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- paaH
- Uniprot ID:
- P76083
- Molecular weight:
- 51732
Reactions
| (S)-3-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA + NADP(+) = 3-acetoacetyl-CoA + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphorus-oxygen lyase activity
- Specific function:
- In association with DosC is involved in the production and removal of the second messenger c-di-GMP in response to changing O(2) levels. Has phosphodiesterase (PDE) activity with c- di-GMP (PubMed:15995192), very poor activity on cAMP (PubMed:15995192) but not with cGMP, bis(p-nitrophenyl) phosphate or p-nitrophenyl phosphate (PubMed:11970957). Cyclic-di-GMP is a second messenger which controls cell surface-associated traits in bacteria
- Gene Name:
- dosP
- Uniprot ID:
- P76129
- Molecular weight:
- 90260
Reactions
| Cyclic di-3',5'-guanylate + H(2)O = 5'-phosphoguanylyl(3'->5')guanosine. |
- General function:
- Involved in N-succinylarginine dihydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the hydrolysis of N(2)-succinylarginine into N(2)-succinylornithine, ammonia and CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- astB
- Uniprot ID:
- P76216
- Molecular weight:
- 49298
Reactions
| N(2)-succinyl-L-arginine + 2 H(2)O = N(2)-succinyl-L-ornithine + 2 NH(3) + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NAD-dependent reduction of succinylglutamate semialdehyde into succinylglutamate. Also shows activity with decanal or succinic semialdehyde as the electron donor and NAD as the electron acceptor. No activity is detected with NADP as the electron acceptor. Therefore, is an aldehyde dehydrogenase with broad substrate specificity
- Gene Name:
- astD
- Uniprot ID:
- P76217
- Molecular weight:
- 53026
Reactions
| N-succinyl-L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O = N-succinyl-L-glutamate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NAD(+)-dependent oxidative decarboxylation of D-malate into pyruvate. Is essential for aerobic growth on D- malate as the sole carbon source. But is not required for anaerobic D-malate utilization, although DmlA is expressed and active in those conditions. Appears to be not able to use L- tartrate as a substrate for dehydrogenation instead of D-malate
- Gene Name:
- dmlA
- Uniprot ID:
- P76251
- Molecular weight:
- 40315
Reactions
| (R)-malate + NAD(+) = pyruvate + CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in D-cysteine desulfhydrase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the alpha,beta-elimination reaction of D- cysteine and of several D-cysteine derivatives. It could be a defense mechanism against D-cysteine. Can also catalyze the degradation of 3-chloro-D-alanine
- Gene Name:
- dcyD
- Uniprot ID:
- P76316
- Molecular weight:
- 35153
Reactions
| D-cysteine + H(2)O = H(2)S + NH(3) + pyruvate. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- UDP-glucose + 2 NAD(+) + H(2)O = UDP- glucuronate + 2 NADH
- Gene Name:
- ugd
- Uniprot ID:
- P76373
- Molecular weight:
- 43656
Reactions
| UDP-glucose + 2 NAD(+) + H(2)O = UDP-glucuronate + 2 NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in diacylglycerol kinase activity
- Specific function:
- In vitro phosphorylates phosphatidylglycerol but not diacylglycerol; the in vivo substrate is unknown
- Gene Name:
- yegS
- Uniprot ID:
- P76407
- Molecular weight:
- 32038
- General function:
- Involved in phosphomethylpyrimidine kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of hydroxymethylpyrimidine phosphate (HMP-P) to HMP-PP, and of HMP to HMP-P. Shows no activity with pyridoxal, pyridoxamine or pyridoxine
- Gene Name:
- thiD
- Uniprot ID:
- P76422
- Molecular weight:
- 28633
Reactions
| ATP + 4-amino-5-hydroxymethyl-2-methylpyrimidine = ADP + 4-amino-5-phosphonooxymethyl-2-methylpyrimidine. |
| ATP + 4-amino-2-methyl-5-phosphomethylpyrimidine = ADP + 4-amino-2-methyl-5-diphosphomethylpyrimidine. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydroxyethylthiazole kinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + 4-methyl-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)thiazole = ADP + 4-methyl-5-(2-phosphonooxyethyl)thiazole
- Gene Name:
- thiM
- Uniprot ID:
- P76423
- Molecular weight:
- 27339
Reactions
| ATP + 4-methyl-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)thiazole = ADP + 4-methyl-5-(2-phosphonooxyethyl)thiazole. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-malate + NADP(+) = pyruvate + CO(2) + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- maeB
- Uniprot ID:
- P76558
- Molecular weight:
- 82417
Reactions
| (S)-malate + NADP(+) = pyruvate + CO(2) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the hydrolytic deamination of guanine, producing xanthine and ammonia
- Gene Name:
- guaD
- Uniprot ID:
- P76641
- Molecular weight:
- 50244
Reactions
| Guanine + H(2)O = xanthine + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the cleavage of the C5-C6 bond of 2-hydroxy-6- oxononadienedioate and 2-hydroxy-6-oxononatrienedioate, a dienol ring fission product of the bacterial meta-cleavage pathway for degradation of phenylpropionic acid
- Gene Name:
- mhpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P77044
- Molecular weight:
- 32585
Reactions
| (2E,4Z)-2-hydroxy-6-oxonona-2,4-diene-1,9-dioate + H(2)O = (2E)-2-hydroxypenta-2,4-dienoate + succinate. |
| (2E,4Z,7E)-2-hydroxy-6-oxonona-2,4,7-triene-1,9-dioate + H(2)O = (2E)-2-hydroxypenta-2,4-dienoate + fumarate. |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxal kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Phosphorylates B6 vitamers; functions in a salvage pathway. Uses pyridoxamine, but has negligible activity toward pyridoxal and pyridoxine as substrates
- Gene Name:
- pdxY
- Uniprot ID:
- P77150
- Molecular weight:
- 31322
Reactions
| ATP + pyridoxal = ADP + pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- (R)-glycerate + NAD(P)(+) = 2-hydroxy-3- oxopropanoate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- glxR
- Uniprot ID:
- P77161
- Molecular weight:
- 30800
Reactions
| D-glycerate + NAD(P)(+) = 2-hydroxy-3-oxopropanoate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in flavin adenine dinucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Xanthine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = urate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- yagS
- Uniprot ID:
- P77324
- Molecular weight:
- 33858
Reactions
| Xanthine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = urate + NADH. |
| Hypoxanthine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = xanthine + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in glycerate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + (R)-glycerate = ADP + 3-phospho-(R)- glycerate
- Gene Name:
- glxK
- Uniprot ID:
- P77364
- Molecular weight:
- 38734
Reactions
| ATP + (R)-glycerate = ADP + 3-phospho-(R)-glycerate. |
- General function:
- Involved in dimethyl sulfoxide reductase activity
- Specific function:
- Terminal reductase during anaerobic growth on various sulfoxide and N-oxide compounds
- Gene Name:
- ynfE
- Uniprot ID:
- P77374
- Molecular weight:
- 89779
- General function:
- Involved in hydroxymethyl-, formyl- and related transferase activity
- Specific function:
- Bifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of UDP-glucuronic acid (UDP-GlcUA) to UDP-4-keto- arabinose (UDP-Ara4O) and the addition of a formyl group to UDP-4- amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinose (UDP-L-Ara4N) to form UDP-L-4-formamido- arabinose (UDP-L-Ara4FN). The modified arabinose is attached to lipid A and is required for resistance to polymyxin and cationic antimicrobial peptides
- Gene Name:
- arnA
- Uniprot ID:
- P77398
- Molecular weight:
- 74288
Reactions
| UDP-alpha-D-glucuronate + NAD(+) = UDP-beta-L-threo-pentapyranos-4-ulose + CO(2) + NADH. |
| 10-formyltetrahydrofolate + UDP-4-amino-4-deoxy-beta-L-arabinose = 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate + UDP-4-deoxy-4-formamido-beta-L-arabinose. |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the formation of an hydroxyacyl-CoA by addition of water on enoyl-CoA. Also exhibits 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA epimerase and 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase activities. Strongly involved in the anaerobic degradation of long and medium-chain fatty acids in the presence of nitrate and weakly involved in the aerobic degradation of long-chain fatty acids
- Gene Name:
- fadJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P77399
- Molecular weight:
- 77072
Reactions
| (3S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA = trans-2(or 3)-enoyl-CoA + H(2)O. |
| (S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA + NAD(+) = 3-oxoacyl-CoA + NADH. |
| (S)-3-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA = (R)-3-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, acting on carbon-nitrogen (but not peptide) bonds, in linear amidines
- Specific function:
- Involved in the anaerobic utilization of allantoin. Converts allantoate to (S)-ureidoglycolate and ammonia
- Gene Name:
- allC
- Uniprot ID:
- P77425
- Molecular weight:
- 45694
- General function:
- Involved in metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Cysteine desulfurases mobilize the sulfur from L- cysteine to yield L-alanine, an essential step in sulfur metabolism for biosynthesis of a variety of sulfur-containing biomolecules. Component of the suf operon, which is activated and required under specific conditions such as oxidative stress and iron limitation. Acts as a potent selenocysteine lyase in vitro, that mobilizes selenium from L-selenocysteine. Selenocysteine lyase activity is however unsure in vivo
- Gene Name:
- sufS
- Uniprot ID:
- P77444
- Molecular weight:
- 44433
Reactions
| L-cysteine + acceptor = L-alanine + S-sulfanyl-acceptor. |
| L-selenocysteine + reduced acceptor = selenide + L-alanine + acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the acyloin condensation reaction between C atoms 2 and 3 of pyruvate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to yield 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate (DXP)
- Gene Name:
- dxs
- Uniprot ID:
- P77488
- Molecular weight:
- 67616
Reactions
| Pyruvate + D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate = 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Xanthine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = urate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- yagR
- Uniprot ID:
- P77489
- Molecular weight:
- 78088
Reactions
| Xanthine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = urate + NADH. |
| Hypoxanthine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = xanthine + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the anaerobic utilization of allantoin
- Gene Name:
- allD
- Uniprot ID:
- P77555
- Molecular weight:
- 37967
Reactions
| (S)-ureidoglycolate + NAD(P)(+) = oxalureate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the specific phosphorylation of 1,6-anhydro-N- acetylmuramic acid (anhMurNAc) with the simultaneous cleavage of the 1,6-anhydro ring, generating MurNAc-6-P. Is required for the utilization of anhMurNAc either imported from the medium or derived from its own cell wall murein, and thus plays a role in cell wall recycling
- Gene Name:
- anmK
- Uniprot ID:
- P77570
- Molecular weight:
- 39496
Reactions
| ATP + 1,6-anhydro-N-acetyl-beta-muramate + H(2)O = ADP + N-acetylmuramate 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (acetylating) activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the conversion of acetaldehyde to acetyl-CoA, using NAD(+) and coenzyme A. Is the final enzyme in the meta- cleavage pathway for the degradation of 3-phenylpropanoate. Functions as a chaperone protein for folding of mhpE
- Gene Name:
- mhpF
- Uniprot ID:
- P77580
- Molecular weight:
- 33442
Reactions
| Acetaldehyde + CoA + NAD(+) = acetyl-CoA + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in cellular amino acid biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- yahI
- Uniprot ID:
- P77624
- Molecular weight:
- 33931
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the multicomponent 3-phenylpropionate dioxygenase, that converts 3-phenylpropionic acid (PP) and cinnamic acid (CI) into 3-phenylpropionate-dihydrodiol (PP- dihydrodiol) and cinnamic acid-dihydrodiol (CI-dihydrodiol), respectively
- Gene Name:
- hcaD
- Uniprot ID:
- P77650
- Molecular weight:
- 43978
Reactions
| Reduced ferredoxin + NAD(+) = oxidized ferredoxin + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in allantoinase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the conversion of allantoin (5- ureidohydantoin) to allantoic acid by hydrolytic cleavage of the five-member hydantoin ring
- Gene Name:
- allB
- Uniprot ID:
- P77671
- Molecular weight:
- 49601
Reactions
| (S)-allantoin + H(2)O = allantoate. |
- General function:
- Involved in aminobutyraldehyde dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidation of 1-pyrroline, which is spontaneously formed from 4-aminobutanal, leading to 4- aminobutanoate (GABA). Can also oxidize n-alkyl medium-chain aldehydes, but with a lower catalytic efficiency
- Gene Name:
- ydcW
- Uniprot ID:
- P77674
- Molecular weight:
- 50830
Reactions
| 4-aminobutanal + NAD(+) + H(2)O = 4-aminobutanoate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in ureidoglycolate hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the anaerobic utilization of allantoin. Reinforces the induction of genes involved in the degradation of allantoin and glyoxylate by producing glyoxylate
- Gene Name:
- allA
- Uniprot ID:
- P77731
- Molecular weight:
- 18169
Reactions
| (S)-ureidoglycolate + H(2)O = glyoxylate + 2 NH(3) + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in dimethyl sulfoxide reductase activity
- Specific function:
- Terminal reductase during anaerobic growth on various sulfoxide and N-oxide compounds
- Gene Name:
- ynfF
- Uniprot ID:
- P77783
- Molecular weight:
- 89986
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Specific for pyrimidine substrates. Acts on 5-methyl- dCTP, CTP and dCTP in decreasing order
- Gene Name:
- nudG
- Uniprot ID:
- P77788
- Molecular weight:
- 15046
Reactions
| CTP + H(2)O = CMP + diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in glutamate-ammonia ligase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the breakdown of putrescine via the biosynthesis of gamma-L-glutamylputrescine
- Gene Name:
- puuA
- Uniprot ID:
- P78061
- Molecular weight:
- 53177
Reactions
| ATP + L-glutamate + putrescine = ADP + phosphate + gamma-L-glutamylputrescine. |
- General function:
- Involved in thiosulfate sulfurtransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Thiosulfate + cyanide = sulfite + thiocyanate
- Gene Name:
- ynjE
- Uniprot ID:
- P78067
- Molecular weight:
- 48228
Reactions
| Thiosulfate + cyanide = sulfite + thiocyanate. |
- General function:
- Involved in FMN reductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes an NAD(P)H-dependent reduction of FMN, but is also able to reduce FAD or riboflavin
- Gene Name:
- ssuE
- Uniprot ID:
- P80644
- Molecular weight:
- 21253
Reactions
| FMNH(2) + NADP(+) = FMN + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in alkanesulfonate monooxygenase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in desulfonation of aliphatic sulfonates. Catalyzes the conversion of pentanesulfonic acid to sulfite and pentaldehyde and is able to desulfonate a wide range of sulfonated substrates including C-2 to C-10 unsubstituted linear alkanesulfonates, substituted ethanesulfonic acids and sulfonated buffers
- Gene Name:
- ssuD
- Uniprot ID:
- P80645
- Molecular weight:
- 41736
Reactions
| An alkanesufonate (R-CH(2)-SO(3)H) + FMNH(2) + O(2) = an aldehyde (R-CHO) + FMN + sulfite + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Acts almost equally well on phenylacetaldehyde, 4- hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde
- Gene Name:
- feaB
- Uniprot ID:
- P80668
- Molecular weight:
- 53699
Reactions
| Phenylacetaldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O = phenylacetate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Presumed to be a dehydrogenase, but possibly an oxidase. Participates in limited purine salvage (requires aspartate) but does not support aerobic growth on purines as the sole carbon source (purine catabolism). Deletion results in increased adenine sensitivity, suggesting that this protein contributes to the conversion of adenine to guanine nucleotides during purine salvage
- Gene Name:
- xdhA
- Uniprot ID:
- Q46799
- Molecular weight:
- 81320
Reactions
| Xanthine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = urate + NADH. |
| Hypoxanthine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = xanthine + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in flavin adenine dinucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Presumed to be a dehydrogenase, but possibly an oxidase. Participates in limited purine salvage (requires aspartate) but does not support aerobic growth on purines as the sole carbon source (purine catabolism)
- Gene Name:
- xdhB
- Uniprot ID:
- Q46800
- Molecular weight:
- 31557
Reactions
| Xanthine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = urate + NADH. |
| Hypoxanthine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = xanthine + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Iron-sulfur subunit of the xanthine dehydrogenase complex
- Gene Name:
- xdhC
- Uniprot ID:
- Q46801
- Molecular weight:
- 16922
- General function:
- Involved in cellular amino acid biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- yqeA
- Uniprot ID:
- Q46807
- Molecular weight:
- 33071
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reduction of 2,5-diketo-D-gluconic acid (25DKG) to 2-keto-L-gulonic acid (2KLG). It is also capable of stereoselective -keto ester reductions on ethyl acetoacetate and other 2-substituted derivatives
- Gene Name:
- dkgA
- Uniprot ID:
- Q46857
- Molecular weight:
- 31109
Reactions
| 2-dehydro-D-gluconate + NADP(+) = 2,5-didehydro-D-gluconate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the formation of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C- methyl-D-erythritol from CTP and 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4- phosphate (MEP)
- Gene Name:
- ispD
- Uniprot ID:
- Q46893
- Molecular weight:
- 25737
Reactions
| CTP + 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate = diphosphate + 4-(cytidine 5'-diphospho)-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on other nitrogenous compounds as donors, with NAD or NADP as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of 7-cyano-7- deazaguanine (preQ0) to 7-aminomethyl-7-deazaguanine (preQ1)
- Gene Name:
- queF
- Uniprot ID:
- Q46920
- Molecular weight:
- 32587
Reactions
| 7-aminomethyl-7-carbaguanine + 2 NADP(+) = 7-cyano-7-carbaguanine + 2 NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the removal of elemental sulfur and selenium atoms from L-cysteine, L-cystine, L-selenocysteine, and L- selenocystine to produce L-alanine. L-cysteine sulfinic acid is the best substrate. Functions as a selenium delivery protein in the pathway for the biosynthesis of selenophosphate
- Gene Name:
- csdA
- Uniprot ID:
- Q46925
- Molecular weight:
- 43234
- General function:
- Involved in 3-phenylpropionate dioxygenase activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the multicomponent 3-phenylpropionate dioxygenase. Converts 3-phenylpropionic acid (PP) and cinnamic acid (CI) into 3-phenylpropionate-dihydrodiol (PP-dihydrodiol) and cinnamic acid-dihydrodiol (CI-dihydrodiol), respectively
- Gene Name:
- hcaF
- Uniprot ID:
- Q47140
- Molecular weight:
- 20579
Reactions
| 3-phenylpropanoate + NADH + O(2) = 3-(cis-5,6-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,3-dien-1-yl)propanoate + NAD(+). |
| (2E)-3-phenylprop-2-enoate + NADH + O(2) = (2E)-3-(2,3-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate + NAD(+). |
- General function:
- Involved in homocysteine S-methyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes methyl transfer from S-methylmethionine or S- adenosylmethionine (less efficient) to homocysteine, selenohomocysteine and less efficiently selenocysteine
- Gene Name:
- mmuM
- Uniprot ID:
- Q47690
- Molecular weight:
- 33422
Reactions
| S-methyl-L-methionine + L-homocysteine = 2 L-methionine. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in copper export. May also be involved in silver export
- Gene Name:
- copA
- Uniprot ID:
- Q59385
- Molecular weight:
- 87872
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Cu(+)(In) = ADP + phosphate + Cu(+)(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- ytfR
- Uniprot ID:
- Q6BEX0
- Molecular weight:
- 55259
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, in phosphorus-containing anhydrides
- Specific function:
- Acts on ADP-mannose and ADP-glucose as well as ADP- ribose. Prevents glycogen biosynthesis. The reaction catalyzed by this enzyme is a limiting step of the gluconeogenic process
- Gene Name:
- nudF
- Uniprot ID:
- Q93K97
- Molecular weight:
- 23667
Reactions
| ADP-ribose + H(2)O = AMP + D-ribose 5-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Reduces trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) into trimethylamine; an anaerobic reaction coupled to energy-yielding reactions. Can also reduce other N- and S-oxide compounds such as 4-methylmorpholine-N-oxide and biotin sulfoxide (BSO), but with a lower catalytic efficiency
- Gene Name:
- torZ
- Uniprot ID:
- P46923
- Molecular weight:
- 88964
Reactions
| Trimethylamine + 2 (ferricytochrome c)-subunit + H(2)O = trimethylamine N-oxide + 2 (ferrocytochrome c)-subunit + 2 H(+). |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring glycosyl groups
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes heptose transfer to the lipopolysaccharide core. It transfers a heptose, called heptose(III), to the heptose(II) of the inner core
- Gene Name:
- rfaQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P25742
- Molecular weight:
- 38730
- General function:
- Involved in biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Involved in the addition of the first glucose residue to the lipopolysaccharide core
- Gene Name:
- rfaG
- Uniprot ID:
- P25740
- Molecular weight:
- 42284
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of heptose(II) of the outer membrane lipopolysaccharide core
- Gene Name:
- rfaY
- Uniprot ID:
- P27240
- Molecular weight:
- 27461
- General function:
- Involved in lipopolysaccharide biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Confers a modal distribution of chain length on the O- antigen component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Gives rise to a reduced number of short chain molecules and increases in numbers of longer molecules
- Gene Name:
- wzzB
- Uniprot ID:
- P76372
- Molecular weight:
- 36455
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring glycosyl groups
- Specific function:
- Adds the terminal N-acetyl-D-glucosamine group on the glucose(II) group of LPS
- Gene Name:
- waaU
- Uniprot ID:
- P27242
- Molecular weight:
- 41729
Reactions
| UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine + lipopolysaccharide = UDP + N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyllipopolysaccharide. |
- General function:
- Involved in biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Adds a galactose goup to a glucose group of LPS
- Gene Name:
- rfaB
- Uniprot ID:
- P27127
- Molecular weight:
- 40826
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring glycosyl groups
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- rfaF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37692
- Molecular weight:
- 39042
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of heptose(I) of the outer membrane lipopolysaccharide core
- Gene Name:
- rfaP
- Uniprot ID:
- P25741
- Molecular weight:
- 30872
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring glycosyl groups
- Specific function:
- Heptose transfer to the lipopolysaccharide core. It transfers the innnermost heptose to [4'-P](3-deoxy-D-manno- octulosonic acid)2-IVA
- Gene Name:
- rfaC
- Uniprot ID:
- P24173
- Molecular weight:
- 35544
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport
- Gene Name:
- artI
- Uniprot ID:
- P30859
- Molecular weight:
- 26929
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport. Binds L-arginine with high affinity
- Gene Name:
- artJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P30860
- Molecular weight:
- 26829
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- artQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE34
- Molecular weight:
- 26217
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Has low ATPase activity. The sufBCD complex acts synergistically with sufE to stimulate the cysteine desulfurase activity of sufS. The sufBCD complex contributes to the assembly or repair of oxygen-labile iron-sulfur clusters under oxidative stress. May facilitate iron uptake from extracellular iron chelators under iron limitation
- Gene Name:
- sufC
- Uniprot ID:
- P77499
- Molecular weight:
- 27582
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system ydcSTUV
- Gene Name:
- ydcS
- Uniprot ID:
- P76108
- Molecular weight:
- 42295
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Probably part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system ydcSTUV. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- ydcT
- Uniprot ID:
- P77795
- Molecular weight:
- 37040
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system ydcSTUV; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ydcU
- Uniprot ID:
- P77156
- Molecular weight:
- 34360
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system ydcSTUV; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ydcV
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFR9
- Molecular weight:
- 28722
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- yjfF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37772
- Molecular weight:
- 34977
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- ytfQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P39325
- Molecular weight:
- 34344
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ytfT
- Uniprot ID:
- P39328
- Molecular weight:
- 35659
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for maltose; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- malF
- Uniprot ID:
- P02916
- Molecular weight:
- 57013
- General function:
- Involved in cobalamin transport
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex BtuCDF involved in vitamin B12 import. Involved in the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- btuC
- Uniprot ID:
- P06609
- Molecular weight:
- 34949
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex fhuCDB involved in iron(3+)-hydroxamate import. Responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fhuB
- Uniprot ID:
- P06972
- Molecular weight:
- 70422
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for phosphate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- pstA
- Uniprot ID:
- P07654
- Molecular weight:
- 32321
- General function:
- Involved in lipopolysaccharide transport
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex lptBFG involved in the translocation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from the inner membrane to the outer membrane
- Gene Name:
- lptG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ADC6
- Molecular weight:
- 39618
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for L-arabinose. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- araH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE26
- Molecular weight:
- 34211
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- artM
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE30
- Molecular weight:
- 24914
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP (TC 3.A.1.6.1) involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- cysW
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEB0
- Molecular weight:
- 32537
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- dppB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEF8
- Molecular weight:
- 37497
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- dppC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEG1
- Molecular weight:
- 32308
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for glutamine; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- glnP
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEQ6
- Molecular weight:
- 24364
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for aspartate/glutamate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- gltJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AER3
- Molecular weight:
- 27502
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for aspartate/glutamate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- gltK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AER5
- Molecular weight:
- 24914
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for histidine; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- hisM
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEU3
- Molecular weight:
- 26870
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for branched-chain amino acids. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrates across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- livH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEX7
- Molecular weight:
- 32982
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for molybdenum; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- modB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AF01
- Molecular weight:
- 24939
- General function:
- Involved in lipopolysaccharide-transporting ATPase acti
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex lptBFG involved in the translocation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from the inner membrane to the outer membrane
- Gene Name:
- lptF
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AF98
- Molecular weight:
- 40357
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a nickel transport system, probably translocates nickel through the bacterial inner membrane
- Gene Name:
- nikC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFA9
- Molecular weight:
- 30362
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for oligopeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- oppB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFH2
- Molecular weight:
- 33443
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for oligopeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- oppC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFH6
- Molecular weight:
- 33022
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine and spermidine
- Gene Name:
- potB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFK4
- Molecular weight:
- 31062
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine and spermidine
- Gene Name:
- potC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFK6
- Molecular weight:
- 29111
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine
- Gene Name:
- potI
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFL1
- Molecular weight:
- 30540
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for phosphate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- pstC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGH8
- Molecular weight:
- 34121
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ribose. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- rbsC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGI1
- Molecular weight:
- 33452
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for D-xylose. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- xylH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGI4
- Molecular weight:
- 41030
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for sn-glycerol-3-phosphate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ugpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P10905
- Molecular weight:
- 33264
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for sn-glycerol-3-phosphate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ugpE
- Uniprot ID:
- P10906
- Molecular weight:
- 31499
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a multicomponent binding-protein-dependent transport system for glycine betaine/L-proline
- Gene Name:
- proW
- Uniprot ID:
- P14176
- Molecular weight:
- 37619
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for citrate-dependent Fe(3+). Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fecD
- Uniprot ID:
- P15029
- Molecular weight:
- 34131
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for citrate-dependent Fe(3+). Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fecC
- Uniprot ID:
- P15030
- Molecular weight:
- 34892
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP (TC 3.A.1.6.1) involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- cysU
- Uniprot ID:
- P16701
- Molecular weight:
- 30292
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for branched-chain amino acids. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrates across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- livM
- Uniprot ID:
- P22729
- Molecular weight:
- 46269
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for galactoside. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- mglC
- Uniprot ID:
- P23200
- Molecular weight:
- 35550
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ferric enterobactin. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fepD
- Uniprot ID:
- P23876
- Molecular weight:
- 33871
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ferric enterobactin. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fepG
- Uniprot ID:
- P23877
- Molecular weight:
- 34910
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Somehow involved in the cytochrome D branch of aerobic respiration. Seems to be a component of a transport system
- Gene Name:
- cydC
- Uniprot ID:
- P23886
- Molecular weight:
- 62920
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Somehow involved in the cytochrome D branch of aerobic respiration. Seems to be a component of a transport system
- Gene Name:
- cydD
- Uniprot ID:
- P29018
- Molecular weight:
- 65055
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine
- Gene Name:
- potH
- Uniprot ID:
- P31135
- Molecular weight:
- 35489
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex thiBPQ involved in thiamine import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- thiP
- Uniprot ID:
- P31549
- Molecular weight:
- 59532
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system AlsBAC for D-allose; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- alsC
- Uniprot ID:
- P32720
- Molecular weight:
- 34315
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- yehW
- Uniprot ID:
- P33359
- Molecular weight:
- 25514
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- yehY
- Uniprot ID:
- P33361
- Molecular weight:
- 41138
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a nickel transport system, probably translocates nickel through the bacterial inner membrane
- Gene Name:
- nikB
- Uniprot ID:
- P33591
- Molecular weight:
- 35248
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for histidine; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- hisQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P52094
- Molecular weight:
- 24649
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in lipid A export and possibly also in glycerophospholipid export and for biogenesis of the outer membrane. Transmembrane domains (TMD) form a pore in the inner membrane and the ATP-binding domain (NBD) is responsible for energy generation
- Gene Name:
- msbA
- Uniprot ID:
- P60752
- Molecular weight:
- 64460
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for maltose; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- malG
- Uniprot ID:
- P68183
- Molecular weight:
- 32225
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex gsiABCD involved in glutathione import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- gsiC
- Uniprot ID:
- P75798
- Molecular weight:
- 34066
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex gsiABCD involved in glutathione import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- gsiD
- Uniprot ID:
- P75799
- Molecular weight:
- 33238
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system for aliphatic sulfonates. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ssuC
- Uniprot ID:
- P75851
- Molecular weight:
- 28925
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ddpABCDF, which is probably involved in D,D-dipeptide transport. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ddpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P77308
- Molecular weight:
- 37345
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ddpABCDF, which is probably involved in D,D-dipeptide transport. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ddpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P77463
- Molecular weight:
- 31971
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system for taurine. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- tauC
- Uniprot ID:
- Q47539
- Molecular weight:
- 29812
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the ADP transfer to D-glycero-D-manno-heptose 1-phosphate, yielding ADP-D,D-heptose
- Gene Name:
- hldE
- Uniprot ID:
- P76658
- Molecular weight:
- 51050
Reactions
| ATP + D-glycero-beta-D-manno-heptose 7-phosphate = ADP + D-glycero-beta-D-manno-heptose 1,7-bisphosphate. |
| ATP + D-glycero-beta-D-manno-heptose 1-phosphate = diphosphate + ADP-D-glycero-beta-D-manno-heptose. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Links a guanosine 5'-phosphate to molydopterin (MPT) forming molybdopterin guanine dinucleotide (MGD)
- Gene Name:
- mobA
- Uniprot ID:
- P32173
- Molecular weight:
- 21643
Reactions
| GTP + molybdenum cofactor = diphosphate + guanylyl molybdenum cofactor. |
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a nickel transport system, probably represents the nickel binder
- Gene Name:
- nikA
- Uniprot ID:
- P33590
- Molecular weight:
- 58718
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in electron transfer (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- napG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAL3
- Molecular weight:
- 24924
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- This protein specifically binds sulfate and is involved in its transmembrane transport
- Gene Name:
- sbp
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG78
- Molecular weight:
- 36659
- General function:
- Involved in GTP binding
- Specific function:
- GTP-driven Fe(2+) uptake system
- Gene Name:
- feoB
- Uniprot ID:
- P33650
- Molecular weight:
- 84473
- General function:
- Involved in coenzyme binding
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- mdaB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEY5
- Molecular weight:
- 21891
- General function:
- Involved in intramolecular lyase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the interconversion of beta-pyran and beta- furan forms of D-ribose. It also catalyzes the conversion between beta-allofuranose and beta-allopyranose
- Gene Name:
- rbsD
- Uniprot ID:
- P04982
- Molecular weight:
- 15292
Reactions
| Beta-D-ribopyranose = beta-D-ribofuranose. |
| Beta-D-allopyranose = beta-D-allofuranose. |
- General function:
- Involved in protein binding
- Specific function:
- Transaminase converting thymidine diphosphate(TDP)-4- keto-6-deoxy-D-glucose to TDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-D-galactose, the immediate precursor of the ECA sugar TDP-Fuc4NAc
- Gene Name:
- rffC
- Uniprot ID:
- P27832
- Molecular weight:
- 24220
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex MetNIQ involved in methionine import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable). It has also been shown to be involved in formyl-L-methionine transport
- Gene Name:
- metN
- Uniprot ID:
- P30750
- Molecular weight:
- 37788
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ddpABCDF, which is probably involved in D,D-dipeptide transport. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- ddpD
- Uniprot ID:
- P77268
- Molecular weight:
- 36100
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for glutamine. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- glnQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P10346
- Molecular weight:
- 26731
- General function:
- Involved in sulfur compound metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system for aliphatic sulfonates. Putative binding protein
- Gene Name:
- ssuA
- Uniprot ID:
- P75853
- Molecular weight:
- 34557
- General function:
- Involved in maltose transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity maltose membrane transport system malEFGK. Initial receptor for the active transport of and chemotaxis toward maltooligosaccharides
- Gene Name:
- malE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEX9
- Molecular weight:
- 43387
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- yneI
- Uniprot ID:
- P76149
- Molecular weight:
- 49717
Reactions
| Succinate semialdehyde + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = succinate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in Mo-molybdopterin cofactor biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the insertion of molybdate into adenylated molybdopterin with the concomitant release of AMP
- Gene Name:
- moeA
- Uniprot ID:
- P12281
- Molecular weight:
- 44067
Reactions
| Adenylyl-molybdopterin + molybdate = molybdenum cofactor + AMP. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- hyfJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P77453
- Molecular weight:
- 15577
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Binds ferrienterobactin; part of the binding-protein- dependent transport system for uptake of ferrienterobactin
- Gene Name:
- fepB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEL6
- Molecular weight:
- 34283
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for oligopeptides. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- oppF
- Uniprot ID:
- P77737
- Molecular weight:
- 37197
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- ygfA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AC28
- Molecular weight:
- 21105
- General function:
- Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis
- Specific function:
- Makes part of the rut operon, which is required for the utilization of pyrimidines as sole nitrogen source
- Gene Name:
- rutC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFQ5
- Molecular weight:
- 13763
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring pentosyl groups
- Specific function:
- IGPS catalyzes the conversion of PRFAR and glutamine to IGP, AICAR and glutamate. The hisH subunit provides the glutamine amidotransferase activity that produces the ammonia necessary to hisF for the synthesis of IGP and AICAR
- Gene Name:
- hisH
- Uniprot ID:
- P60595
- Molecular weight:
- 21653
Reactions
| 5-[(5-phospho-1-deoxyribulos-1-ylamino)methylideneamino]-1-(5-phosphoribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide + L-glutamine = imidazole-glycerol phosphate + 5-aminoimidazol-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide + L-glutamate + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity D-xylose membrane transport system. Binds with high affinity to xylose
- Gene Name:
- xylF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37387
- Molecular weight:
- 35734
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ZnuABC involved in zinc import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- znuC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9X1
- Molecular weight:
- 27867
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Active on adenosine(5')triphospho(5')adenosine (Ap3A), ADP-ribose, NADH, adenosine(5')diphospho(5')adenosine (Ap2A)
- Gene Name:
- nudE
- Uniprot ID:
- P45799
- Molecular weight:
- 21153
Reactions
| ADP-ribose + H(2)O = AMP + D-ribose 5-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in iron-sulfur cluster assembly
- Specific function:
- The sufBCD complex acts synergistically with sufE to stimulate the cysteine desulfurase activity of sufS. The sufBCD complex contributes to the assembly or repair of oxygen-labile iron-sulfur clusters under oxidative stress. May facilitate iron uptake from extracellular iron chelators under iron limitation
- Gene Name:
- sufB
- Uniprot ID:
- P77522
- Molecular weight:
- 54745
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- dppD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAG0
- Molecular weight:
- 35844
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- hyfD
- Uniprot ID:
- P77416
- Molecular weight:
- 51754
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Thioesterase that appears to be involved in phospholipid metabolism. Some specific acyl-ACPs could be physiological substrates. Displays acyl-CoA thioesterase activity on malonyl-CoA in vitro, catalyzing the hydrolysis of the thioester bond
- Gene Name:
- ybgC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A8Z3
- Molecular weight:
- 15562
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- maoC
- Uniprot ID:
- P77455
- Molecular weight:
- 73002
Reactions
| 2-oxepin-2(3H)-ylideneacetyl-CoA + H(2)O = 3-oxo-5,6-dehydrosuberyl-CoA semialdehyde. |
| 3-oxo-5,6-dehydrosuberyl-CoA semialdehyde + NADP(+) + H(2)O = 3-oxo-5,6-dehydrosuberyl-CoA + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reversible formation of acyl-phosphate (acyl-PO(4)) from acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] (acyl-ACP). This enzyme utilizes acyl-ACP as fatty acyl donor, but not acyl-CoA
- Gene Name:
- plsX
- Uniprot ID:
- P27247
- Molecular weight:
- 38214
Reactions
| Acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + phosphate = acyl-phosphate + [acyl-carrier-protein]. |
- General function:
- Involved in GTP binding
- Specific function:
- May bind the guanine nucleotide required for the synthesis of molybdopterin guanine dinucleotide
- Gene Name:
- mobB
- Uniprot ID:
- P32125
- Molecular weight:
- 19363
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Probably catalyzes the hydrolysis of L-ascorbate-6-P into 3-keto-L-gulonate-6-P. Is essential for L-ascorbate utilization under anaerobic conditions. Also shows phosphodiesterase activity, hydrolyzing phosphodiester bond in the artificial chromogenic substrate bis-p-nitrophenyl phosphate (bis- pNPP)
- Gene Name:
- ulaG
- Uniprot ID:
- P39300
- Molecular weight:
- 40060
Reactions
| L-ascorbate 6-phosphate + H(2)O = 3-dehydro-L-gulonate 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- May be involved in an alternative pathway for phosphopantetheinyl transfer and holo-ACP synthesis in E.coli. The native apo-protein substrate is unknown. Is able to functionally replace AcpS in vivo but only when expressed at high levels
- Gene Name:
- acpT
- Uniprot ID:
- P37623
- Molecular weight:
- 21768
Reactions
| CoA + [protein-X] = adenosine 3',5'-bisphosphate + phosphopantetheinyl-[protein-X]. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in electron transfer
- Gene Name:
- napH
- Uniprot ID:
- P33934
- Molecular weight:
- 31873
- General function:
- Involved in Mo-molybdopterin cofactor biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the adenylation of molybdopterin as part of the biosynthesis of the molybdenum-cofactor
- Gene Name:
- mog
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AF03
- Molecular weight:
- 21222
Reactions
| ATP + molybdopterin = diphosphate + adenylyl-molybdopterin. |
- General function:
- Involved in cytochrome bo3 ubiquinol oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Cytochrome o terminal oxidase complex is the component of the aerobic respiratory chain of E.coli that predominates when cells are grown at high aeration
- Gene Name:
- cyoA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABJ1
- Molecular weight:
- 34911
Reactions
| Ubiquinol-8 + O(2) = Ubiquinone-8 + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Inorganic ion transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- cyaY
- Uniprot ID:
- P27838
- Molecular weight:
- 12231
- General function:
- Involved in cytidylyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- ygfJ
- Uniprot ID:
- Q46810
- Molecular weight:
- 21514
Reactions
| CTP + molybdenum cofactor = diphosphate + cytidylyl molybdenum cofactor. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Cell wall formation. The enzyme has a penicillin- insensitive transglycosylase N-terminal domain (formation of linear glycan strands) and a transpeptidase C-terminal domain which may not be functional
- Gene Name:
- pbpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P76577
- Molecular weight:
- 85066
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Converts 3-phenylpropionate-dihydrodiol (PP-dihydrodiol) and cinnamic acid-dihydrodiol (CI-dihydrodiol) into 3-(2,3-dihydroxylphenyl)propanoic acid (DHPP) and 2,3-dihydroxicinnamic acid (DHCI), respectively (By similarity). Converts 3-phenylpropionate-dihydrodiol (PP-dihydrodiol) and cinnamic acid-dihydrodiol (CI-dihydrodiol) into 3-(2,3-dihydroxylphenyl)propanoic acid (DHPP) and 2,3-dihydroxicinnamic acid (DHCI), respectively (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- hcaB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0CI31
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
Reactions
| 3-(cis-5,6-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,3-dien-1-yl)propanoate + NAD(+) = 3-(2,3-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoate + NADH. |
| 3-(cis-5,6-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,3-dien-1-yl)propanoate + NAD(+) = 3-(2,3-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoate + NADH. |
| (2E)-3-(cis-5,6-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,3-dien-1-yl)prop-2-enoate + NAD(+) = (2E)-3-(2,3-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the adenylation by ATP of the carboxyl group of the C-terminal glycine of sulfur carrier protein ThiS
- Gene Name:
- thiF
- Uniprot ID:
- P30138
- Molecular weight:
- 26970
Reactions
| ATP + [ThiS] = diphosphate + adenylyl-[ThiS]. |
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Essential for the uptake of the murein peptide L-alanyl- gamma-D-glutamyl-meso-diaminopimelate. Also transports some alpha- linked peptides such as Pro-Phe-Lys with low affinity. The transport is effected by the oligopeptide permease system
- Gene Name:
- mppA
- Uniprot ID:
- P77348
- Molecular weight:
- 59900
- General function:
- Involved in FMN binding
- Specific function:
- Low-potential electron donor to a number of redox enzymes (Potential)
- Gene Name:
- fldB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABY4
- Molecular weight:
- 19700
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- wcaK
- Uniprot ID:
- P71242
- Molecular weight:
- 47343
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- May be involved in the formation or repair of [Fe-S] clusters present in iron-sulfur proteins (Potential)
- Gene Name:
- nifU
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ACD4
- Molecular weight:
- 13848
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Makes part of the rut operon, which is required for the utilization of pyrimidines as sole nitrogen source
- Gene Name:
- rutE
- Uniprot ID:
- P75894
- Molecular weight:
- 21570
Reactions
| 3-hydroxypropanoate + NADP(+) = 3-oxopropanoate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on NADH or NADPH
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- hyfG
- Uniprot ID:
- P77329
- Molecular weight:
- 63383
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the anaerobic respiratory chain of trimethylamine-N-oxide reductase torZ. Required for electron transfer to the torZ terminal enzyme
- Gene Name:
- torY
- Uniprot ID:
- P52005
- Molecular weight:
- 40286
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- This periplasmic binding protein is involved in an arginine transport system. ArgT and histidine-binding protein J (hisJ) interact with a common membrane-bound receptor, hisP
- Gene Name:
- argT
- Uniprot ID:
- P09551
- Molecular weight:
- 27991
- General function:
- Involved in lipid transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- mviN
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AF16
- Molecular weight:
- 55267
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex BtuCDF involved in vitamin B12 import. Binds vitamin B12 and delivers it to the periplasmic surface of BtuC
- Gene Name:
- btuF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37028
- Molecular weight:
- 29367
- General function:
- Involved in biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- May be a glycosyltransferase involved in the transfer of UDP-GalF and UDP-glucose
- Gene Name:
- yefI
- Uniprot ID:
- P37751
- Molecular weight:
- 43188
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system AlsBAC for D-allose
- Gene Name:
- alsB
- Uniprot ID:
- P39265
- Molecular weight:
- 32910
- General function:
- Involved in FMN binding
- Specific function:
- Low-potential electron donor to a number of redox enzymes (Potential). Involved in the reactivation of inactive cob(II)alamin in methionine synthase
- Gene Name:
- fldA
- Uniprot ID:
- P61949
- Molecular weight:
- 19737
- General function:
- Involved in anaerobic electron transport chain
- Specific function:
- Terminal reductase during anaerobic growth on various sulfoxide and N-oxide compounds. DmsC anchors the dmsAB dimer to the membrane and stabilizes it
- Gene Name:
- dmsC
- Uniprot ID:
- P18777
- Molecular weight:
- 30826
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex gsiABCD involved in glutathione import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- gsiA
- Uniprot ID:
- P75796
- Molecular weight:
- 69113
- General function:
- Involved in carboxy-lyase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the decarboxylation of 3-octaprenyl-4-hydroxy benzoate to 2-octaprenylphenol
- Gene Name:
- ubiD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAB4
- Molecular weight:
- 55603
- General function:
- Involved in RNA binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the ATP-dependent transfer of a sulfur to tRNA to produce 4-thiouridine in position 8 of tRNAs, which functions as a near-UV photosensor. Also catalyzes the transfer of sulfur to the sulfur carrier protein ThiS, forming ThiS-thiocarboxylate. This is a step in the synthesis of thiazole, in the thiamine biosynthesis pathway. The sulfur is donated as persulfide by iscS
- Gene Name:
- thiI
- Uniprot ID:
- P77718
- Molecular weight:
- 54973
Reactions
| L-cysteine + 'activated' tRNA = L-serine + tRNA containing a thionucleotide. |
| [IscS]-SSH + [ThiS]-COAMP = [IscS]-SH + [ThiS]-COSH + AMP. |
- General function:
- Involved in protein complex assembly
- Specific function:
- Required for the export of heme to the periplasm for the biogenesis of c-type cytochromes
- Gene Name:
- ccmC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABM1
- Molecular weight:
- 27885
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Probable b-type cytochrome
- Gene Name:
- hyaC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAM1
- Molecular weight:
- 27597
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP (TC 3.A.1.6.1) involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. This protein specifically binds thiosulfate and is involved in its transmembrane transport
- Gene Name:
- cysP
- Uniprot ID:
- P16700
- Molecular weight:
- 37614
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the rearrangement of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5- phosphate (DXP) to produce the thiazole phosphate moiety of thiamine. Sulfur is provided by the thiocarboxylate moiety of the carrier protein ThiS. In vitro, sulfur can be provided by H(2)S
- Gene Name:
- thiG
- Uniprot ID:
- P30139
- Molecular weight:
- 26896
Reactions
| 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate + 2-iminoacetate + thiocarboxy-adenylate-[sulfur-carrier protein ThiS] = 2-((2R,5Z)-2-carboxy-4-methylthiazol-5(2H)-ylidene)ethyl phosphate + [sulfur-carrier protein ThiS] + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- yehX
- Uniprot ID:
- P33360
- Molecular weight:
- 34424
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of the oligopeptide permease, a binding protein-dependent transport system, it binds peptides up to five amino acids long with high affinity
- Gene Name:
- oppA
- Uniprot ID:
- P23843
- Molecular weight:
- 60899
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex lptBFG involved in the translocation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from the inner membrane to the outer membrane. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- lptB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9V1
- Molecular weight:
- 26800
- General function:
- Involved in 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- yihU
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9V8
- Molecular weight:
- 31158
- General function:
- Involved in structural molecule activity
- Specific function:
- Is able to transfer iron-sulfur clusters to apo- ferredoxin. Multiple cycles of [2Fe2S] cluster formation and transfer are observed, suggesting that iscA acts catalytically. Recruits intracellular free iron so as to provide iron for the assembly of transient iron-sulfur cluster in iscU in the presence of iscS, L-cysteine and the thioredoxin reductase system trxA/trxB
- Gene Name:
- iscA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAC8
- Molecular weight:
- 11556
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- dppF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37313
- Molecular weight:
- 37560
- General function:
- Involved in FMN binding
- Specific function:
- Makes part of the rut operon, which is required for the utilization of pyrimidines as sole nitrogen source
- Gene Name:
- rutF
- Uniprot ID:
- P75893
- Molecular weight:
- 17749
Reactions
| FMNH(2) + NAD(+) = FMN + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in iron-sulfur cluster binding
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- yeiA
- Uniprot ID:
- P25889
- Molecular weight:
- 45069
Reactions
| 5,6-dihydrouracil + NAD(+) = uracil + NADH. |
| 5,6-dihydrothymine + NAD(+) = thymine + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- hyfF
- Uniprot ID:
- P77437
- Molecular weight:
- 56766
- General function:
- Involved in phosphate ion binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex pstSACB involved in phosphate import
- Gene Name:
- pstS
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG82
- Molecular weight:
- 37024
- General function:
- Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism
- Specific function:
- May be part of a multicomponent oxygenase involved in phenylacetyl-CoA hydroxylation
- Gene Name:
- paaB
- Uniprot ID:
- P76078
- Molecular weight:
- 10942
- General function:
- Coenzyme transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Is the sulfur donor in the synthesis of the thiazole phosphate moiety of thiamine phosphate
- Gene Name:
- thiS
- Uniprot ID:
- O32583
- Molecular weight:
- 7311
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Not known; overproduction leads to camphor resistance and chromosome condensation
- Gene Name:
- crcA
- Uniprot ID:
- P37001
- Molecular weight:
- 21770
- General function:
- Energy production and conversion
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- yghZ
- Uniprot ID:
- Q46851
- Molecular weight:
- 38832
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Participates in cysteine desulfuration mediated by sufS. Cysteine desulfuration mobilizes sulfur from L-cysteine to yield L-alanine and constitutes an essential step in sulfur metabolism for biosynthesis of a variety of sulfur-containing biomolecules. Functions as a sulfur acceptor for sufS, by mediating the direct transfer of the sulfur atom from the S-sulfanylcysteine of sufS, an intermediate product of cysteine desulfuration process. Together with the sufBCD complex, it thereby enhances up to 50- fold, the cysteine desulfurase activity of sufS. Component of the suf operon, which is activated and required under specific conditions such as oxidative stress and iron limitation. Does not affect the selenocysteine lyase activity of sufS
- Gene Name:
- sufE
- Uniprot ID:
- P76194
- Molecular weight:
- 15800
- General function:
- Involved in heme transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the export of heme to the periplasm for the biogenesis of c-type cytochromes
- Gene Name:
- ccmB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABL8
- Molecular weight:
- 23618
- General function:
- Involved in lipopolysaccharide transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the translocation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from the inner membrane to the outer membrane
- Gene Name:
- lptC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ADV9
- Molecular weight:
- 21703
- General function:
- Involved in cytochrome o ubiquinol oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Cytochrome o terminal oxidase complex is the component of the aerobic respiratory chain of E.coli that predominates when cells are grown at high aeration
- Gene Name:
- cyoD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABJ6
- Molecular weight:
- 12029
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Monothiol glutaredoxin involved in the biogenesis of iron-sulfur clusters (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- grxD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AC69
- Molecular weight:
- 12879
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- yeaE
- Uniprot ID:
- P76234
- Molecular weight:
- 30986
- General function:
- Involved in lipopolysaccharide biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- wzzE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG00
- Molecular weight:
- 39489
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity L-arabinose membrane transport system. Binds with high affinity to arabinose, but can also bind D-galactose (approximately 2-fold reduction) and D- fucose (approximately 40-fold reduction)
- Gene Name:
- araF
- Uniprot ID:
- P02924
- Molecular weight:
- 35541
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ThiBPQ involved in thiamine import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- thiQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P31548
- Molecular weight:
- 24999
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on paired donors, with incorporation or reduction of molecular oxygen
- Specific function:
- Part of the rut operon, which is required for the utilization of pyrimidines as sole nitrogen source
- Gene Name:
- rutA
- Uniprot ID:
- P75898
- Molecular weight:
- 42219
Reactions
| Uracil + FMNH(2) + O(2) = (Z)-3-ureidoacrylate peracid + FMN + H(2)O. |
| Thymine + FMNH(2) + O(2) = (Z)-2-methylureidoacrylate peracid + FMN + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- IGPS catalyzes the conversion of PRFAR and glutamine to IGP, AICAR and glutamate. The hisF subunit catalyzes the cyclization activity that produces IGP and AICAR from PRFAR using the ammonia provided by the hisH subunit
- Gene Name:
- hisF
- Uniprot ID:
- P60664
- Molecular weight:
- 28454
Reactions
| 5-[(5-phospho-1-deoxyribulos-1-ylamino)methylideneamino]-1-(5-phosphoribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide + L-glutamine = imidazole-glycerol phosphate + 5-aminoimidazol-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide + L-glutamate + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in transport
- Specific function:
- Required for the export of heme to the periplasm for the biogenesis of c-type cytochromes (Potential)
- Gene Name:
- ccmD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABM5
- Molecular weight:
- 7745
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the radical-mediated cleavage of tyrosine to dehydroglycine and p-cresol
- Gene Name:
- thiH
- Uniprot ID:
- P30140
- Molecular weight:
- 43320
Reactions
| L-tyrosine + S-adenosyl-L-methionine + reduced acceptor = 2-iminoacetate + 4-methylphenol + 5'-deoxyadenosine + L-methionine + acceptor + 2 H(+). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, in phosphorus-containing anhydrides
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the hydrolysis of GDP-mannose. Can also use other substrates, catalyzing the hydrolysis of the pyrophosphate bond, releasing a nucleoside monophosphate and a phosphorylated moiety, depending on the substrate
- Gene Name:
- nudK
- Uniprot ID:
- P37128
- Molecular weight:
- 21749
Reactions
| GDP-mannose + H(2)O = GMP + mannose-1-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NADP-dependent oxidation of L-allo- threonine to L-2-amino-3-keto-butyrate, which is spontaneously decarboxylated into aminoacetone. Also acts on L-serine, D-serine, D-threonine, D-3-hydroxyisobutyrate, L-3-hydroxyisobutyrate, D- glycerate and L-glycerate
- Gene Name:
- ydfG
- Uniprot ID:
- P39831
- Molecular weight:
- 27249
Reactions
| 3-hydroxypropanoate + NADP(+) = 3-oxopropanoate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- artP
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAF6
- Molecular weight:
- 27022
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Member of a multicomponent binding-protein-dependent transport system (the proU transporter) which serves as the glycine betaine/L-proline transporter
- Gene Name:
- proX
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFM2
- Molecular weight:
- 36022
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for glutamate and aspartate. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- gltL
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAG3
- Molecular weight:
- 26661
- General function:
- Involved in lipopolysaccharide binding
- Specific function:
- Required for the translocation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from the inner membrane to the outer membrane. May act as a chaperone that facilitates LPS transfer across the aquaeous environment of the periplasm. Interacts specifically with the lipid A domain of LPS
- Gene Name:
- lptA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ADV1
- Molecular weight:
- 20127
- General function:
- Involved in lipopolysaccharide biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- rfaZ
- Uniprot ID:
- P27241
- Molecular weight:
- 32920
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity D-ribose membrane transport system and also serves as the primary chemoreceptor for chemotaxis
- Gene Name:
- rbsB
- Uniprot ID:
- P02925
- Molecular weight:
- 30950
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Component of the leucine-specific transport system
- Gene Name:
- livG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9S7
- Molecular weight:
- 28427
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Participates in the periplasmic electron-transferring activity of hydrogenase 2 during its catalytic turnover
- Gene Name:
- hybA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAJ8
- Molecular weight:
- 36003
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- yeiT
- Uniprot ID:
- P76440
- Molecular weight:
- 44329
Reactions
| 5,6-dihydrouracil + NAD(+) = uracil + NADH. |
| 5,6-dihydrothymine + NAD(+) = thymine + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on NADH or NADPH
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- hyfE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEW1
- Molecular weight:
- 23361
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the esterification, concomitant with transport, of exogenous fatty acids into metabolically active CoA thioesters for subsequent degradation or incorporation into phospholipids. It has a low activity on medium or long chain fatty acids and is maximally active on C6 and C8 substrates
- Gene Name:
- fadK
- Uniprot ID:
- P38135
- Molecular weight:
- 60773
Reactions
| ATP + a short-chain carboxylic acid + CoA = AMP + diphosphate + an acyl-CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in structural molecule activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- sufA
- Uniprot ID:
- P77667
- Molecular weight:
- 13300
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of a multicomponent oxygenase involved in phenylacetyl-CoA hydroxylation
- Gene Name:
- paaA
- Uniprot ID:
- P76077
- Molecular weight:
- 35499
Reactions
| Phenylacetyl-CoA + NADPH + O(2) = 2-(1,2-epoxy-1,2-dihydrophenyl)acetyl-CoA + NADP(+) + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the high-affinity histidine permease, a binding-protein-dependent transport system. The other components are proteins hisQ, hisM, and hisP
- Gene Name:
- hisJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEU0
- Molecular weight:
- 28483
- General function:
- Involved in acyl-CoA hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Can hydrolyze a broad range of acyl-CoA thioesters. Its physiological function is not known
- Gene Name:
- tesB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGG2
- Molecular weight:
- 31966
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Putative L-galactonate oxidoreductase that is required for growth on L-galactonate as the sole carbon source
- Gene Name:
- yjjN
- Uniprot ID:
- P39400
- Molecular weight:
- 36448
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- Cytochrome oxidase subunit
- Gene Name:
- appB
- Uniprot ID:
- P26458
- Molecular weight:
- 42423
- General function:
- Energy production and conversion
- Specific function:
- A possible function for this protein is to guide the assembly of the membrane sector of the ATPase enzyme complex
- Gene Name:
- atpI
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABC0
- Molecular weight:
- 13632
- General function:
- Involved in arsenite transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in arsenical resistance. Thought to form the channel of an arsenite pump
- Gene Name:
- arsB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AB93
- Molecular weight:
- 45497
- General function:
- Inorganic ion transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- The phage shock protein (psp) operon (pspABCDE) may play a significant role in the competition for survival under nutrient- or energy-limited conditions. PspE catalyzes the sulfur-transfer reaction from thiosulfate to cyanide, to form sulfite and thiocyanate. Also able to use dithiol (dithiothreitol) as an alternate sulfur acceptor. Also possesses a very low mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase activity
- Gene Name:
- pspE
- Uniprot ID:
- P23857
- Molecular weight:
- 11475
Reactions
| Thiosulfate + cyanide = sulfite + thiocyanate. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, acting on carbon-nitrogen (but not peptide) bonds, in linear amides
- Specific function:
- Makes part of the rut operon, which is required for the utilization of pyrimidines as sole nitrogen source
- Gene Name:
- rutB
- Uniprot ID:
- P75897
- Molecular weight:
- 25209
Reactions
| (Z)-3-ureidoacrylate peracid + H(2)O = (Z)-3-peroxyaminoacrylate + NH(3). |
| (Z)-3-ureidoacrylate + H(2)O = (Z)-3-aminoacrylate + CO(2) + NH(3). |
| (Z)-2-methyl-ureidoacrylate peracid + H(2)O = (Z)-2-methyl-peroxyaminoacrylate + CO(2) + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Reduces trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) into trimethylamine; an anaerobic reaction coupled to energy-yielding reactions
- Gene Name:
- torA
- Uniprot ID:
- P33225
- Molecular weight:
- 94455
Reactions
| Trimethylamine + 2 (ferricytochrome c)-subunit + H(2)O = trimethylamine N-oxide + 2 (ferrocytochrome c)-subunit + 2 H(+). |
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid transport
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of the leucine, isoleucine, valine, (threonine) transport system, which is one of the two periplasmic binding protein-dependent transport systems of the high-affinity transport of the branched-chain amino acids
- Gene Name:
- livJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AD96
- Molecular weight:
- 39076
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity zinc uptake transport system
- Gene Name:
- znuB
- Uniprot ID:
- P39832
- Molecular weight:
- 27728
- General function:
- Involved in protein-heme linkage
- Specific function:
- Heme chaperone required for the biogenesis of c-type cytochromes. Transiently binds heme delivered by CcmC and transfers the heme to apo-cytochromes in a process facilitated by CcmF and CcmH
- Gene Name:
- ccmE
- Uniprot ID:
- P69490
- Molecular weight:
- 17698
- General function:
- Involved in nucleoside-triphosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- yjjX
- Uniprot ID:
- P39411
- Molecular weight:
- 18213
Reactions
| A nucleoside triphosphate + H(2)O = a nucleoside diphosphate + monophosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex NikABCDE involved in nickel import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- nikD
- Uniprot ID:
- P33593
- Molecular weight:
- 26820
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Ni(2+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + Ni(2+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Oxygenase that introduces the hydroxyl group at carbon four of 2-octaprenyl-6-methoxyphenol resulting in the formation of 2-octaprenyl-6-methoxy-1,4-benzoquinone
- Gene Name:
- ubiH
- Uniprot ID:
- P25534
- Molecular weight:
- 42288
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups
- Specific function:
- Required, probably indirectly, for the hydroxylation of 2-octaprenylphenol to 2-octaprenyl-6-hydroxy-phenol, the fourth step in ubiquinone biosynthesis. Specific for aerobically grown log-phase cells
- Gene Name:
- ubiB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6A0
- Molecular weight:
- 63202
- General function:
- Inorganic ion transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Probably involved in the transfer of electrons from the quinone pool to the type-c cytochromes
- Gene Name:
- nrfD
- Uniprot ID:
- P32709
- Molecular weight:
- 35042
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Component of the leucine-specific transport system
- Gene Name:
- livF
- Uniprot ID:
- P22731
- Molecular weight:
- 26310
- General function:
- Involved in metal ion binding
- Specific function:
- Probable b-type cytochrome
- Gene Name:
- hybB
- Uniprot ID:
- P37180
- Molecular weight:
- 43602
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ddpABCDF, which is probably involved in D,D-dipeptide transport. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- ddpF
- Uniprot ID:
- P77622
- Molecular weight:
- 34621
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- The disulfide bond functions as an electron carrier in the glutathione-dependent synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides by the enzyme ribonucleotide reductase. In addition, it is also involved in reducing some disulfides in a coupled system with glutathione reductase
- Gene Name:
- grxC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AC62
- Molecular weight:
- 9137
- General function:
- Energy production and conversion
- Specific function:
- Cytochrome oxidase subunit
- Gene Name:
- appC
- Uniprot ID:
- P26459
- Molecular weight:
- 57919
- General function:
- Involved in Mo-molybdopterin cofactor biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the adenylation by ATP of the carboxyl group of the C-terminal glycine of sulfur carrier protein moaD
- Gene Name:
- moeB
- Uniprot ID:
- P12282
- Molecular weight:
- 26719
Reactions
| ATP + [molybdopterin-synthase sulfur-carrier protein]-Gly-Gly = diphosphate + [molybdopterin-synthase sulfur-carrier protein]-Gly-Gly-AMP. |
- General function:
- Involved in prosthetic group biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Transfers 2-(5''-triphosphoribosyl)-3'- dephosphocoenzyme-A on a serine residue to the apo-acyl carrier protein (gamma chain) of the citrate lyase to yield holo-acyl carrier protein
- Gene Name:
- citX
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6G5
- Molecular weight:
- 20270
Reactions
| 2'-(5-triphosphoribosyl)-3'-dephospho-CoA + citrate lyase apo-[acyl-carrier-protein] = citrate lyase holo-[acyl-carrier-protein] + diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Binds citrate-dependent Fe(3+); part of the binding- protein-dependent transport system for uptake of citrate-dependent Fe(3+)
- Gene Name:
- fecB
- Uniprot ID:
- P15028
- Molecular weight:
- 33146
- General function:
- Involved in protein binding
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- rfaS
- Uniprot ID:
- P27126
- Molecular weight:
- 36730
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the anaerobic respiratory chain of trimethylamine-N-oxide reductase torA. Acts by transferring electrons from the membranous menaquinones to torA. This transfer probably involves an electron transfer pathway from menaquinones to the N-terminal domain of torC, then from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, and finally to torA. TorC apocytochrome negatively autoregulates the torCAD operon probably by inhibiting the torS kinase activity
- Gene Name:
- torC
- Uniprot ID:
- P33226
- Molecular weight:
- 43606
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Dipeptide-binding protein of a transport system that can be subject to osmotic shock. DppA is also required for peptide chemotaxis
- Gene Name:
- dppA
- Uniprot ID:
- P23847
- Molecular weight:
- 60293
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- This protein is involved in the active transport of galactose and glucose. It plays a role in the chemotaxis towards the two sugars by interacting with the trg chemoreceptor
- Gene Name:
- mglB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEE5
- Molecular weight:
- 35712
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex NikABCDE involved in nickel import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- nikE
- Uniprot ID:
- P33594
- Molecular weight:
- 29721
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Ni(2+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + Ni(2+)(In). |
- General function:
- Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones
- Specific function:
- Probable chaperone. Has ATPase activity. Not stimulated by dnaJ
- Gene Name:
- hscC
- Uniprot ID:
- P77319
- Molecular weight:
- 61986
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Probably involved in the transfer of electrons from the quinone pool to the type-c cytochromes
- Gene Name:
- nrfC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAK7
- Molecular weight:
- 24567
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- kdpF
- Uniprot ID:
- P36937
- Molecular weight:
- 3072
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- sn-glycerol-3-phosphate and glycerophosphoryl diester- binding protein interacts with the binding protein-dependent transport system ugpACE
- Gene Name:
- ugpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG80
- Molecular weight:
- 48448
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- hyfC
- Uniprot ID:
- P77858
- Molecular weight:
- 34359
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex TauABC involved in taurine import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- tauB
- Uniprot ID:
- Q47538
- Molecular weight:
- 28297
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + taurine(Out) = ADP + phosphate + taurine(In). |
- General function:
- Inorganic ion transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of a D-methionine permease, a binding protein-dependent, ATP-driven transport system
- Gene Name:
- metQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P28635
- Molecular weight:
- 29432
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ModABC involved in molybdenum import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- modC
- Uniprot ID:
- P09833
- Molecular weight:
- 39102
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + molybdate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + molybdate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the formation of 2-(5''-triphosphoribosyl)-3'- dephosphocoenzyme-A, the precursor of the prosthetic group of the holo-acyl carrier protein (gamma chain) of citrate lyase, from ATP and dephospho-CoA
- Gene Name:
- citG
- Uniprot ID:
- P77231
- Molecular weight:
- 31644
Reactions
| ATP + 3-dephospho-CoA = 2'-(5-triphosphoribosyl)-3'-dephospho-CoA + adenine. |
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules
- Gene Name:
- osmF
- Uniprot ID:
- P33362
- Molecular weight:
- 32609
- General function:
- Involved in thiamine biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the synthesis of the hydroxymethylpyrimidine phosphate (HMP-P) moiety of thiamine from aminoimidazole ribotide (AIR) in a radical S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM)-dependent reaction
- Gene Name:
- thiC
- Uniprot ID:
- P30136
- Molecular weight:
- 70850
Reactions
| 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole + S-adenosyl-L-methionine = 4-amino-2-methyl-5-phosphomethylpyrimidine + 5'-deoxyadenosine + L-methionine + formate + CO. |
- General function:
- Involved in argininosuccinate synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the ATP-dependent conversion of 7-carboxy-7- deazaguanine (CDG) to 7-cyano-7-deazaguanine (preQ(0))
- Gene Name:
- queC
- Uniprot ID:
- P77756
- Molecular weight:
- 25514
Reactions
| 7-carboxy-7-carbaguanine + NH(3) + ATP = 7-cyano-7-carbaguanine + ADP + phosphate + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for oligopeptides. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- oppD
- Uniprot ID:
- P76027
- Molecular weight:
- 37188
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- yeiU
- Uniprot ID:
- P76445
- Molecular weight:
- 26759
- General function:
- Involved in metal ion binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity zinc uptake transport system
- Gene Name:
- znuA
- Uniprot ID:
- P39172
- Molecular weight:
- 33777
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- hyfI
- Uniprot ID:
- P77668
- Molecular weight:
- 28101
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- May be part of a multicomponent oxygenase involved in phenylacetyl-CoA hydroxylation
- Gene Name:
- paaD
- Uniprot ID:
- P76080
- Molecular weight:
- 18324
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- Cytochrome d terminal oxidase complex is the component of the aerobic respiratory chain of E.coli that predominates when cells are grown at low aeration
- Gene Name:
- cydB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABK2
- Molecular weight:
- 42453
Reactions
| Ubiquinol-8 + O(2) = Ubiquinone-8 + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in methyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Methyltransferase required for the conversion of dimethylmenaquinone (DMKH2) to menaquinone (MKH2) and the conversion of 2-polyprenyl-6-methoxy-1,4-benzoquinol (DDMQH2) to 2-polyprenyl-3-methyl-6-methoxy-1,4-benzoquinol (DMQH2)
- Gene Name:
- ubiE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A887
- Molecular weight:
- 28073
Reactions
| A demethylmenaquinone + S-adenosyl-L-methionine = a menaquinol + S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine. |
| S-adenosyl-L-methionine + 2-methoxy-6-all-trans-polyprenyl-1,4-benzoquinol = S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + 6-methoxy-3-methyl-2-all-trans-polyprenyl-1,4-benzoquinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in heme binding
- Specific function:
- Plays a role in nitrite reduction
- Gene Name:
- nrfB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABL1
- Molecular weight:
- 20714
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring hexosyl groups
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the synthesis of Und-PP-GlcNAc-ManNAcA (Lipid II), the second lipid-linked intermediate involved in ECA synthesis
- Gene Name:
- wecG
- Uniprot ID:
- P27836
- Molecular weight:
- 27928
Reactions
| UDP-ManNAcA + Und-PP-GlcNAc = UDP + Und-PP-GlcNAc-ManNAcA. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, quinone or similar compound as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Aldose sugar dehydrogenase with broad substrate specificity. The physiological substrate is unknown. Can oxidize glucose to gluconolactone. Can also utilize D-arabinose, L- arabinose and 2-deoxy-glucose. Has higher activity towards oligomeric sugars, such as maltose, maltotriose or cellobiose. It may function to input sugar-derived electrons into the respiratory network
- Gene Name:
- yliI
- Uniprot ID:
- P75804
- Molecular weight:
- 41054
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- hyfB
- Uniprot ID:
- P23482
- Molecular weight:
- 72582
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- One of at least two accessory proteins for anaerobic nitric oxide (NO) reductase. Reduces the rubredoxin moiety of NO reductase
- Gene Name:
- norW
- Uniprot ID:
- P37596
- Molecular weight:
- 41403
Reactions
| Reduced NO reductase rubredoxin + NAD(+) = oxidized NO reductase rubredoxin + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in iron-sulfur cluster assembly
- Specific function:
- The sufBCD complex acts synergistically with sufE to stimulate the cysteine desulfurase activity of sufS. The sufBCD complex contributes to the assembly or repair of oxygen-labile iron-sulfur clusters under oxidative stress. May facilitate iron uptake from extracellular iron chelators under iron limitation. Required for the stability of the fhuF protein
- Gene Name:
- sufD
- Uniprot ID:
- P77689
- Molecular weight:
- 46822
- General function:
- Energy production and conversion
- Specific function:
- Small subunit of the periplasmic nitrate reductase (NAP). Only expressed at high levels during aerobic growth. NapAB complex receives electrons from the membrane-anchored tetraheme napC protein, thus allowing electron flow between membrane and periplasm. Essential function for nitrate assimilation and may have a role in anaerobic metabolism
- Gene Name:
- napB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABL3
- Molecular weight:
- 16297
- General function:
- Involved in lipopolysaccharide-1,6-galactosyltransferas
- Specific function:
- May be a glycosyltransferase involved in the transfer of UDP-GalF to the lipopolysaccharide
- Gene Name:
- yefG
- Uniprot ID:
- P37749
- Molecular weight:
- 37757
- General function:
- Involved in cytochrome-c oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Cytochrome o terminal oxidase complex is the component of the aerobic respiratory chain of E.coli that predominates when cells are grown at high aeration. This ubiquinol oxidase shows proton pump activity across the membrane in addition to the electron transfer
- Gene Name:
- cyoB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABI8
- Molecular weight:
- 74367
Reactions
| Ubiquinol-8 + O(2) = Ubiquinone-8 + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Amino acid transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for putrescine. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- potG
- Uniprot ID:
- P31134
- Molecular weight:
- 41930
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, for other substituted phosphate groups
- Specific function:
- CDP-diacylglycerol + L-serine = CMP + (3-sn- phosphatidyl)-L-serine
- Gene Name:
- pssA
- Uniprot ID:
- P23830
- Molecular weight:
- 52801
Reactions
| CDP-diacylglycerol + L-serine = CMP + (3-sn-phosphatidyl)-L-serine. |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)propionate hydroxylase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the insertion of one atom of molecular oxygen into position 2 of the phenyl ring of 3-(3- hydroxyphenyl)propionate (3-HPP) and hydroxycinnamic acid (3HCI)
- Gene Name:
- mhpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P77397
- Molecular weight:
- 62185
Reactions
| 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate + NADH + O(2) = 3-(2,3-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoate + H(2)O + NAD(+). |
| (2E)-3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate + NADH + O(2) = (2E)-3-(2,3-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate + H(2)O + NAD(+). |
- General function:
- Involved in protein binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in reducing some disulfides in a coupled system with glutathione reductase. Does not act as hydrogen donor for ribonucleotide reductase
- Gene Name:
- grxB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AC59
- Molecular weight:
- 24350
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex gsiABCD involved in glutathione import
- Gene Name:
- gsiB
- Uniprot ID:
- P75797
- Molecular weight:
- 56470
- General function:
- Involved in anaerobic electron transport chain
- Specific function:
- Terminal reductase during anaerobic growth on various sulfoxide and N-oxide compounds. The C subunit anchors the other two subunits to the membrane and stabilize the catalytic subunits
- Gene Name:
- ynfH
- Uniprot ID:
- P76173
- Molecular weight:
- 30523
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system for taurine
- Gene Name:
- tauA
- Uniprot ID:
- Q47537
- Molecular weight:
- 34266
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex SsuABC involved in aliphatic sulfonates import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- ssuB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAI1
- Molecular weight:
- 27738
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- The disulfide bond functions as an electron carrier in the glutathione-dependent synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides by the enzyme ribonucleotide reductase. In addition, it is also involved in reducing some disulfides in a coupled system with glutathione reductase
- Gene Name:
- grxA
- Uniprot ID:
- P68688
- Molecular weight:
- 9685
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- hycC
- Uniprot ID:
- P16429
- Molecular weight:
- 64076
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Participates in various redox reactions through the reversible oxidation of its active center dithiol to a disulfide and catalyzes dithiol-disulfide exchange reactions
- Gene Name:
- trxA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AA25
- Molecular weight:
- 11807
- General function:
- Involved in glycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase acti
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the transfer of an acyl group from acyl-ACP to glycerol-3-phosphate (G3P) to form lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). This enzyme can also utilize acyl-CoA as fatty acyl donor, but not acyl-PO(4) (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- plsY
- Uniprot ID:
- P60782
- Molecular weight:
- 22193
Reactions
| Acyl-CoA + sn-glycerol 3-phosphate = CoA + 1-acyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate. |
| Acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + sn-glycerol 3-phosphate = [acyl-carrier-protein] + 1-acyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for glutamate and aspartate. Binds to both aspartate and glutamate
- Gene Name:
- gltI
- Uniprot ID:
- P37902
- Molecular weight:
- 33420
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring glycosyl groups
- Specific function:
- UDP-galactose + lipopolysaccharide = UDP + 3- alpha-D-galactosyl-[lipopolysaccharide glucose]
- Gene Name:
- rfaI
- Uniprot ID:
- P27128
- Molecular weight:
- 39423
Reactions
| UDP-galactose + lipopolysaccharide = UDP + 3-alpha-D-galactosyl-[lipopolysaccharide glucose]. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, acting on carbon-nitrogen (but not peptide) bonds, in linear amides
- Specific function:
- Makes part of the rut operon, which is required for the utilization of pyrimidines as sole nitrogen source
- Gene Name:
- rutD
- Uniprot ID:
- P75895
- Molecular weight:
- 28898
Reactions
| (Z)-3-aminoacrylate + H(2)O = malonate semialdehyde + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the transfer of endogenously produced octanoic acid from octanoyl-acyl-carrier-protein onto the lipoyl domains of lipoate-dependent enzymes. Lipoyl-ACP can also act as a substrate although octanoyl-ACP is likely to be the physiological substrate
- Gene Name:
- lipB
- Uniprot ID:
- P60720
- Molecular weight:
- 23882
Reactions
| Octanoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + protein = protein N(6)-(octanoyl)lysine + [acyl-carrier-protein]. |
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid transport
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of the leucine-specific transport system, which is one of the two periplasmic binding protein-dependent transport systems of the high-affinity transport of the branched-chain amino acids in E.coli
- Gene Name:
- livK
- Uniprot ID:
- P04816
- Molecular weight:
- 39378
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Probable electron transfer protein for hydrogenase 4
- Gene Name:
- hyfH
- Uniprot ID:
- P77423
- Molecular weight:
- 20159
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of a multicomponent oxygenase involved in phenylacetyl-CoA hydroxylation
- Gene Name:
- paaC
- Uniprot ID:
- P76079
- Molecular weight:
- 27877
- General function:
- Involved in fatty acid biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Carrier of the growing fatty acid chain in fatty acid biosynthesis
- Gene Name:
- acpP
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6A8
- Molecular weight:
- 8640
- General function:
- Energy production and conversion
- Specific function:
- Cytochrome d terminal oxidase complex is the component of the aerobic respiratory chain of E.coli that predominates when cells are grown at low aeration
- Gene Name:
- cydA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABJ9
- Molecular weight:
- 58205
Reactions
| Ubiquinol-8 + O(2) = Ubiquinone-8 + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Amino acid transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- The glycine cleavage system catalyzes the degradation of glycine. The H protein shuttles the methylamine group of glycine from the P protein to the T protein
- Gene Name:
- gcvH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6T9
- Molecular weight:
- 13811
- General function:
- Coenzyme transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- ubiX
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG03
- Molecular weight:
- 20695
- General function:
- Replication, recombination and repair
- Specific function:
- Involved in the GO system responsible for removing an oxidatively damaged form of guanine (7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine) from DNA and the nucleotide pool. 8-oxo-dGTP is inserted opposite dA and dC residues of template DNA with almost equal efficiency thus leading to A.T to G.C transversions. MutT specifically degrades 8-oxo-dGTP to the monophosphate
- Gene Name:
- mutT
- Uniprot ID:
- P08337
- Molecular weight:
- 14927
Reactions
| 8-oxo-dGTP + H(2)O = 8-oxo-dGMP + diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Could be involved in ECA polysaccharide chain elongation
- Gene Name:
- wzyE
- Uniprot ID:
- P27835
- Molecular weight:
- 51517
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Probable electron transfer protein for hydrogenase 4
- Gene Name:
- hyfA
- Uniprot ID:
- P23481
- Molecular weight:
- 22154
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Anaerobic nitric oxide reductase; uses NADH to detoxify nitric oxide (NO), protecting several 4Fe-4S NO-sensitive enzymes. Has at least 2 reductase partners, only one of which (NorW, flavorubredoxin reductase) has been identified. NO probably binds to the di-iron center; electrons enter from the reductase at rubredoxin and are transferred sequentially to the FMN center and the di-iron center. Also able to function as an aerobic oxygen reductase
- Gene Name:
- norV
- Uniprot ID:
- Q46877
- Molecular weight:
- 54234
- General function:
- Involved in heme binding
- Specific function:
- Mediates electron flow from quinones to the napAB complex
- Gene Name:
- napC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABL5
- Molecular weight:
- 23100
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a glutamine-transport system glnHPQ
- Gene Name:
- glnH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEQ3
- Molecular weight:
- 27190
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Reutilizes the intact tripeptide L-alanyl-gamma-D- glutamyl-meso-diaminopimelate by linking it to UDP-N-acetylmuramic acid
- Gene Name:
- mpl
- Uniprot ID:
- P37773
- Molecular weight:
- 49874
- General function:
- Involved in heme-copper terminal oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Cytochrome o terminal oxidase complex is the component of the aerobic respiratory chain of E.coli that predominates when cells are grown at high aeration
- Gene Name:
- cyoC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABJ3
- Molecular weight:
- 22623
Reactions
| Ubiquinol-8 + O(2) = Ubiquinone-8 + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine. Polyamine binding protein
- Gene Name:
- potF
- Uniprot ID:
- P31133
- Molecular weight:
- 40839
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ddpABCDF, which is probably involved in D,D-dipeptide transport
- Gene Name:
- ddpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P76128
- Molecular weight:
- 57641
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine and spermidine. Polyamine binding protein
- Gene Name:
- potD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFK9
- Molecular weight:
- 38867
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex fhuCDB involved in iron(3+)-hydroxamate import. Binds the iron(3+)-hydroxamate complex and transfers it to the membrane-bound permease. Required for the transport of all iron(3+)-hydroxamate siderophores such as ferrichrome, gallichrome, desferrioxamine, coprogen, aerobactin, shizokinen, rhodotorulic acid and the antibiotic albomycin
- Gene Name:
- fhuD
- Uniprot ID:
- P07822
- Molecular weight:
- 32998
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex thiBPQ involved in thiamine import
- Gene Name:
- thiB
- Uniprot ID:
- P31550
- Molecular weight:
- 36163
- General function:
- Involved in unfolded protein binding
- Specific function:
- Chaperone required for proper molybdenum cofactor insertion and final assembly of the membrane-bound respiratory nitrate reductase 1. Required for the insertion of the molybdenum into the apo-NarG subunit, maybe by keeping NarG in an appropriate competent-open conformation for the molybdenum cofactor insertion to occur. NarJ maintains the apoNarGH complex in a soluble state. Upon insertion of the molybdenum cofactor, NarJ seems to dissociate from the activated soluble NarGH complex, before its association with the NarI subunit on the membrane
- Gene Name:
- narJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AF26
- Molecular weight:
- 26449
- General function:
- Involved in molybdate transmembrane-transporting ATPase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the transport of molybdenum into the cell. Binds molybdate with high specificity and affinity
- Gene Name:
- modA
- Uniprot ID:
- P37329
- Molecular weight:
- 27364
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- hycD
- Uniprot ID:
- P16430
- Molecular weight:
- 33029
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- ftnA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A998
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- eutE
- Uniprot ID:
- P77445
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- yiaY
- Uniprot ID:
- P37686
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- eutG
- Uniprot ID:
- P76553
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- paoA
- Uniprot ID:
- P77165
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- yfcG
- Uniprot ID:
- P77526
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- yeaW
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABR7
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- aes
- Uniprot ID:
- P23872
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- nrfE
- Uniprot ID:
- P32710
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- nfsA
- Uniprot ID:
- P17117
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- nemA
- Uniprot ID:
- P77258
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Functions as a holding molecular chaperone (holdase) which stabilizes unfolding intermediates and rapidly releases them in an active form once stress has abated. Plays an important role in protecting cells from severe heat shock and starvation, as well as in acid resistance of stationary-phase cells. It uses temperature-induced exposure of structured hydrophobic domains to capture and stabilizes early unfolding and denatured protein intermediates under severe thermal stress. Catalyzes the conversion of methylglyoxal (MG) to D-lactate in a single glutathione (GSH)-independent step. It can also use phenylglyoxal as substrate. Glyoxalase activity protects cells against dicarbonyl stress. Displays an aminopeptidase activity that is specific against peptide substrates with alanine or basic amino acids (lysine, arginine) at N-terminus. Functions as a holding molecular chaperone (holdase) which stabilizes unfolding intermediates and rapidly releases them in an active form once stress has abated. Plays an important role in protecting cells from severe heat shock and starvation, as well as in acid resistance of stationary-phase cells. It uses temperature-induced exposure of structured hydrophobic domains to capture and stabilizes early unfolding and denatured protein intermediates under severe thermal stress. Catalyzes the conversion of methylglyoxal (MG) to D-lactate in a single glutathione (GSH)-independent step. It can also use phenylglyoxal as substrate. Glyoxalase activity protects cells against dicarbonyl stress. Displays an aminopeptidase activity that is specific against peptide substrates with alanine or basic amino acids (lysine, arginine) at N-terminus.
- Gene Name:
- hchA
- Uniprot ID:
- P31658
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
Reactions
| (R)-lactate = methylglyoxal + H(2)O. |
| (R)-lactate = methylglyoxal + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Inorganic ion transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- May perform analogous functions in iron detoxification and storage to that of animal ferritins
- Gene Name:
- bfr
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABD3
- Molecular weight:
- 18495
Reactions
| 4 Fe(2+) + 4 H(+) + O(2) = 4 Fe(3+) + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Inorganic ion transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex PhnCDE involved in phosphonates, phosphate esters, phosphite and phosphate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- phnC
- Uniprot ID:
- P16677
- Molecular weight:
- 29430
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + phosphonate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + phosphonate(In). |
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of pseudouridine to pseudouridine 5'-phosphate (PsiMP)
- Gene Name:
- psuK
- Uniprot ID:
- P30235
- Molecular weight:
- 33573
Reactions
| ATP + pseudouridine = ADP + pseudouridine 5'-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis
- Specific function:
- Transfers and isomerizes the ribose moiety from AdoMet to the 7-aminomethyl group of 7-deazaguanine (preQ1-tRNA) to give epoxyqueuosine (oQ-tRNA)
- Gene Name:
- queA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A7F9
- Molecular weight:
- 39430
Reactions
| S-adenosylmethionine + 7-aminomethyl-7-deazaguanosine = methionine + adenine + epoxyqueuosine. |
- General function:
- Inorganic ion transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- yqjH
- Uniprot ID:
- Q46871
- Molecular weight:
- 28871
Reactions
| 2 Fe(II) + 2 an apo-siderophore + NADP(+) + H(+) = 2 an Fe(III)-siderophore + NADPH. |
- General function:
- oxidative phosphorylation
- Specific function:
- Required for correct functioning of cytochrome bd-I oxidase. This protein and AppX may have some functional overlap.
- Gene Name:
- cydX
- Uniprot ID:
- P56100
- Molecular weight:
- 4041
- General function:
- cardiolipin biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the synthesis of cardiolipin (CL) (diphosphatidylglycerol) from phosphatidylglycerol (PG) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE).
- Gene Name:
- clsC
- Uniprot ID:
- P75919
- Molecular weight:
- 53665
Reactions
| Phosphatidylglycerol + phosphatidylethanolamine = diphosphatidylglycerol + ethanolamine |
- General function:
- protein phosphorylation
- Specific function:
- A protein kinase that (auto)phosphorylates on Ser and Thr residues (PubMed:17302814). Probably acts to suppress the effects of stress linked to accumulation of reactive oxygen species. Protects cells from stress by antagonizing the MazE-MazF TA module, probably indirectly as it has not been seen to phosphorylate MazE, MazF or MazG (PubMed:23416055). Probably involved in the extracytoplasmic stress response (PubMed:9159398).
- Gene Name:
- srkA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0C0K3
- Molecular weight:
- 38120
Reactions
| ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein |
- General function:
- zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Not known; probable catabolic enzyme.
- Gene Name:
- rspB
- Uniprot ID:
- P38105
- Molecular weight:
- 36563
Reactions
| = |
- General function:
- threonylcarbamoyladenosine biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Required for the formation of a threonylcarbamoyl group on adenosine at position 37 (t(6)A37) in tRNAs that read codons beginning with adenine. Catalyzes the conversion of L-threonine, bicarbonate/CO(2) and ATP to give threonylcarbamoyl-AMP (TC-AMP) as the acyladenylate intermediate, with the release of pyrophosphate. Is also able to catalyze the reverse reaction in vitro, i.e. the formation of ATP from TC-AMP and PPi. Shows higher affinity for the full-length tRNA(Thr) lacking only the t(6)A37 modification than for its fully modified counterpart. Could also be required for the maturation of 16S rRNA. Binds to double-stranded RNA but does not interact tightly with either of the ribosomal subunits, or the 70S particles.
- Gene Name:
- tsaC
- Uniprot ID:
- P45748
- Molecular weight:
- 20767
Reactions
| L-threonine + ATP + bicarbonate = L-threonylcarbamoyladenylate + diphosphate + H(2)O |
- General function:
- organic phosphonate catabolic process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the hydrolysis of the cyclic ribose-phosphate to form alpha-D-ribose 1,5-bisphosphate.
- Gene Name:
- phnP
- Uniprot ID:
- P16692
- Molecular weight:
- 27847
Reactions
| 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1,2-cyclic phosphate + H(2)O = alpha-D-ribose 1,5-bisphosphate |
- General function:
- organic phosphonate catabolic process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the hydrolysis of alpha-D-ribose 1-methylphosphonate triphosphate (RPnTP) to form alpha-D-ribose 1-methylphosphonate phosphate (PRPn) and diphosphate.
- Gene Name:
- phnM
- Uniprot ID:
- P16689
- Molecular weight:
- 42010
Reactions
| Alpha-D-ribose 1-methylphosphonate 5-triphosphate + H(2)O = alpha-D-ribose 1-methylphosphonate 5-phosphate + diphosphate |
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in potassium-transporting ATPase activity
- Specific function:
- One of the components of the high-affinity ATP-driven potassium transport (or KDP) system, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of hydrogen and potassium ions
- Gene Name:
- kdpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P03959
- Molecular weight:
- 59189
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + K(+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + K(+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- One of the components of the high-affinity ATP-driven potassium transport (or KDP) system, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of hydrogen and potassium ions
- Gene Name:
- kdpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P03960
- Molecular weight:
- 72198
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + K(+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + K(+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in potassium-transporting ATPase activity
- Specific function:
- One of the components of the high-affinity ATP-driven potassium transport (or KDP) system, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of hydrogen and potassium ions. The C subunit may be involved in assembly of the KDP complex
- Gene Name:
- kdpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P03961
- Molecular weight:
- 20267
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + K(+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + K(+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex RbsABCD involved in ribose import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- rbsA
- Uniprot ID:
- P04983
- Molecular weight:
- 55041
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + monosaccharide(Out) = ADP + phosphate + monosaccharide(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex BtuCDF involved in vitamin B12 import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- btuD
- Uniprot ID:
- P06611
- Molecular weight:
- 27081
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + vitamin B12(Out) = ADP + phosphate + vitamin B12(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for histidine. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- hisP
- Uniprot ID:
- P07109
- Molecular weight:
- 28653
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex fhuCDB involved in iron(3+)-hydroxamate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- fhuC
- Uniprot ID:
- P07821
- Molecular weight:
- 28886
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + iron chelate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + iron chelate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism
- Specific function:
- Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- atpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6E6
- Molecular weight:
- 15068
- General function:
- Involved in 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate:hydrogen symporter activity
- Specific function:
- The 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate permease transports the degraded pectin products into the bacterial cell, where they serve as carbon and energy sources. This is a hydrogen coupled transport system
- Gene Name:
- kdgT
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A712
- Molecular weight:
- 33669
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex AraFGH involved in arabinose import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- araG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAF3
- Molecular weight:
- 55018
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + monosaccharide(Out) = ADP + phosphate + monosaccharide(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex MglABC involved in galactose/methyl galactoside import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- mglA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAG8
- Molecular weight:
- 56415
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + monosaccharide(Out) = ADP + phosphate + monosaccharide(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex pstSACB involved in phosphate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- pstB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAH0
- Molecular weight:
- 29027
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + phosphate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + phosphate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Key component of the proton channel; it plays a direct role in the translocation of protons across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- atpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AB98
- Molecular weight:
- 30303
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the F(0) channel, it forms part of the peripheral stalk, linking F(1) to F(0)
- Gene Name:
- atpF
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABA0
- Molecular weight:
- 17264
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism
- Specific function:
- This protein is part of the stalk that links CF(0) to CF(1). It either transmits conformational changes from CF(0) to CF(1) or is implicated in proton conduction
- Gene Name:
- atpH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABA4
- Molecular weight:
- 19332
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism
- Specific function:
- Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane. The gamma chain is believed to be important in regulating ATPase activity and the flow of protons through the CF(0) complex
- Gene Name:
- atpG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABA6
- Molecular weight:
- 31577
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane. The alpha chain is a regulatory subunit
- Gene Name:
- atpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABB0
- Molecular weight:
- 55222
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + H(+)(In) = ADP + phosphate + H(+)(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane. The catalytic sites are hosted primarily by the beta subunits
- Gene Name:
- atpD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABB4
- Molecular weight:
- 50325
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + H(+)(In) = ADP + phosphate + H(+)(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex UgpABCE involved in sn-glycerol-3-phosphate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable). Can also transport glycerophosphoryl diesters
- Gene Name:
- ugpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P10907
- Molecular weight:
- 39524
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + glycerol-3-phosphate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + glycerol-3-phosphate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in carbohydrate transport
- Specific function:
- Mediates the uptake of L-fucose across the boundary membrane with the concomitant transport of protons into the cell (symport system). Can also transport L-galactose and D-arabinose, but at reduced rates compared with L-fucose. Is not able to transport L-rhamnose and L-arabinose
- Gene Name:
- fucP
- Uniprot ID:
- P11551
- Molecular weight:
- 47544
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for citrate-dependent Fe(3+). Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- fecE
- Uniprot ID:
- P15031
- Molecular weight:
- 28191
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- cysA
- Uniprot ID:
- P16676
- Molecular weight:
- 41059
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + sulfate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + sulfate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the formation of an hydroxyacyl-CoA by addition of water on enoyl-CoA. Also exhibits 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA epimerase and 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase activities. Involved in the aerobic and anaerobic degradation of long-chain fatty acids
- Gene Name:
- fadB
- Uniprot ID:
- P21177
- Molecular weight:
- 79593
Reactions
| (S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA + NAD(+) = 3-oxoacyl-CoA + NADH. |
| (3S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA = trans-2(or 3)-enoyl-CoA + H(2)O. |
| (S)-3-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA = (R)-3-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA. |
| (3Z)-dodec-3-enoyl-CoA = (2E)-dodec-2-enoyl-CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ferric enterobactin. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- fepC
- Uniprot ID:
- P23878
- Molecular weight:
- 29784
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for D-methionine and the toxic methionine analog alpha-methyl- methionine. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- metI
- Uniprot ID:
- P31547
- Molecular weight:
- 23256
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex AlsBAC involved in D-allose import. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- alsA
- Uniprot ID:
- P32721
- Molecular weight:
- 56744
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + monosaccharide(Out) = ADP + phosphate + monosaccharide(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex XylFGH involved in xylose import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable). The XylFGH system can also transport ribose in absence of xylose
- Gene Name:
- xylG
- Uniprot ID:
- P37388
- Molecular weight:
- 56470
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + monosaccharide(Out) = ADP + phosphate + monosaccharide(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex MalEFGK involved in maltose/maltodextrin import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- malK
- Uniprot ID:
- P68187
- Molecular weight:
- 40990
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + maltose(Out) = ADP + phosphate + maltose(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Key component of the F(0) channel; it plays a direct role in translocation across the membrane. A homomeric c-ring of 10 subunits forms the central stalk rotor element with the F(1) delta and epsilon subunits
- Gene Name:
- atpE
- Uniprot ID:
- P68699
- Molecular weight:
- 8256
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex PotABCD involved in spermidine/putrescine import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- potA
- Uniprot ID:
- P69874
- Molecular weight:
- 43028
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + polyamine(Out) = ADP + phosphate + polyamine(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- ytfR
- Uniprot ID:
- Q6BEX0
- Molecular weight:
- 55259
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport
- Gene Name:
- artI
- Uniprot ID:
- P30859
- Molecular weight:
- 26929
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport. Binds L-arginine with high affinity
- Gene Name:
- artJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P30860
- Molecular weight:
- 26829
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- artM
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE32
- Molecular weight:
- 24914
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- artQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE34
- Molecular weight:
- 26217
- General function:
- Lipid transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Responsible for the intake of short-chain fatty acids
- Gene Name:
- atoE
- Uniprot ID:
- P76460
- Molecular weight:
- 47527
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Intake of galactonate into the cell
- Gene Name:
- dgoT
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AA76
- Molecular weight:
- 47076
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the bidirectional transport of formate
- Gene Name:
- focB
- Uniprot ID:
- P77733
- Molecular weight:
- 30564
- General function:
- Involved in transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Uptake of galactose across the boundary membrane with the concomitant transport of protons into the cell (symport system)
- Gene Name:
- galP
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEP1
- Molecular weight:
- 50982
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Uptake of D-glucarate
- Gene Name:
- gudP
- Uniprot ID:
- Q46916
- Molecular weight:
- 49142
- General function:
- Involved in transmembrane transport
- Specific function:
- Probable permease involved in the uptake of 3- phenylpropionic acid
- Gene Name:
- hcaT
- Uniprot ID:
- Q47142
- Molecular weight:
- 41592
- General function:
- Involved in gluconate transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Transports L-idonate, D-gluconate and 5-keto-D- gluconate, from the periplasm across the inner membrane
- Gene Name:
- idnT
- Uniprot ID:
- P39344
- Molecular weight:
- 46041
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Responsible for melibiose transport. It is capable of using hydrogen, sodium, and lithium cations as coupling cations for cotransport, depending on the particular sugar transported (symport system)
- Gene Name:
- melB
- Uniprot ID:
- P02921
- Molecular weight:
- 52217
- General function:
- Involved in transmembrane transport
- Specific function:
- Could be a transporter for 3-phenylpropionate (hydrocinnamic acid)
- Gene Name:
- mhpT
- Uniprot ID:
- P77589
- Molecular weight:
- 41550
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- May act as a nitrite transporter
- Gene Name:
- nirC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AC26
- Molecular weight:
- 28562
- General function:
- Involved in inorganic phosphate transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Low-affinity inorganic phosphate transport
- Gene Name:
- pitB
- Uniprot ID:
- P43676
- Molecular weight:
- 53808
- General function:
- Involved in transmembrane transport
- Specific function:
- Involved in the efflux of sugars. The physiological role may be the detoxification of non-metabolizable sugar analogs. Can transport IPTG, lactose and glucose. Has broad substrate specificity, with preferences for glucosides or galactosides with alkyl or aryl substituents
- Gene Name:
- setA
- Uniprot ID:
- P31675
- Molecular weight:
- 42713
- General function:
- Involved in transmembrane transport
- Specific function:
- Involved in the efflux of sugars. The physiological role may be the detoxification of non-metabolizable sugar analogs. Can transport lactose and glucose
- Gene Name:
- setB
- Uniprot ID:
- P33026
- Molecular weight:
- 42746
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- shiA
- Uniprot ID:
- P76350
- Molecular weight:
- 47817
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Has low ATPase activity. The sufBCD complex acts synergistically with sufE to stimulate the cysteine desulfurase activity of sufS. The sufBCD complex contributes to the assembly or repair of oxygen-labile iron-sulfur clusters under oxidative stress. May facilitate iron uptake from extracellular iron chelators under iron limitation
- Gene Name:
- sufC
- Uniprot ID:
- P77499
- Molecular weight:
- 27582
- General function:
- Involved in nucleoside transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Nucleoside transport
- Gene Name:
- xapB
- Uniprot ID:
- P45562
- Molecular weight:
- 46139
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system ydcSTUV
- Gene Name:
- ydcS
- Uniprot ID:
- P76108
- Molecular weight:
- 42295
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Probably part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system ydcSTUV. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- ydcT
- Uniprot ID:
- P77795
- Molecular weight:
- 37040
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system ydcSTUV; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ydcU
- Uniprot ID:
- P77156
- Molecular weight:
- 34360
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system ydcSTUV; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ydcV
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFR9
- Molecular weight:
- 28722
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Probably part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system yecCS for an amino acid. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- yecC
- Uniprot ID:
- P37774
- Molecular weight:
- 27677
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system yecCS for an amino acid; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- yecS
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFT2
- Molecular weight:
- 24801
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Part of the tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic (TRAP) transport system yiaMNO involved in the uptake of 2,3- diketo-L-gulonate
- Gene Name:
- yiaM
- Uniprot ID:
- P37674
- Molecular weight:
- 17516
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Part of the tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic (TRAP) transport system yiaMNO involved in the uptake of 2,3- diketo-L-gulonate
- Gene Name:
- yiaN
- Uniprot ID:
- P37675
- Molecular weight:
- 45368
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- yjfF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37772
- Molecular weight:
- 34977
- General function:
- Involved in transmembrane transport
- Specific function:
- Responsible for the transport of L-galactonate from the periplasm across the inner membrane (Probable). Is essential for growth on L-galactonate as the sole carbon source
- Gene Name:
- yjjL
- Uniprot ID:
- P39398
- Molecular weight:
- 49440
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- ytfQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P39325
- Molecular weight:
- 34344
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ytfT
- Uniprot ID:
- P39328
- Molecular weight:
- 35659
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex lsrABCD involved in autoinducer 2 (AI-2) import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- lsrC
- Uniprot ID:
- B1XEA2
- Molecular weight:
- 36394
- General function:
- Involved in cobalamin transport
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex BtuCDF involved in vitamin B12 import. Involved in the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- btuC
- Uniprot ID:
- B1XG18
- Molecular weight:
- 34949
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the import of threonine and serine into the cell, with the concomitant import of a proton (symport system)
- Gene Name:
- tdcC
- Uniprot ID:
- B1XGT1
- Molecular weight:
- 48878
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for maltose; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- malF
- Uniprot ID:
- P02916
- Molecular weight:
- 57013
- General function:
- Involved in transport
- Specific function:
- Responsible for transport of beta-galactosides into the cell, with the concomitant import of a proton (symport system)
- Gene Name:
- lacY
- Uniprot ID:
- P02920
- Molecular weight:
- 46503
- General function:
- Involved in receptor activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the active translocation of vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) across the outer membrane to the periplasmic space. It derives its energy for transport by interacting with the trans-periplasmic membrane protein tonB. Is also a receptor for bacteriophages BF23 and C1, and for A and E colicins
- Gene Name:
- btuB
- Uniprot ID:
- P06129
- Molecular weight:
- 68407
- General function:
- Involved in cobalamin transport
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex BtuCDF involved in vitamin B12 import. Involved in the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- btuC
- Uniprot ID:
- P06609
- Molecular weight:
- 34949
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex fhuCDB involved in iron(3+)-hydroxamate import. Responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fhuB
- Uniprot ID:
- P06972
- Molecular weight:
- 70422
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for phosphate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- pstA
- Uniprot ID:
- P07654
- Molecular weight:
- 32321
- General function:
- Involved in transport
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- rhtA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AA67
- Molecular weight:
- 31168
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Aldohexuronate transport system
- Gene Name:
- exuT
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AA78
- Molecular weight:
- 51571
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Uptake of D-galactarate
- Gene Name:
- garP
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AA80
- Molecular weight:
- 49009
- General function:
- Involved in nucleobase transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for cytosine transport into the cell
- Gene Name:
- codB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AA82
- Molecular weight:
- 43649
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in transporting tryptophan across the cytoplasmic membrane
- Gene Name:
- mtr
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAD2
- Molecular weight:
- 44332
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in transporting tyrosine across the cytoplasmic membrane
- Gene Name:
- tyrP
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAD4
- Molecular weight:
- 42819
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the import of serine into the cell. May be required for phage C1 adsorption by interacting with drcB. May also be involved in ampicillin sensitivity
- Gene Name:
- sdaC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAD6
- Molecular weight:
- 46906
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the import of threonine and serine into the cell, with the concomitant import of a proton (symport system)
- Gene Name:
- tdcC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAD8
- Molecular weight:
- 48878
- General function:
- Involved in transport
- Specific function:
- Permease that is involved in the transport across the cytoplasmic membrane of D-alanine, D-serine and glycine
- Gene Name:
- cycA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAE0
- Molecular weight:
- 51659
- General function:
- Involved in transport
- Specific function:
- Permease that is involved in the transport across the cytoplasmic membrane of proline
- Gene Name:
- proY
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAE2
- Molecular weight:
- 50215
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probable transporter whose substrate is unknown. Is not involved in aerobic D-malate transport
- Gene Name:
- yeaV
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABD1
- Molecular weight:
- 52881
- General function:
- Involved in C4-dicarboxylate transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Responsible for the transport of C4-dicarboxylates from the periplasm across the inner membrane
- Gene Name:
- dcuA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABN5
- Molecular weight:
- 45750
- General function:
- Involved in C4-dicarboxylate transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Responsible for the transport of C4-dicarboxylates from the periplasm across the inner membrane
- Gene Name:
- dcuB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABN9
- Molecular weight:
- 47935
- General function:
- Involved in C4-dicarboxylate transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Responsible for the transport of C4-dicarboxylates during anaerobic growth
- Gene Name:
- dcuC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABP3
- Molecular weight:
- 48412
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the bidirectional transport of formate
- Gene Name:
- focA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AC23
- Molecular weight:
- 30991
- General function:
- Involved in gluconate transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- High-affinity gluconate transporter with fairly broad specificity, including low affinity for glucuronate, several disaccharides, and some hexoses, but not glucose
- Gene Name:
- gntP
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AC94
- Molecular weight:
- 47137
- General function:
- Involved in gluconate transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the gluconate utilization system Gnt-I; low- affinity intake of gluconate
- Gene Name:
- gntU
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AC96
- Molecular weight:
- 46416
- General function:
- Involved in lipopolysaccharide transport
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex lptBFG involved in the translocation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from the inner membrane to the outer membrane
- Gene Name:
- lptG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ADC6
- Molecular weight:
- 39618
- General function:
- Involved in transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Uptake of arabinose across the boundary membrane with the concomitant transport of protons into the cell (symport system)
- Gene Name:
- araE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE24
- Molecular weight:
- 51684
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for L-arabinose. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- araH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE26
- Molecular weight:
- 34211
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- artM
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE30
- Molecular weight:
- 24914
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP (TC 3.A.1.6.1) involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- cysW
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEB0
- Molecular weight:
- 32537
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- dppB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEF8
- Molecular weight:
- 37497
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- dppC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEG1
- Molecular weight:
- 32308
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for glutamine; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- glnP
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEQ6
- Molecular weight:
- 24364
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for aspartate/glutamate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- gltJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AER3
- Molecular weight:
- 27502
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for aspartate/glutamate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- gltK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AER5
- Molecular weight:
- 24914
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for histidine; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- hisM
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEU3
- Molecular weight:
- 26870
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Uptake of alpha-ketoglutarate across the boundary membrane with the concomitant import of a cation (symport system)
- Gene Name:
- kgtP
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEX3
- Molecular weight:
- 47052
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for branched-chain amino acids. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrates across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- livH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEX7
- Molecular weight:
- 32982
- General function:
- Involved in transmembrane transport
- Specific function:
- Efflux pump driven by the proton motive force. Confers resistance to basic, aromatic and lipophilic drugs as well as neutral, non-aromatic, zwitterionic or non-aromatic hydrophilic antibiotics
- Gene Name:
- cmr
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEY8
- Molecular weight:
- 44320
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for molybdenum; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- modB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AF01
- Molecular weight:
- 24939
- General function:
- Involved in lipopolysaccharide-transporting ATPase acti
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex lptBFG involved in the translocation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from the inner membrane to the outer membrane
- Gene Name:
- lptF
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AF98
- Molecular weight:
- 40357
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a nickel transport system, probably translocates nickel through the bacterial inner membrane
- Gene Name:
- nikC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFA9
- Molecular weight:
- 30362
- General function:
- Involved in nucleoside:sodium symporter activity
- Specific function:
- Transports nucleosides with a high affinity except guanosine and deoxyguanosine. Driven by a proton motive force
- Gene Name:
- nupC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFF2
- Molecular weight:
- 43475
- General function:
- Involved in nucleoside transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Transports nucleosides with a high affinity. Driven by a proton motive force
- Gene Name:
- nupG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFF4
- Molecular weight:
- 46389
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for oligopeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- oppB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFH2
- Molecular weight:
- 33443
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for oligopeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- oppC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFH6
- Molecular weight:
- 33022
- General function:
- Involved in inorganic phosphate transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Low-affinity inorganic phosphate transport. Can also transport arsenate
- Gene Name:
- pitA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFJ7
- Molecular weight:
- 53389
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine and spermidine
- Gene Name:
- potB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFK4
- Molecular weight:
- 31062
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine and spermidine
- Gene Name:
- potC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFK6
- Molecular weight:
- 29111
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine
- Gene Name:
- potI
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFL1
- Molecular weight:
- 30540
- General function:
- Involved in secondary active sulfate transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Possible sulfate transporter
- Gene Name:
- ychM
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFR2
- Molecular weight:
- 59428
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex lsrABCD involved in autoinducer 2 (AI-2) import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- lsrD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFS1
- Molecular weight:
- 34456
- General function:
- Involved in transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Uptake of D-xylose across the boundary membrane with the concomitant transport of protons into the cell (symport system)
- Gene Name:
- xylE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGF4
- Molecular weight:
- 53608
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for phosphate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- pstC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGH8
- Molecular weight:
- 34121
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ribose. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- rbsC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGI1
- Molecular weight:
- 33452
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for D-xylose. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- xylH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGI4
- Molecular weight:
- 41030
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Transport of uracil in the cell
- Gene Name:
- uraA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGM7
- Molecular weight:
- 45060
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Specific, proton motive force-dependent high-affinity transporter for xanthine
- Gene Name:
- xanP
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGM9
- Molecular weight:
- 48868
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Proton symporter that senses osmotic shifts and responds by importing osmolytes such as proline, glycine betaine, stachydrine, pipecolic acid, ectoine and taurine. It is both an osmosensor and an osmoregulator which is available to participate early in the bacterial osmoregulatory response
- Gene Name:
- proP
- Uniprot ID:
- P0C0L7
- Molecular weight:
- 54845
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for sn-glycerol-3-phosphate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ugpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P10905
- Molecular weight:
- 33264
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for sn-glycerol-3-phosphate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ugpE
- Uniprot ID:
- P10906
- Molecular weight:
- 31499
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a multicomponent binding-protein-dependent transport system for glycine betaine/L-proline
- Gene Name:
- proW
- Uniprot ID:
- P14176
- Molecular weight:
- 37619
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for citrate-dependent Fe(3+). Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fecD
- Uniprot ID:
- P15029
- Molecular weight:
- 34131
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for citrate-dependent Fe(3+). Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fecC
- Uniprot ID:
- P15030
- Molecular weight:
- 34892
- General function:
- Involved in transport
- Specific function:
- Permease that is involved in the transport across the cytoplasmic membrane of the aromatic amino acids (phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan)
- Gene Name:
- aroP
- Uniprot ID:
- P15993
- Molecular weight:
- 49690
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for phosphonates; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- phnE
- Uniprot ID:
- P16683
- Molecular weight:
- 28383
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP (TC 3.A.1.6.1) involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- cysU
- Uniprot ID:
- P16701
- Molecular weight:
- 30292
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for branched-chain amino acids. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrates across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- livM
- Uniprot ID:
- P22729
- Molecular weight:
- 46269
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in tryptophan transport across the cytoplasmic membrane. Plays a role in transporting tryptophan which is to be used catabolically
- Gene Name:
- tnaB
- Uniprot ID:
- P23173
- Molecular weight:
- 45210
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for galactoside. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- mglC
- Uniprot ID:
- P23200
- Molecular weight:
- 35550
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ferric enterobactin. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fepD
- Uniprot ID:
- P23876
- Molecular weight:
- 33871
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ferric enterobactin. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fepG
- Uniprot ID:
- P23877
- Molecular weight:
- 34910
- General function:
- Involved in transport
- Specific function:
- Permease that is involved in the transport across the cytoplasmic membrane of phenylalanine
- Gene Name:
- pheP
- Uniprot ID:
- P24207
- Molecular weight:
- 50677
- General function:
- Involved in transport
- Specific function:
- Transporter for GABA
- Gene Name:
- gabP
- Uniprot ID:
- P25527
- Molecular weight:
- 51080
- General function:
- Involved in transport
- Specific function:
- Permease that is involved in the transport across the cytoplasmic membrane of lysine
- Gene Name:
- lysP
- Uniprot ID:
- P25737
- Molecular weight:
- 53575
- General function:
- Involved in transmembrane transport
- Specific function:
- Involved in the efflux of sugars. The physiological role may be the reduction of the intracellular concentration of toxic sugars or sugar metabolites. Transports L-arabinose and to a lesser extent IPTG. Seems to contribute to the control of the arabinose regulon
- Gene Name:
- sotB
- Uniprot ID:
- P31122
- Molecular weight:
- 42538
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine
- Gene Name:
- potH
- Uniprot ID:
- P31135
- Molecular weight:
- 35489
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- High-affinity uptake of adenine
- Gene Name:
- purP
- Uniprot ID:
- P31466
- Molecular weight:
- 46865
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex thiBPQ involved in thiamine import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- thiP
- Uniprot ID:
- P31549
- Molecular weight:
- 59532
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system AlsBAC for D-allose; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- alsC
- Uniprot ID:
- P32720
- Molecular weight:
- 34315
- General function:
- Involved in lactate transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Transports L-lactate across the membrane. Can also transport D-lactate and glycolate. Seems to be driven by a proton motive force
- Gene Name:
- lldP
- Uniprot ID:
- P33231
- Molecular weight:
- 59168
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- yehW
- Uniprot ID:
- P33359
- Molecular weight:
- 25514
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- yehY
- Uniprot ID:
- P33361
- Molecular weight:
- 41138
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a nickel transport system, probably translocates nickel through the bacterial inner membrane
- Gene Name:
- nikB
- Uniprot ID:
- P33591
- Molecular weight:
- 35248
- General function:
- Involved in peptide transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Proton-dependent permease that transports di- and tripeptides. Has a clear preference for dipeptides and tripeptides composed of L-amino acids, and discriminates dipeptides on the basis of the position of charges within the substrate
- Gene Name:
- dtpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P36837
- Molecular weight:
- 53575
- General function:
- Involved in ion channel activity
- Specific function:
- Proton-coupled chloride transporter. Functions as antiport system and exchanges two chloride ions for 1 proton. Probably acts as an electrical shunt for an outwardly-directed proton pump that is linked to amino acid decarboxylation, as part of the extreme acid resistance (XAR) response
- Gene Name:
- clcA
- Uniprot ID:
- P37019
- Molecular weight:
- 50348
- General function:
- Involved in peptide transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probable proton-dependent permease that transports di- and tripeptides. Shows significantly higher specificity towards dipeptides
- Gene Name:
- yjdL
- Uniprot ID:
- P39276
- Molecular weight:
- 53054
- General function:
- Involved in gluconate transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the gluconate utilization system Gnt-I; high- affinity intake of gluconate
- Gene Name:
- gntT
- Uniprot ID:
- P39835
- Molecular weight:
- 45966
- General function:
- Involved in transmembrane transport
- Specific function:
- May be a sugar-cation symporter involved in sialic acid transport as it is required for sialic acid uptake
- Gene Name:
- nanT
- Uniprot ID:
- P41036
- Molecular weight:
- 53551
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- May be involved in fructoselysine transport
- Gene Name:
- frlA
- Uniprot ID:
- P45539
- Molecular weight:
- 47576
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for histidine; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- hisQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P52094
- Molecular weight:
- 24649
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in lipid A export and possibly also in glycerophospholipid export and for biogenesis of the outer membrane. Transmembrane domains (TMD) form a pore in the inner membrane and the ATP-binding domain (NBD) is responsible for energy generation
- Gene Name:
- msbA
- Uniprot ID:
- P60752
- Molecular weight:
- 64460
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Specific, proton motive force-dependent high-affinity transporter for xanthine
- Gene Name:
- xanQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P67444
- Molecular weight:
- 49108
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for maltose; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- malG
- Uniprot ID:
- P68183
- Molecular weight:
- 32225
- General function:
- Involved in nucleobase transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Transport of allantoin
- Gene Name:
- ybbW
- Uniprot ID:
- P75712
- Molecular weight:
- 52456
- General function:
- Involved in peptide transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probable proton-dependent permease that transports dipeptides
- Gene Name:
- dtpD
- Uniprot ID:
- P75742
- Molecular weight:
- 54158
- General function:
- Involved in cation transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in zinc efflux across the cytoplasmic membrane, thus reducing zinc accumulation in the cytoplasm and rendering bacteria more resistant to zinc. It may contribute to zinc homeostasis at low concentrations of zinc, whereas zntA is required for growth at more toxic concentrations
- Gene Name:
- zitB
- Uniprot ID:
- P75757
- Molecular weight:
- 34678
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex gsiABCD involved in glutathione import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- gsiC
- Uniprot ID:
- P75798
- Molecular weight:
- 34066
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex gsiABCD involved in glutathione import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- gsiD
- Uniprot ID:
- P75799
- Molecular weight:
- 33238
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system for aliphatic sulfonates. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ssuC
- Uniprot ID:
- P75851
- Molecular weight:
- 28925
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Makes part of the rut operon, which is required for the utilization of pyrimidines as sole nitrogen source
- Gene Name:
- rutG
- Uniprot ID:
- P75892
- Molecular weight:
- 45557
- General function:
- Involved in peptide transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Proton-dependent permease that transports di- and tripeptides as well as structurally related peptidomimetics such as aminocephalosporins into the cell. Has a clear preference for dipeptides and tripeptides composed of L-amino acids, and discriminates dipeptides on the basis of the position of charges within the substrate
- Gene Name:
- dtpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P77304
- Molecular weight:
- 53991
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ddpABCDF, which is probably involved in D,D-dipeptide transport. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ddpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P77308
- Molecular weight:
- 37345
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ddpABCDF, which is probably involved in D,D-dipeptide transport. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ddpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P77463
- Molecular weight:
- 31971
- General function:
- Involved in transport
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- ansP
- Uniprot ID:
- P77610
- Molecular weight:
- 54233
- General function:
- Involved in lactate transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Transports glycolate across the membrane. Can also transport L-lactate and D-lactate. Seems to be driven by a proton motive force
- Gene Name:
- glcA
- Uniprot ID:
- Q46839
- Molecular weight:
- 58920
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system for taurine. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- tauC
- Uniprot ID:
- Q47539
- Molecular weight:
- 29812
- General function:
- Involved in transport
- Specific function:
- Transporter for the intake of S-methylmethionine
- Gene Name:
- mmuP
- Uniprot ID:
- Q47689
- Molecular weight:
- 50525
- General function:
- Involved in cation transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Low-affinity potassium transport system. Interacts with trk system potassium uptake protein trkA. TrkE increases the affinity of the system
- Gene Name:
- trkG
- Uniprot ID:
- P23849
- Molecular weight:
- 53943
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a nickel transport system, probably represents the nickel binder
- Gene Name:
- nikA
- Uniprot ID:
- P33590
- Molecular weight:
- 58718
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- This protein specifically binds sulfate and is involved in its transmembrane transport
- Gene Name:
- sbp
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG78
- Molecular weight:
- 36659
- General function:
- Involved in GTP binding
- Specific function:
- GTP-driven Fe(2+) uptake system
- Gene Name:
- feoB
- Uniprot ID:
- P33650
- Molecular weight:
- 84473
- General function:
- Involved in transmembrane transport
- Specific function:
- Probably acts as a permease in the beta-lactamase induction system and in peptidoglycan recycling
- Gene Name:
- ampG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE16
- Molecular weight:
- 53245
- General function:
- Involved in transport
- Specific function:
- Part of the tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic (TRAP) transport system yiaMNO involved in the uptake of 2,3- diketo-L-gulonate. This protein specifically binds 2,3-diketo-L- gulonate. Is not able to bind either L-ascorbate or dehydroascorbate
- Gene Name:
- yiaO
- Uniprot ID:
- P37676
- Molecular weight:
- 35970
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex MetNIQ involved in methionine import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable). It has also been shown to be involved in formyl-L-methionine transport
- Gene Name:
- metN
- Uniprot ID:
- P30750
- Molecular weight:
- 37788
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ddpABCDF, which is probably involved in D,D-dipeptide transport. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- ddpD
- Uniprot ID:
- P77268
- Molecular weight:
- 36100
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for glutamine. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- glnQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P10346
- Molecular weight:
- 26731
- General function:
- Involved in sulfur compound metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system for aliphatic sulfonates. Putative binding protein
- Gene Name:
- ssuA
- Uniprot ID:
- P75853
- Molecular weight:
- 34557
- General function:
- Involved in maltose transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity maltose membrane transport system malEFGK. Initial receptor for the active transport of and chemotaxis toward maltooligosaccharides
- Gene Name:
- malE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEX9
- Molecular weight:
- 43387
- General function:
- Involved in transmembrane transport
- Specific function:
- Part of a cation efflux system that mediates resistance to copper and silver
- Gene Name:
- cusB
- Uniprot ID:
- P77239
- Molecular weight:
- 44304
- General function:
- Involved in sodium:dicarboxylate symporter activity
- Specific function:
- This carrier protein is part of the Na(+)-independent, binding-protein-independent glutamate-aspartate transport system
- Gene Name:
- gltP
- Uniprot ID:
- P21345
- Molecular weight:
- 47159
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Binds ferrienterobactin; part of the binding-protein- dependent transport system for uptake of ferrienterobactin
- Gene Name:
- fepB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEL6
- Molecular weight:
- 34283
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for oligopeptides. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- oppF
- Uniprot ID:
- P77737
- Molecular weight:
- 37197
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity D-xylose membrane transport system. Binds with high affinity to xylose
- Gene Name:
- xylF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37387
- Molecular weight:
- 35734
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ZnuABC involved in zinc import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- znuC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9X1
- Molecular weight:
- 27867
- General function:
- Involved in transmembrane transport
- Specific function:
- AcrAB is a drug efflux protein with a broad substrate specificity
- Gene Name:
- acrA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE06
- Molecular weight:
- 42196
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- dppD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAG0
- Molecular weight:
- 35844
- General function:
- Involved in spermidine transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the excretion of spermidine. Can also confer resistance to deoxycholate and SDS
- Gene Name:
- mdtI
- Uniprot ID:
- P69210
- Molecular weight:
- 11720
- General function:
- Involved in cation transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- According to PubMed:8496184 the natural activity of this protein is as a calcium/proton antiporter, but it can act as a weak sodium/proton antiporter. The presence of a preferred substrate and normal pH cytoplasmic values might prevent significant sodium/proton antiporter activity
- Gene Name:
- chaA
- Uniprot ID:
- P31801
- Molecular weight:
- 39168
- General function:
- Involved in potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Responsible for the low-affinity transport of potassium into the cell, with the probable concomitant uptake of protons (symport system). Can also transport cesium
- Gene Name:
- kup
- Uniprot ID:
- P63183
- Molecular weight:
- 69293
- General function:
- Involved in ion channel activity
- Specific function:
- Probably acts as an electrical shunt for an outwardly- directed proton pump that is linked to amino acid decarboxylation, as part of the extreme acid resistance (XAR) response
- Gene Name:
- clcB
- Uniprot ID:
- P76175
- Molecular weight:
- 44153
- General function:
- Involved in transport
- Specific function:
- Imports putrescine
- Gene Name:
- puuP
- Uniprot ID:
- P76037
- Molecular weight:
- 50853
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Essential for the uptake of the murein peptide L-alanyl- gamma-D-glutamyl-meso-diaminopimelate. Also transports some alpha- linked peptides such as Pro-Phe-Lys with low affinity. The transport is effected by the oligopeptide permease system
- Gene Name:
- mppA
- Uniprot ID:
- P77348
- Molecular weight:
- 59900
- General function:
- Involved in sodium ion transport
- Specific function:
- Na(+)/H(+) antiporter that extrudes sodium in exchange for external protons. Catalyzes the exchange of 2 H(+) per Na(+). Can mediate sodium uptake when a transmembrane pH gradient is applied. Active at alkaline pH. Activity is strongly down- regulated below pH 6.5
- Gene Name:
- nhaA
- Uniprot ID:
- P13738
- Molecular weight:
- 41355
- General function:
- Involved in spermidine transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the excretion of spermidine. Can also confer resistance to deoxycholate and SDS
- Gene Name:
- mdtJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P69212
- Molecular weight:
- 13115
- General function:
- Involved in cation transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the constitutive potassium transport systems trkG and trkH. May regulate the transport activity of trkG and trkH systems. Binds to NAD+ and NADH
- Gene Name:
- trkA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGI8
- Molecular weight:
- 50367
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- This periplasmic binding protein is involved in an arginine transport system. ArgT and histidine-binding protein J (hisJ) interact with a common membrane-bound receptor, hisP
- Gene Name:
- argT
- Uniprot ID:
- P09551
- Molecular weight:
- 27991
- General function:
- Involved in lipid transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- mviN
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AF16
- Molecular weight:
- 55267
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex BtuCDF involved in vitamin B12 import. Binds vitamin B12 and delivers it to the periplasmic surface of BtuC
- Gene Name:
- btuF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37028
- Molecular weight:
- 29367
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system AlsBAC for D-allose
- Gene Name:
- alsB
- Uniprot ID:
- P39265
- Molecular weight:
- 32910
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex gsiABCD involved in glutathione import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- gsiA
- Uniprot ID:
- P75796
- Molecular weight:
- 69113
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- H(+)-stimulated, highly selective, manganese uptake system. Can also transport cadmium, cobalt, iron, zinc and to a lesser extent nickel and copper. Involved in response to reactive oxygen
- Gene Name:
- mntH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A769
- Molecular weight:
- 44193
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Non-specific porin
- Gene Name:
- ompN
- Uniprot ID:
- P77747
- Molecular weight:
- 41220
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of a cation efflux system that mediates resistance to copper and silver
- Gene Name:
- cusA
- Uniprot ID:
- P38054
- Molecular weight:
- 114706
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP (TC 3.A.1.6.1) involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. This protein specifically binds thiosulfate and is involved in its transmembrane transport
- Gene Name:
- cysP
- Uniprot ID:
- P16700
- Molecular weight:
- 37614
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- High-affinity uptake of choline driven by a proton- motive force
- Gene Name:
- betT
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABC9
- Molecular weight:
- 75842
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- yehX
- Uniprot ID:
- P33360
- Molecular weight:
- 34424
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of the oligopeptide permease, a binding protein-dependent transport system, it binds peptides up to five amino acids long with high affinity
- Gene Name:
- oppA
- Uniprot ID:
- P23843
- Molecular weight:
- 60899
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- dppF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37313
- Molecular weight:
- 37560
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- yddG
- Uniprot ID:
- P46136
- Molecular weight:
- 31539
- General function:
- Involved in phosphate ion binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex pstSACB involved in phosphate import
- Gene Name:
- pstS
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG82
- Molecular weight:
- 37024
- General function:
- Involved in cation transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Iron-efflux transporter responsible for iron detoxification. Also able to transport Zn(2+) in a proton- dependent manner
- Gene Name:
- fieF
- Uniprot ID:
- P69380
- Molecular weight:
- 32927
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Uptake of inorganic phosphate, phosphorylated compounds, and some other negatively charged solutes
- Gene Name:
- phoE
- Uniprot ID:
- P02932
- Molecular weight:
- 38922
- General function:
- Involved in cation transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Low-affinity potassium transport system. Interacts with trk system potassium uptake protein trkA and requires trkE for transport activity
- Gene Name:
- trkH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFZ7
- Molecular weight:
- 52959
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid transport
- Specific function:
- Conducts the efflux of homoserine and homoserine lactone
- Gene Name:
- rhtB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG34
- Molecular weight:
- 22427
- General function:
- Involved in symporter activity
- Specific function:
- Responsible for the aerobic transport of the dicarboxylates fumarate, L- and D-malate and to a lesser extent succinate, from the periplasm across the inner membrane
- Gene Name:
- dctA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A830
- Molecular weight:
- 45436
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity L-arabinose membrane transport system. Binds with high affinity to arabinose, but can also bind D-galactose (approximately 2-fold reduction) and D- fucose (approximately 40-fold reduction)
- Gene Name:
- araF
- Uniprot ID:
- P02924
- Molecular weight:
- 35541
- General function:
- Involved in receptor activity
- Specific function:
- This receptor binds the ferrichrome-iron ligand. It interacts with the tonB protein, which is responsible for energy coupling of the ferrichrome-promoted iron transport system. Acts as a receptor for bacteriophage T5 as well as T1, phi80 and colicin M. Binding of T5 triggers the opening of a high conductance ion channel. Can also transport the antibiotic albomycin
- Gene Name:
- fhuA
- Uniprot ID:
- P06971
- Molecular weight:
- 82182
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ThiBPQ involved in thiamine import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- thiQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P31548
- Molecular weight:
- 24999
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in a peptide intake transport system that plays a role in the resistance to antimicrobial peptides
- Gene Name:
- sapD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAH4
- Molecular weight:
- 37660
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- artP
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAF6
- Molecular weight:
- 27022
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for glutamate and aspartate. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- gltL
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAG3
- Molecular weight:
- 26661
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity D-ribose membrane transport system and also serves as the primary chemoreceptor for chemotaxis
- Gene Name:
- rbsB
- Uniprot ID:
- P02925
- Molecular weight:
- 30950
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Component of the leucine-specific transport system
- Gene Name:
- livG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9S7
- Molecular weight:
- 28427
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the high-affinity histidine permease, a binding-protein-dependent transport system. The other components are proteins hisQ, hisM, and hisP
- Gene Name:
- hisJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEU0
- Molecular weight:
- 28483
- General function:
- Involved in receptor activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the uptake of Fe(3+) via coprogen, ferrioxamine B, and rhodotorulic acid
- Gene Name:
- fhuE
- Uniprot ID:
- P16869
- Molecular weight:
- 81232
- General function:
- Involved in solute:hydrogen antiporter activity
- Specific function:
- Transport system that facilitates potassium-efflux, possibly by potassium-proton antiport
- Gene Name:
- kefC
- Uniprot ID:
- P03819
- Molecular weight:
- 67795
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid transport
- Specific function:
- Conducts the efflux of threonine
- Gene Name:
- rhtC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG38
- Molecular weight:
- 22474
- General function:
- Involved in copper ion binding
- Specific function:
- Part of a cation efflux system that mediates resistance to copper and silver. Binds one copper per polypeptide
- Gene Name:
- cusF
- Uniprot ID:
- P77214
- Molecular weight:
- 12251
- General function:
- Involved in receptor activity
- Specific function:
- FecA is the outer membrane receptor protein in the Fe(3+) dicitrate transport system
- Gene Name:
- fecA
- Uniprot ID:
- P13036
- Molecular weight:
- 85321
- General function:
- Involved in transmembrane transport
- Specific function:
- Involved in excretion of nitrite produced by the dissimilatory reduction of nitrate
- Gene Name:
- narK
- Uniprot ID:
- P10903
- Molecular weight:
- 49693
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid transport
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of the leucine, isoleucine, valine, (threonine) transport system, which is one of the two periplasmic binding protein-dependent transport systems of the high-affinity transport of the branched-chain amino acids
- Gene Name:
- livJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AD96
- Molecular weight:
- 39076
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity zinc uptake transport system
- Gene Name:
- znuB
- Uniprot ID:
- P39832
- Molecular weight:
- 27728
- General function:
- Involved in siderophore transport
- Specific function:
- Exports the siderophore enterobactin out of the cell
- Gene Name:
- entS
- Uniprot ID:
- P24077
- Molecular weight:
- 43281
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex NikABCDE involved in nickel import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- nikD
- Uniprot ID:
- P33593
- Molecular weight:
- 26820
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Ni(2+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + Ni(2+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Component of the leucine-specific transport system
- Gene Name:
- livF
- Uniprot ID:
- P22731
- Molecular weight:
- 26310
- General function:
- Involved in protein transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the tonB-dependent energy-dependent transport of various receptor-bound substrates. Protects exbD from proteolytic degradation and functionally stabilizes tonB
- Gene Name:
- exbB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABU7
- Molecular weight:
- 26287
- General function:
- Involved in rhamnose transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Uptake of L-rhamnose across the boundary membrane with the concomitant transport of protons into the cell (symport system). Can also transport L-mannose and L-xylose, but at reduced rates
- Gene Name:
- rhaT
- Uniprot ID:
- P27125
- Molecular weight:
- 37319
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ddpABCDF, which is probably involved in D,D-dipeptide transport. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- ddpF
- Uniprot ID:
- P77622
- Molecular weight:
- 34621
- General function:
- Involved in efflux transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- ygaH
- Uniprot ID:
- P43667
- Molecular weight:
- 12023
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Binds citrate-dependent Fe(3+); part of the binding- protein-dependent transport system for uptake of citrate-dependent Fe(3+)
- Gene Name:
- fecB
- Uniprot ID:
- P15028
- Molecular weight:
- 33146
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of a cation efflux system that mediates resistance to copper and silver. In pathogenic strains it allows the bacteria to invade brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMEC) thus allowing it to cross the blood-brain barrier and cause neonatal meningitis
- Gene Name:
- cusC
- Uniprot ID:
- P77211
- Molecular weight:
- 50269
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Dipeptide-binding protein of a transport system that can be subject to osmotic shock. DppA is also required for peptide chemotaxis
- Gene Name:
- dppA
- Uniprot ID:
- P23847
- Molecular weight:
- 60293
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- This protein is involved in the active transport of galactose and glucose. It plays a role in the chemotaxis towards the two sugars by interacting with the trg chemoreceptor
- Gene Name:
- mglB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEE5
- Molecular weight:
- 35712
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- OmpF is a porin that forms passive diffusion pores which allow small molecular weight hydrophilic materials across the outer membrane. It is also a receptor for the bacteriophage T2
- Gene Name:
- ompF
- Uniprot ID:
- P02931
- Molecular weight:
- 39333
- General function:
- Involved in solute:hydrogen antiporter activity
- Specific function:
- Transport system that facilitates potassium-efflux, possibly by potassium-proton antiport
- Gene Name:
- kefB
- Uniprot ID:
- P45522
- Molecular weight:
- 66411
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex NikABCDE involved in nickel import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- nikE
- Uniprot ID:
- P33594
- Molecular weight:
- 29721
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Ni(2+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + Ni(2+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in cell envelope formation. Is produced in extremely low amounts
- Gene Name:
- acrF
- Uniprot ID:
- P24181
- Molecular weight:
- 111454
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- kdpF
- Uniprot ID:
- P36937
- Molecular weight:
- 3072
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- sn-glycerol-3-phosphate and glycerophosphoryl diester- binding protein interacts with the binding protein-dependent transport system ugpACE
- Gene Name:
- ugpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG80
- Molecular weight:
- 48448
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probable cadaverine/lysine antiporter or part of it
- Gene Name:
- cadB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAE8
- Molecular weight:
- 46665
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the tonB-dependent energy-dependent transport of various receptor-bound substrates
- Gene Name:
- exbD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABV2
- Molecular weight:
- 15527
- General function:
- Involved in receptor activity
- Specific function:
- This protein is involved in the initial step of iron uptake by binding ferrienterobactin (Fe-ENT), an iron chelatin siderophore that allows E.coli to extract iron from the environment. FepA also acts as a receptor for colicins B and D
- Gene Name:
- fepA
- Uniprot ID:
- P05825
- Molecular weight:
- 82106
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Interacts with outer membrane receptor proteins that carry out high-affinity binding and energy dependent uptake into the periplasmic space of specific substrates such as cobalamin, and various iron compounds (such as iron dicitrate, enterochelin, aerobactin, etc.). In the absence of tonB these receptors bind their substrates but do not carry out active transport. TonB also interacts with some colicins and is involved in the energy- dependent, irreversible steps of bacteriophages phi 80 and T1 infection. It could act to transduce energy from the cytoplasmic membrane to specific energy-requiring processes in the outer membrane, resulting in the release into the periplasm of ligands bound by these outer membrane proteins
- Gene Name:
- tonB
- Uniprot ID:
- P02929
- Molecular weight:
- 26094
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex TauABC involved in taurine import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- tauB
- Uniprot ID:
- Q47538
- Molecular weight:
- 28297
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + taurine(Out) = ADP + phosphate + taurine(In). |
- General function:
- Inorganic ion transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of a D-methionine permease, a binding protein-dependent, ATP-driven transport system
- Gene Name:
- metQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P28635
- Molecular weight:
- 29432
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- This protein is part of an active transport system that transports exogenous cyanate into E.coli cells
- Gene Name:
- cynX
- Uniprot ID:
- P17583
- Molecular weight:
- 41360
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ModABC involved in molybdenum import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- modC
- Uniprot ID:
- P09833
- Molecular weight:
- 39102
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + molybdate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + molybdate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in sodium:hydrogen antiporter activity
- Specific function:
- Na(+)/H(+) antiporter that extrudes sodium in exchange for external protons. Catalyzes the exchange of 3 H(+) per 2 Na(+). Has a high affinity for sodium, but can also transport lithium. Activity is weakly pH-dependent. Essential for regulation of intracellular pH under alkaline conditions
- Gene Name:
- nhaB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFA7
- Molecular weight:
- 56728
- General function:
- Involved in branched-chain aliphatic amino acid transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the LIV-II transport system for branched- chain amino acids. This LIV-II transport system may be H(+)- coupled
- Gene Name:
- brnQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AD99
- Molecular weight:
- 46208
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules
- Gene Name:
- osmF
- Uniprot ID:
- P33362
- Molecular weight:
- 32609
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Participates in the efflux of aminoglycosides. Confers resistance to a variety of these substances
- Gene Name:
- acrD
- Uniprot ID:
- P24177
- Molecular weight:
- 113046
- General function:
- Amino acid transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- ygaZ
- Uniprot ID:
- P76630
- Molecular weight:
- 26107
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for oligopeptides. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- oppD
- Uniprot ID:
- P76027
- Molecular weight:
- 37188
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for proper expression of outer membrane protein genes such as ompF, nmpC, protein 2, hemolysin, colicin V, or colicin E1. May be specialized for signal sequence independent, extracellular secretion in Gram-negative bacteria
- Gene Name:
- tolC
- Uniprot ID:
- P02930
- Molecular weight:
- 53740
- General function:
- Involved in metal ion binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity zinc uptake transport system
- Gene Name:
- znuA
- Uniprot ID:
- P39172
- Molecular weight:
- 33777
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- AcrAB is a drug efflux protein with a broad substrate specificity
- Gene Name:
- acrB
- Uniprot ID:
- P31224
- Molecular weight:
- 113573
- General function:
- Involved in transmembrane transport
- Specific function:
- May affect specific membrane functions, such as septum formation during cell division, and cell membrane permeability
- Gene Name:
- acrE
- Uniprot ID:
- P24180
- Molecular weight:
- 41317
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probable putrescine-ornithine antiporter
- Gene Name:
- potE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAF1
- Molecular weight:
- 46495
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid transport
- Specific function:
- Involved in the export of arginine. Important to control the intracellular level of arginine and the correct balance between arginine and lysine. May also be involved in the export of canavanine (a plant-derived antimetabolite)
- Gene Name:
- argO
- Uniprot ID:
- P11667
- Molecular weight:
- 23175
- General function:
- Amino acid transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for putrescine. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- potG
- Uniprot ID:
- P31134
- Molecular weight:
- 41930
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex gsiABCD involved in glutathione import
- Gene Name:
- gsiB
- Uniprot ID:
- P75797
- Molecular weight:
- 56470
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system for taurine
- Gene Name:
- tauA
- Uniprot ID:
- Q47537
- Molecular weight:
- 34266
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex SsuABC involved in aliphatic sulfonates import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- ssuB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAI1
- Molecular weight:
- 27738
- General function:
- Involved in receptor activity
- Specific function:
- Not yet known. Postulated to participate in iron transport. Outer membrane receptor for colicins IA and IB
- Gene Name:
- cirA
- Uniprot ID:
- P17315
- Molecular weight:
- 73895
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Forms passive diffusion pores which allow small molecular weight hydrophilic materials across the outer membrane
- Gene Name:
- ompC
- Uniprot ID:
- P06996
- Molecular weight:
- 40368
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for glutamate and aspartate. Binds to both aspartate and glutamate
- Gene Name:
- gltI
- Uniprot ID:
- P37902
- Molecular weight:
- 33420
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid transport
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of the leucine-specific transport system, which is one of the two periplasmic binding protein-dependent transport systems of the high-affinity transport of the branched-chain amino acids in E.coli
- Gene Name:
- livK
- Uniprot ID:
- P04816
- Molecular weight:
- 39378
- General function:
- Involved in transmembrane transport
- Specific function:
- Involved in excretion of nitrite produced by the dissimilatory reduction of nitrate
- Gene Name:
- narU
- Uniprot ID:
- P37758
- Molecular weight:
- 49890
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a glutamine-transport system glnHPQ
- Gene Name:
- glnH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEQ3
- Molecular weight:
- 27190
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine. Polyamine binding protein
- Gene Name:
- potF
- Uniprot ID:
- P31133
- Molecular weight:
- 40839
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ddpABCDF, which is probably involved in D,D-dipeptide transport
- Gene Name:
- ddpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P76128
- Molecular weight:
- 57641
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine and spermidine. Polyamine binding protein
- Gene Name:
- potD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFK9
- Molecular weight:
- 38867
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- May play a role in the defense against osmotic shock
- Gene Name:
- kch
- Uniprot ID:
- P31069
- Molecular weight:
- 46062
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex fhuCDB involved in iron(3+)-hydroxamate import. Binds the iron(3+)-hydroxamate complex and transfers it to the membrane-bound permease. Required for the transport of all iron(3+)-hydroxamate siderophores such as ferrichrome, gallichrome, desferrioxamine, coprogen, aerobactin, shizokinen, rhodotorulic acid and the antibiotic albomycin
- Gene Name:
- fhuD
- Uniprot ID:
- P07822
- Molecular weight:
- 32998
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex thiBPQ involved in thiamine import
- Gene Name:
- thiB
- Uniprot ID:
- P31550
- Molecular weight:
- 36163
- General function:
- Involved in receptor activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the active transport across the outer membrane of iron complexed with catecholate siderophores such as dihydroxybenzoylserine and dihydroxybenzoate. It derives its energy for transport by interacting with the trans-periplasmic membrane protein tonB. Can also transport catechol-substitued cephalosporins. Receptor for microcins M, H47 and E492
- Gene Name:
- fiu
- Uniprot ID:
- P75780
- Molecular weight:
- 81960
- General function:
- Involved in molybdate transmembrane-transporting ATPase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the transport of molybdenum into the cell. Binds molybdate with high specificity and affinity
- Gene Name:
- modA
- Uniprot ID:
- P37329
- Molecular weight:
- 27364
- General function:
- Inorganic ion transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex PhnCDE involved in phosphonates, phosphate esters, phosphite and phosphate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- phnC
- Uniprot ID:
- P16677
- Molecular weight:
- 29430
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + phosphonate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + phosphonate(In). |
- General function:
- ATPase activity, coupled to transmembrane movement of substances
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex LsrABCD involved in autoinducer 2 (AI-2) import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable). This protein is essential for aerobic growth.
- Gene Name:
- lsrA
- Uniprot ID:
- P77257
- Molecular weight:
- 55820
- General function:
- periplasmic space
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex LsrABCD involved in autoinducer 2 (AI-2) import. Binds AI-2 and delivers it to the LsrC and LsrD permeases (Probable).
- Gene Name:
- lsrB
- Uniprot ID:
- P76142
- Molecular weight:
- 36684
- General function:
- transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system for cystine.
- Gene Name:
- fliY
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEM9
- Molecular weight:
- 29038
- General function:
- alkylphosphonate transport
- Specific function:
- Phosphonate binding protein that is part of the phosphonate uptake system. Exhibits high affinity for 2-aminoethylphosphonate, and somewhat less affinity to ethylphosphonate, methylphosphonate, phosphonoacetate and phenylphosphonate.
- Gene Name:
- phnD
- Uniprot ID:
- P16682
- Molecular weight:
- 37370