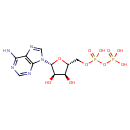
ADP (ECMDB01341) (M2MDB000345)
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- Provides the precursors necessary for DNA synthesis. Catalyzes the biosynthesis of deoxyribonucleotides from the corresponding ribonucleotides. R1 contains the binding sites for both substrates and allosteric effectors and carries out the actual reduction of the ribonucleotide. It also provides redox- active cysteines
- Gene Name:
- nrdA
- Uniprot ID:
- P00452
- Molecular weight:
- 85774
Reactions
| 2'-deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate + thioredoxin disulfide + H(2)O = ribonucleoside diphosphate + thioredoxin. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the ATP-dependent phosphorylation of L- homoserine to L-homoserine phosphate. Is also able to phosphorylate the hydroxy group on gamma-carbon of L-homoserine analogs when the functional group at the alpha-position is a carboxyl, an ester, or even a hydroxymethyl group. Neither L- threonine nor L-serine are substrates of the enzyme
- Gene Name:
- thrB
- Uniprot ID:
- P00547
- Molecular weight:
- 33623
Reactions
| ATP + L-homoserine = ADP + O-phospho-L-homoserine. |
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid binding
- Specific function:
- L-homoserine + NAD(P)(+) = L-aspartate 4- semialdehyde + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- thrA
- Uniprot ID:
- P00561
- Molecular weight:
- 89119
Reactions
| L-homoserine + NAD(P)(+) = L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde + NAD(P)H. |
| ATP + L-aspartate = ADP + 4-phospho-L-aspartate. |
- General function:
- Involved in cellular amino acid biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- L-homoserine + NAD(P)(+) = L-aspartate 4- semialdehyde + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- metL
- Uniprot ID:
- P00562
- Molecular weight:
- 88887
Reactions
| L-homoserine + NAD(P)(+) = L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde + NAD(P)H. |
| ATP + L-aspartate = ADP + 4-phospho-L-aspartate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-glutamine + tRNA(Gln) = AMP + diphosphate + L-glutaminyl-tRNA(Gln)
- Gene Name:
- glnS
- Uniprot ID:
- P00962
- Molecular weight:
- 63477
Reactions
| ATP + L-glutamine + tRNA(Gln) = AMP + diphosphate + L-glutaminyl-tRNA(Gln). |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- 2 ATP + L-glutamine + HCO(3)(-) + H(2)O = 2 ADP + phosphate + L-glutamate + carbamoyl phosphate
- Gene Name:
- carB
- Uniprot ID:
- P00968
- Molecular weight:
- 117841
Reactions
| 2 ATP + L-glutamine + HCO(3)(-) + H(2)O = 2 ADP + phosphate + L-glutamate + carbamoyl phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in potassium-transporting ATPase activity
- Specific function:
- One of the components of the high-affinity ATP-driven potassium transport (or KDP) system, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of hydrogen and potassium ions
- Gene Name:
- kdpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P03959
- Molecular weight:
- 59189
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + K(+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + K(+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- One of the components of the high-affinity ATP-driven potassium transport (or KDP) system, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of hydrogen and potassium ions
- Gene Name:
- kdpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P03960
- Molecular weight:
- 72198
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + K(+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + K(+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in potassium-transporting ATPase activity
- Specific function:
- One of the components of the high-affinity ATP-driven potassium transport (or KDP) system, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of hydrogen and potassium ions. The C subunit may be involved in assembly of the KDP complex
- Gene Name:
- kdpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P03961
- Molecular weight:
- 20267
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + K(+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + K(+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + gamma-L-glutamyl-L-cysteine + glycine = ADP + phosphate + glutathione
- Gene Name:
- gshB
- Uniprot ID:
- P04425
- Molecular weight:
- 35561
Reactions
| ATP + gamma-L-glutamyl-L-cysteine + glycine = ADP + phosphate + glutathione. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex RbsABCD involved in ribose import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- rbsA
- Uniprot ID:
- P04983
- Molecular weight:
- 55041
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + monosaccharide(Out) = ADP + phosphate + monosaccharide(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in RNA binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in mRNA degradation. Hydrolyzes single-stranded polyribonucleotides processively in the 3'- to 5'-direction
- Gene Name:
- pnp
- Uniprot ID:
- P05055
- Molecular weight:
- 77100
Reactions
| RNA(n+1) + phosphate = RNA(n) + a nucleoside diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in bis(5'-nucleosyl)-tetraphosphatase (symmetrical) activity
- Specific function:
- Hydrolyzes diadenosine 5',5'''-P1,P4-tetraphosphate to yield ADP
- Gene Name:
- apaH
- Uniprot ID:
- P05637
- Molecular weight:
- 31296
Reactions
| P(1),P(4)-bis(5'-adenosyl) tetraphosphate + H(2)O = 2 ADP. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex BtuCDF involved in vitamin B12 import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- btuD
- Uniprot ID:
- P06611
- Molecular weight:
- 27081
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + vitamin B12(Out) = ADP + phosphate + vitamin B12(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- ATP + D-fructose 6-phosphate = ADP + D- fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
- Gene Name:
- pfkB
- Uniprot ID:
- P06999
- Molecular weight:
- 32456
Reactions
| ATP + D-fructose 6-phosphate = ADP + D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for histidine. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- hisP
- Uniprot ID:
- P07109
- Molecular weight:
- 28653
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex fhuCDB involved in iron(3+)-hydroxamate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- fhuC
- Uniprot ID:
- P07821
- Molecular weight:
- 28886
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + iron chelate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + iron chelate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Cell wall formation
- Gene Name:
- ddlB
- Uniprot ID:
- P07862
- Molecular weight:
- 32839
Reactions
| ATP + 2 D-alanine = ADP + phosphate + D-alanyl-D-alanine. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + 2-(formamido)-N(1)-(5-phospho-D- ribosyl)acetamidine = ADP + phosphate + 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D- ribosyl)imidazole
- Gene Name:
- purM
- Uniprot ID:
- P08178
- Molecular weight:
- 36854
Reactions
| ATP + 2-(formamido)-N(1)-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)acetamidine = ADP + phosphate + 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole. |
- General function:
- Involved in tetrahydrofolylpolyglutamate synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Conversion of folates to polyglutamate derivatives
- Gene Name:
- folC
- Uniprot ID:
- P08192
- Molecular weight:
- 45405
Reactions
| ATP + tetrahydropteroyl-(gamma-Glu)(n) + L-glutamate = ADP + phosphate + tetrahydropteroyl-(gamma-Glu)(n+1). |
| ATP + 7,8-dihydropteroate + L-glutamate = ADP + phosphate + 7,8-dihydropteroylglutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- ATP + L(or D)-ribulose = ADP + L(or D)- ribulose 5-phosphate
- Gene Name:
- araB
- Uniprot ID:
- P08204
- Molecular weight:
- 61089
Reactions
| ATP + L(or D)-ribulose = ADP + L(or D)-ribulose 5-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-aspartate = ADP + 4-phospho-L- aspartate
- Gene Name:
- lysC
- Uniprot ID:
- P08660
- Molecular weight:
- 48531
Reactions
| ATP + L-aspartate = ADP + 4-phospho-L-aspartate. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- Possesses an ATPase activity that is dependent on the presence of AIR (aminoimidazole ribonucleotide). The association of purK and purE produces an enzyme complex capable of converting AIR to CAIR efficiently under physiological condition
- Gene Name:
- purK
- Uniprot ID:
- P09029
- Molecular weight:
- 39461
Reactions
| ATP + 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole + HCO(3)(-) = ADP + phosphate + 5-carboxyamino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- ATP + D-xylulose = ADP + D-xylulose 5- phosphate
- Gene Name:
- xylB
- Uniprot ID:
- P09099
- Molecular weight:
- 52618
Reactions
| ATP + D-xylulose = ADP + D-xylulose 5-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the activation of acetate to acetyl CoA and the secretion of acetate. During anaerobic growth of the organism, this enzyme is also involved in the synthesis of most of the ATP formed catabolically
- Gene Name:
- ackA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6A3
- Molecular weight:
- 43290
Reactions
| ATP + acetate = ADP + acetyl phosphate. |
| ATP + propanoate = ADP + propanoyl phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in acetylglutamate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + N-acetyl-L-glutamate = ADP + N-acetyl-L- glutamate 5-phosphate
- Gene Name:
- argB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6C8
- Molecular weight:
- 27159
Reactions
| ATP + N-acetyl-L-glutamate = ADP + N-acetyl-L-glutamate 5-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in shikimate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the specific phosphorylation of the 3-hydroxyl group of shikimic acid using ATP as a cosubstrate
- Gene Name:
- aroK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6D7
- Molecular weight:
- 19538
Reactions
| ATP + shikimate = ADP + shikimate 3-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in shikimate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the specific phosphorylation of the 3-hydroxyl group of shikimic acid using ATP as a cosubstrate
- Gene Name:
- aroL
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6E1
- Molecular weight:
- 19151
Reactions
| ATP + shikimate = ADP + shikimate 3-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism
- Specific function:
- Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- atpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6E6
- Molecular weight:
- 15068
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + 7,8-diaminononanoate + CO(2) = ADP + phosphate + dethiobiotin
- Gene Name:
- ynfK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6E9
- Molecular weight:
- 24981
Reactions
| ATP + 7,8-diaminononanoate + CO(2) = ADP + phosphate + dethiobiotin. |
- General function:
- Involved in glutamine catabolic process
- Specific function:
- 2 ATP + L-glutamine + HCO(3)(-) + H(2)O = 2 ADP + phosphate + L-glutamate + carbamoyl phosphate
- Gene Name:
- carA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6F1
- Molecular weight:
- 41431
Reactions
| 2 ATP + L-glutamine + HCO(3)(-) + H(2)O = 2 ADP + phosphate + L-glutamate + carbamoyl phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Key enzyme in the regulation of glycerol uptake and metabolism
- Gene Name:
- glpK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6F3
- Molecular weight:
- 56230
Reactions
| ATP + glycerol = ADP + sn-glycerol 3-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in cytidylate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP, dATP, and GTP are equally effective as phosphate donors. CMP and dCMP are the best phosphate acceptors
- Gene Name:
- cmk
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6I0
- Molecular weight:
- 24746
Reactions
| ATP + (d)CMP = ADP + (d)CDP. |
- General function:
- Involved in pantothenate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + (R)-pantothenate = ADP + (R)-4'- phosphopantothenate
- Gene Name:
- coaA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6I3
- Molecular weight:
- 36359
Reactions
| ATP + (R)-pantothenate = ADP + (R)-4'-phosphopantothenate. |
- General function:
- Involved in dephospho-CoA kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of the 3'-hydroxyl group of dephosphocoenzyme A to form coenzyme A
- Gene Name:
- coaE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6I9
- Molecular weight:
- 22622
Reactions
| ATP + 3'-dephospho-CoA = ADP + CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in adenylylsulfate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the synthesis of activated sulfate
- Gene Name:
- cysC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6J1
- Molecular weight:
- 22321
Reactions
| ATP + adenylyl sulfate = ADP + 3'-phosphoadenylyl sulfate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Cell wall formation
- Gene Name:
- ddlA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6J8
- Molecular weight:
- 39315
Reactions
| ATP + 2 D-alanine = ADP + phosphate + D-alanyl-D-alanine. |
- General function:
- Involved in galactokinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + D-galactose = ADP + alpha-D-galactose 1- phosphate
- Gene Name:
- galK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6T3
- Molecular weight:
- 41442
Reactions
| ATP + D-galactose = ADP + alpha-D-galactose 1-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Synthesizes alpha-1,4-glucan chains using ADP-glucose
- Gene Name:
- glgA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6U8
- Molecular weight:
- 52822
Reactions
| ADP-glucose + (1,4-alpha-D-glucosyl)(n) = ADP + (1,4-alpha-D-glucosyl)(n+1). |
- General function:
- Involved in glucokinase activity
- Specific function:
- Not highly important in E.coli as glucose is transported into the cell by the PTS system already as glucose 6-phosphate
- Gene Name:
- glk
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6V8
- Molecular weight:
- 34723
Reactions
| ATP + D-glucose = ADP + D-glucose 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in glutamate-cysteine ligase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-glutamate + L-cysteine = ADP + phosphate + gamma-L-glutamyl-L-cysteine
- Gene Name:
- gshA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6W9
- Molecular weight:
- 58269
Reactions
| ATP + L-glutamate + L-cysteine = ADP + phosphate + gamma-L-glutamyl-L-cysteine. |
- General function:
- Involved in thymidylate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reversible phosphorylation of deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP) to deoxythymidine diphosphate (dTDP), using ATP as its preferred phosphoryl donor. Situated at the junction of both de novo and salvage pathways of deoxythymidine triphosphate (dTTP) synthesis, is essential for DNA synthesis and cellular growth
- Gene Name:
- tmk
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A720
- Molecular weight:
- 23783
Reactions
| ATP + dTMP = ADP + dTDP. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleoside diphosphate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Major role in the synthesis of nucleoside triphosphates other than ATP. The ATP gamma phosphate is transferred to the NDP beta phosphate via a ping-pong mechanism, using a phosphorylated active-site intermediate
- Gene Name:
- ndk
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A763
- Molecular weight:
- 15463
Reactions
| ATP + nucleoside diphosphate = ADP + nucleoside triphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + D-fructose 6-phosphate = ADP + D- fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
- Gene Name:
- pfkA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A796
- Molecular weight:
- 34842
Reactions
| ATP + D-fructose 6-phosphate = ADP + D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphoglycerate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + 3-phospho-D-glycerate = ADP + 3-phospho- D-glyceroyl phosphate
- Gene Name:
- pgk
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A799
- Molecular weight:
- 41118
Reactions
| ATP + 3-phospho-D-glycerate = ADP + 3-phospho-D-glyceroyl phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reversible transfer of the terminal phosphate of ATP to form a long-chain polyphosphate (polyP). Can form linear polymers of orthophosphate with chain lengths up to 1000 or more. Can also act in the reverse direction to form ATP in the presence of excess ADP. Can also use GTP instead of ATP; but the efficiency of GTP is 5% that of ATP
- Gene Name:
- ppk
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A7B1
- Molecular weight:
- 80431
Reactions
| ATP + (phosphate)(n) = ADP + (phosphate)(n+1). |
- General function:
- Involved in NAD+ kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of NAD to NADP. Utilizes ATP and other nucleoside triphosphates as well as inorganic polyphosphate as a source of phosphorus
- Gene Name:
- ppnK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A7B3
- Molecular weight:
- 32566
Reactions
| ATP + NAD(+) = ADP + NADP(+). |
- General function:
- Involved in cellular amino acid biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group to glutamate to form glutamate 5-phosphate which rapidly cyclizes to 5- oxoproline
- Gene Name:
- proB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A7B5
- Molecular weight:
- 39056
Reactions
| ATP + L-glutamate = ADP + L-glutamate 5-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D- ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxylate + L-aspartate = ADP + phosphate + (S)-2-(5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4- carboxamido)succinate
- Gene Name:
- purC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A7D7
- Molecular weight:
- 26995
Reactions
| ATP + 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxylate + L-aspartate = ADP + phosphate + (S)-2-(5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamido)succinate. |
- General function:
- Involved in CTP synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the ATP-dependent amination of UTP to CTP with either L-glutamine or ammonia as the source of nitrogen
- Gene Name:
- pyrG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A7E5
- Molecular weight:
- 60374
Reactions
| ATP + UTP + NH(3) = ADP + phosphate + CTP. |
- General function:
- Involved in cellular amino acid biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reversible phosphorylation of UMP to UDP, with ATP as the most efficient phosphate donor
- Gene Name:
- pyrH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A7E9
- Molecular weight:
- 25970
Reactions
| ATP + UMP = ADP + UDP. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + succinate + CoA = ADP + phosphate + succinyl-CoA
- Gene Name:
- sucC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A836
- Molecular weight:
- 41392
Reactions
| ATP + succinate + CoA = ADP + phosphate + succinyl-CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + uridine = ADP + UMP
- Gene Name:
- udk
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A8F4
- Molecular weight:
- 24353
Reactions
| ATP + uridine = ADP + UMP. |
| ATP + cytidine = ADP + CMP. |
- General function:
- Involved in glutamate-ammonia ligase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-glutamate + NH(3) = ADP + phosphate + L-glutamine
- Gene Name:
- glnA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9C5
- Molecular weight:
- 51903
Reactions
| ATP + L-glutamate + NH(3) = ADP + phosphate + L-glutamine. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- ATP + D-ribose = ADP + D-ribose 5-phosphate
- Gene Name:
- rbsK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9J6
- Molecular weight:
- 32290
Reactions
| ATP + D-ribose = ADP + D-ribose 5-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- Controls translation of mRNA for both itself and the alpha-subunit (accA) by binding to a probable hairpin in the 5' of the mRNA. Binding to mRNA inhibits translation; this is partially relieved by acetyl-CoA. Increasing amounts of mRNA also inhibit enzyme activity
- Gene Name:
- accD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9Q5
- Molecular weight:
- 33322
Reactions
| ATP + acetyl-CoA + HCO(3)(-) = ADP + phosphate + malonyl-CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex AraFGH involved in arabinose import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- araG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAF3
- Molecular weight:
- 55018
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + monosaccharide(Out) = ADP + phosphate + monosaccharide(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex MglABC involved in galactose/methyl galactoside import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- mglA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAG8
- Molecular weight:
- 56415
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + monosaccharide(Out) = ADP + phosphate + monosaccharide(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex pstSACB involved in phosphate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- pstB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAH0
- Molecular weight:
- 29027
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + phosphate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + phosphate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Key component of the proton channel; it plays a direct role in the translocation of protons across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- atpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AB98
- Molecular weight:
- 30303
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the F(0) channel, it forms part of the peripheral stalk, linking F(1) to F(0)
- Gene Name:
- atpF
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABA0
- Molecular weight:
- 17264
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism
- Specific function:
- This protein is part of the stalk that links CF(0) to CF(1). It either transmits conformational changes from CF(0) to CF(1) or is implicated in proton conduction
- Gene Name:
- atpH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABA4
- Molecular weight:
- 19332
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism
- Specific function:
- Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane. The gamma chain is believed to be important in regulating ATPase activity and the flow of protons through the CF(0) complex
- Gene Name:
- atpG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABA6
- Molecular weight:
- 31577
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane. The alpha chain is a regulatory subunit
- Gene Name:
- atpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABB0
- Molecular weight:
- 55222
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + H(+)(In) = ADP + phosphate + H(+)(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane. The catalytic sites are hosted primarily by the beta subunits
- Gene Name:
- atpD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABB4
- Molecular weight:
- 50325
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + H(+)(In) = ADP + phosphate + H(+)(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, catalyzing transmembrane movement of substances
- Specific function:
- Mediates magnesium influx to the cytosol
- Gene Name:
- mgtA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABB8
- Molecular weight:
- 99466
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Mg(2+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + Mg(2+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase (ACC) complex. First, biotin carboxylase catalyzes the carboxylation of biotin on its carrier protein (BCCP) and then the CO(2) group is transferred by the carboxyltransferase to acetyl-CoA to form malonyl-CoA
- Gene Name:
- accA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABD5
- Molecular weight:
- 35241
Reactions
| ATP + acetyl-CoA + HCO(3)(-) = ADP + phosphate + malonyl-CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of the acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase complex; first, biotin carboxylase catalyzes the carboxylation of the carrier protein and then the transcarboxylase transfers the carboxyl group to form malonyl-CoA
- Gene Name:
- accB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABD8
- Molecular weight:
- 16687
- General function:
- Involved in diacylglycerol kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Recycling of diacylglycerol produced during the turnover of membrane phospholipid
- Gene Name:
- dgkA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABN1
- Molecular weight:
- 13245
Reactions
| ATP + 1,2-diacylglycerol = ADP + 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + pyruvate = ADP + phosphoenolpyruvate
- Gene Name:
- pykF
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AD61
- Molecular weight:
- 50729
Reactions
| ATP + pyruvate = ADP + phosphoenolpyruvate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- ATP-dependent phosphorylation of adenosylcobinamide and adds GMP to adenosylcobinamide phosphate
- Gene Name:
- cobU
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE76
- Molecular weight:
- 20164
Reactions
| ATP or GTP + adenosylcobinamide = adenosylcobinamide phosphate + ADP or GDP. |
| GTP + adenosylcobinamide phosphate = diphosphate + adenosylcobinamide-GDP. |
- General function:
- Amino acid transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the formation of an amide bond between glutathione and spermidine coupled with hydrolysis of ATP; also catalyzes the hydrolysis of glutathionylspermidine to glutathione and spermidine
- Gene Name:
- gsp
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AES0
- Molecular weight:
- 70531
Reactions
| Glutathione + spermidine + ATP = glutathionylspermidine + ADP + phosphate. |
| Glutathionylspermidine + H(2)O = glutathione + spermidine. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- ATP + inosine = ADP + IMP
- Gene Name:
- gsk
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEW6
- Molecular weight:
- 48448
Reactions
| ATP + inosine = ADP + IMP. |
- General function:
- Involved in 1-phosphofructokinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + D-fructose 1-phosphate = ADP + D- fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
- Gene Name:
- fruK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEW9
- Molecular weight:
- 33755
Reactions
| ATP + D-fructose 1-phosphate = ADP + D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + D-ribulose 5-phosphate = ADP + D- ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate
- Gene Name:
- prkB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEX5
- Molecular weight:
- 32344
Reactions
| ATP + D-ribulose 5-phosphate = ADP + D-ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleoside-triphosphate diphosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- mazG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEY3
- Molecular weight:
- 30412
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O = AMP + diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in FMN adenylyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + riboflavin = ADP + FMN
- Gene Name:
- ribF
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG40
- Molecular weight:
- 34734
Reactions
| ATP + riboflavin = ADP + FMN. |
| ATP + FMN = diphosphate + FAD. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + succinate + CoA = ADP + phosphate + succinyl-CoA
- Gene Name:
- sucD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGE9
- Molecular weight:
- 29777
Reactions
| ATP + succinate + CoA = ADP + phosphate + succinyl-CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + thiamine phosphate = ADP + thiamine diphosphate
- Gene Name:
- thiL
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGG0
- Molecular weight:
- 35070
Reactions
| ATP + thiamine phosphate = ADP + thiamine diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Efficient electron donor for the essential enzyme ribonucleotide reductase. Is also able to reduce the interchain disulfide bridges of insulin
- Gene Name:
- trxC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGG4
- Molecular weight:
- 15555
Reactions
| Protein dithiol + NAD(P)(+) = protein disulfide + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the tagatose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase gatYZ that is required for full activity and stability of the Y subunit. Could have a chaperone-like function for the proper and stable folding of gatY. When expressed alone, gatZ does not show any aldolase activity. Is involved in the catabolism of galactitol
- Gene Name:
- gatZ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0C8J8
- Molecular weight:
- 47108
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the tagatose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase kbaYZ that is required for full activity and stability of the Y subunit. Could have a chaperone-like function for the proper and stable folding of kbaY. When expressed alone, kbaZ does not show any aldolase activity
- Gene Name:
- kbaZ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0C8K0
- Molecular weight:
- 47192
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex UgpABCE involved in sn-glycerol-3-phosphate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable). Can also transport glycerophosphoryl diesters
- Gene Name:
- ugpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P10907
- Molecular weight:
- 39524
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + glycerol-3-phosphate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + glycerol-3-phosphate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in [isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP+)] kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Bifunctional enzyme which can phosphorylate or dephosphorylate isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) on a specific serine residue. This is a regulatory mechanism which enables bacteria to bypass the Krebs cycle via the glyoxylate shunt in response to the source of carbon. When bacteria are grown on glucose, IDH is fully active and unphosphorylated, but when grown on acetate or ethanol, the activity of IDH declines drastically concomitant with its phosphorylation
- Gene Name:
- aceK
- Uniprot ID:
- P11071
- Molecular weight:
- 67698
Reactions
| ATP + [isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP(+))] = ADP + [isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP(+))] phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-fuculose = ADP + L-fuculose 1- phosphate
- Gene Name:
- fucK
- Uniprot ID:
- P11553
- Molecular weight:
- 53235
Reactions
| ATP + L-fuculose = ADP + L-fuculose 1-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in kinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + propanoate = ADP + propanoyl phosphate
- Gene Name:
- tdcD
- Uniprot ID:
- P11868
- Molecular weight:
- 43384
Reactions
| ATP + propanoate = ADP + propanoyl phosphate. |
| ATP + acetate = ADP + acetyl phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in cell wall formation. Catalyzes the final step in the synthesis of UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-pentapeptide, the precursor of murein
- Gene Name:
- murF
- Uniprot ID:
- P11880
- Molecular weight:
- 47447
Reactions
| ATP + UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-gamma-D-glutamyl-L-lysine + D-alanyl-D-alanine = ADP + phosphate + UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-gamma-D-glutamyl-L-lysyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + 7,8-diaminononanoate + CO(2) = ADP + phosphate + dethiobiotin
- Gene Name:
- bioD
- Uniprot ID:
- P13000
- Molecular weight:
- 24139
Reactions
| ATP + 7,8-diaminononanoate + CO(2) = ADP + phosphate + dethiobiotin. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in a multicomponent binding-protein-dependent transport system for glycine betaine/L-proline
- Gene Name:
- proV
- Uniprot ID:
- P14175
- Molecular weight:
- 44162
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Member of the two-component regulatory system zraS/zraR. May function as a membrane-associated protein kinase that phosphorylates zraR in response to high concentrations of zinc or lead in the medium
- Gene Name:
- zraS
- Uniprot ID:
- P14377
- Molecular weight:
- 51031
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Cell wall formation. Catalyzes the addition of glutamate to the nucleotide precursor UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine (UMA)
- Gene Name:
- murD
- Uniprot ID:
- P14900
- Molecular weight:
- 46973
Reactions
| ATP + UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine + glutamate = ADP + phosphate + UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for citrate-dependent Fe(3+). Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- fecE
- Uniprot ID:
- P15031
- Molecular weight:
- 28191
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + N(2)-formyl-N(1)-(5-phospho-D- ribosyl)glycinamide + L-glutamine + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate + 2- (formamido)-N(1)-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)acetamidine + L-glutamate
- Gene Name:
- purL
- Uniprot ID:
- P15254
- Molecular weight:
- 141402
Reactions
| ATP + N(2)-formyl-N(1)-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)glycinamide + L-glutamine + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate + 2-(formamido)-N(1)-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)acetamidine + L-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + 5-phospho-D-ribosylamine + glycine = ADP + phosphate + N(1)-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)glycinamide
- Gene Name:
- purD
- Uniprot ID:
- P15640
- Molecular weight:
- 45940
Reactions
| ATP + 5-phospho-D-ribosylamine + glycine = ADP + phosphate + N(1)-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)glycinamide. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- cysA
- Uniprot ID:
- P16676
- Molecular weight:
- 41059
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + sulfate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + sulfate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in protein binding
- Specific function:
- Belongs to an operon involved in alkylphosphonate uptake and C-P lyase. Exact function not known
- Gene Name:
- phnN
- Uniprot ID:
- P16690
- Molecular weight:
- 20729
Reactions
| ATP + ribose 1,5-bisphosphate = ADP + 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Cell wall formation
- Gene Name:
- murC
- Uniprot ID:
- P17952
- Molecular weight:
- 53626
Reactions
| ATP + UDP-N-acetylmuramate + L-alanine = ADP + phosphate + UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine. |
- General function:
- Involved in nicotinate phosphoribosyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Nicotinate D-ribonucleotide + diphosphate = nicotinate + 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate
- Gene Name:
- pncB
- Uniprot ID:
- P18133
- Molecular weight:
- 45897
Reactions
| Beta-nicotinate D-ribonucleotide + diphosphate = nicotinate + 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- ATP + pyruvate = ADP + phosphoenolpyruvate
- Gene Name:
- pykA
- Uniprot ID:
- P21599
- Molecular weight:
- 51357
Reactions
| ATP + pyruvate = ADP + phosphoenolpyruvate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the addition of meso-diaminopimelic acid to the nucleotide precursor UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamate (UMAG) in the biosynthesis of bacterial cell-wall peptidoglycan. Is also able to use many meso-diaminopimelate analogs as substrates, although much less efficiently, but not L-lysine
- Gene Name:
- murE
- Uniprot ID:
- P22188
- Molecular weight:
- 53343
Reactions
| ATP + UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamate + meso-2,6-diaminoheptanedioate = ADP + phosphate + UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-gamma-glutamyl-meso-2,6-diamino-heptanedioate. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (ATP) activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + oxaloacetate = ADP + phosphoenolpyruvate + CO(2)
- Gene Name:
- pckA
- Uniprot ID:
- P22259
- Molecular weight:
- 59643
Reactions
| ATP + oxaloacetate = ADP + phosphoenolpyruvate + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in thymidine kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Phosphorylates both thymidine and deoxyuridine
- Gene Name:
- tdk
- Uniprot ID:
- P23331
- Molecular weight:
- 23456
Reactions
| ATP + thymidine = ADP + thymidine 5'-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in glycerate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + (R)-glycerate = ADP + 3-phospho-(R)- glycerate
- Gene Name:
- garK
- Uniprot ID:
- P23524
- Molecular weight:
- 39104
Reactions
| ATP + (R)-glycerate = ADP + 3-phospho-(R)-glycerate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Member of the two-component regulatory system phoQ/phoP involved in adaptation to low Mg(2+) environments and the control of acid resistance genes. In presence of low periplasmic Mg(2+) concentrations, phoQ functions as a membrane-associated protein kinase that undergoes autophosphorylation and subsequently transfers the phosphate to phoP, which results in the expression of phoP-activated genes (PAG) and repression of phoP-repressed genes (PRG). In presence of high periplasmic Mg(2+) concentrations, acts as a protein phosphatase that dephosphorylates phospho-phoP, which results in the repression of phoP-activated genes and may lead to expression of some phoP- repressed genes. Mediates magnesium influx to the cytosol by activation of mgtA. Promotes expression of the two- component regulatory system rstA/rstB and transcription of the hemL, mgrB, nagA, slyB, vboR and yrbL genes
- Gene Name:
- phoQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P23837
- Molecular weight:
- 55299
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ferric enterobactin. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- fepC
- Uniprot ID:
- P23878
- Molecular weight:
- 29784
- General function:
- Transcription
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of fructose to fructose-6- P. Has also low level glucokinase activity in vitro. Is not able to phosphorylate D-ribose, D-mannitol, D-sorbitol, inositol, and L-threonine
- Gene Name:
- mak
- Uniprot ID:
- P23917
- Molecular weight:
- 32500
Reactions
| ATP + D-fructose = ADP + D-fructose 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ligase activity
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of the acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase complex; first, biotin carboxylase catalyzes the carboxylation of the carrier protein and then the transcarboxylase transfers the carboxyl group to form malonyl-CoA
- Gene Name:
- accC
- Uniprot ID:
- P24182
- Molecular weight:
- 49320
Reactions
| ATP + biotin-[carboxyl-carrier-protein] + CO(2) = ADP + phosphate + carboxy-biotin-[carboxyl-carrier-protein]. |
| ATP + acetyl-CoA + HCO(3)(-) = ADP + phosphate + malonyl-CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
- Specific function:
- NadR is bifunctional; it interacts with pnuC at low internal NAD levels, permitting transport of NMN intact into the cell. As NAD levels increase within the cell, the affinity of nadR for the operator regions of nadA, nadB, and pncB increases, repressing the transcription of these genes
- Gene Name:
- nadR
- Uniprot ID:
- P27278
- Molecular weight:
- 47346
Reactions
| ATP + nicotinamide ribonucleotide = diphosphate + NAD(+). |
| ATP + N-ribosylnicotinamide = ADP + nicotinamide ribonucleotide. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Transfers the gamma-phosphate of ATP to the 4'-position of a tetraacyldisaccharide 1-phosphate intermediate (termed DS-1- P) to form tetraacyldisaccharide 1,4'-bis-phosphate (lipid IVA)
- Gene Name:
- lpxK
- Uniprot ID:
- P27300
- Molecular weight:
- 35589
Reactions
| ATP + (2-N,3-O-bis(3-hydroxytetradecanoyl)-beta-D-glucosaminyl)-(1->6)-(2-N,3-O-bis(3-hydroxytetradecanoyl)-beta-D-glucosaminyl phosphate) = ADP + (2-N,3-O-bis(3-hydroxytetradecanoyl)-4-O-phosphono-beta-D-glucosaminyl)-(1->6)-(2-N,3-O-bis(3-hydroxytetradecanoyl)-beta-D-glucosaminyl phosphate). |
- General function:
- Involved in acetate-CoA ligase activity
- Specific function:
- Enables the cell to use acetate during aerobic growth to generate energy via the TCA cycle, and biosynthetic compounds via the glyoxylate shunt. Acetylates CheY, the response regulator involved in flagellar movement and chemotaxis
- Gene Name:
- acs
- Uniprot ID:
- P27550
- Molecular weight:
- 72093
Reactions
| ATP + acetate + CoA = AMP + diphosphate + acetyl-CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- 2'-deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate + thioredoxin disulfide + H(2)O = ribonucleoside triphosphate + thioredoxin
- Gene Name:
- nrdD
- Uniprot ID:
- P28903
- Molecular weight:
- 80022
Reactions
| 2'-deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate + thioredoxin disulfide + H(2)O = ribonucleoside triphosphate + thioredoxin. |
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- ATP + 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-galactonate = ADP + 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-galactonate 6-phosphate
- Gene Name:
- dgoK
- Uniprot ID:
- P31459
- Molecular weight:
- 31373
Reactions
| ATP + 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-galactonate = ADP + 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-galactonate 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for D-methionine and the toxic methionine analog alpha-methyl- methionine. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- metI
- Uniprot ID:
- P31547
- Molecular weight:
- 23256
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- ATP + L-rhamnulose = ADP + L-rhamnulose 1- phosphate
- Gene Name:
- rhaB
- Uniprot ID:
- P32171
- Molecular weight:
- 54069
Reactions
| ATP + L-rhamnulose = ADP + L-rhamnulose 1-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Transcription
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of D-allose to D-allose 6- P. Has also low level glucokinase activity in vitro
- Gene Name:
- alsK
- Uniprot ID:
- P32718
- Molecular weight:
- 33821
Reactions
| ATP + D-allose = ADP + D-allose 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex AlsBAC involved in D-allose import. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- alsA
- Uniprot ID:
- P32721
- Molecular weight:
- 56744
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + monosaccharide(Out) = ADP + phosphate + monosaccharide(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes two reactions:the first one is the production of beta-formyl glycinamide ribonucleotide (GAR) from formate, ATP and beta GAR; the second, a side reaction, is the production of acetyl phosphate and ADP from acetate and ATP
- Gene Name:
- purT
- Uniprot ID:
- P33221
- Molecular weight:
- 42433
Reactions
| Formate + ATP + 5'-phospho-ribosylglycinamide = 5'-phosphoribosyl-N-formylglycinamide + ADP + diphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex CcmAB involved in the biogenesis of c-type cytochromes; once thought to export heme, this seems not to be the case, but its exact role is uncertain. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- ccmA
- Uniprot ID:
- P33931
- Molecular weight:
- 23053
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + heme(In) = ADP + phosphate + heme(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex FbpABC involved in Fe(3+) ions import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- fbpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P37009
- Molecular weight:
- 39059
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Fe(3+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + Fe(3+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Provides the precursors necessary for DNA synthesis. Catalyzes the biosynthesis of deoxyribonucleotides from the corresponding ribonucleotides. R2F contains the tyrosyl radical required for catalysis
- Gene Name:
- nrdF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37146
- Molecular weight:
- 36443
Reactions
| 2'-deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate + thioredoxin disulfide + H(2)O = ribonucleoside diphosphate + thioredoxin. |
- General function:
- Involved in cellular amino acid biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- ATP + NH(3) + CO(2) = ADP + carbamoyl phosphate
- Gene Name:
- arcC
- Uniprot ID:
- P37306
- Molecular weight:
- 31644
Reactions
| ATP + NH(3) + CO(2) = ADP + carbamoyl phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex XylFGH involved in xylose import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable). The XylFGH system can also transport ribose in absence of xylose
- Gene Name:
- xylG
- Uniprot ID:
- P37388
- Molecular weight:
- 56470
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + monosaccharide(Out) = ADP + phosphate + monosaccharide(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in export of lead, cadmium, zinc and mercury
- Gene Name:
- zntA
- Uniprot ID:
- P37617
- Molecular weight:
- 76839
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Cd(2+)(In) = ADP + phosphate + Cd(2+)(Out). |
| ATP + H(2)O + Zn(2+)(In) = ADP + phosphate + Zn(2+)(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- ATP + 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-gluconate = ADP + 6- phospho-2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-gluconate
- Gene Name:
- kdgK
- Uniprot ID:
- P37647
- Molecular weight:
- 33962
Reactions
| ATP + 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-gluconate = ADP + 6-phospho-2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-gluconate. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of L-xylulose and 3-keto- L-gulonate. Is involved in L-lyxose utilization via xylulose, and may also be involved in the utilization of 2,3-diketo-L-gulonate
- Gene Name:
- lyx
- Uniprot ID:
- P37677
- Molecular weight:
- 55155
Reactions
| ATP + L-xylulose = ADP + L-xylulose 5-phosphate. |
| ATP + 3-dehydro-L-gulonate = ADP + 3-dehydro-L-gulonate 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in shikimate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + D-gluconate = ADP + 6-phospho-D- gluconate
- Gene Name:
- idnK
- Uniprot ID:
- P39208
- Molecular weight:
- 21004
Reactions
| ATP + D-gluconate = ADP + 6-phospho-D-gluconate. |
- General function:
- Involved in GTPase activity
- Specific function:
- May play a role in 30S ribosomal subunit biogenesis. Unusual circulary permuted GTPase that catalyzes rapid hydrolysis of GTP with a slow catalytic turnover. Dispensible for viability, but important for overall fitness. The intrinsic GTPase activity is stimulated by the presence of 30S (160-fold increase in kcat) or 70S (96 fold increase in kcat) ribosomes (PubMed:14973029). The GTPase is inhibited by aminoglycoside antibiotics such as neomycin and paromycin (PubMed:15466596) streptomycin and spectinomycin (PubMed:15828870). This inhibition is not due to competition for binding sites on the 30S or 70S ribosome (PubMed:15828870)
- Gene Name:
- rsgA
- Uniprot ID:
- P39286
- Molecular weight:
- 39193
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- Provides the precursors necessary for DNA synthesis. Catalyzes the biosynthesis of deoxyribonucleotides from the corresponding ribonucleotides. R1E contains the binding sites for both substrates and allosteric effectors and carries out the actual reduction of the ribonucleotide
- Gene Name:
- nrdE
- Uniprot ID:
- P39452
- Molecular weight:
- 80478
Reactions
| 2'-deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate + thioredoxin disulfide + H(2)O = ribonucleoside diphosphate + thioredoxin. |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxal kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Phosphorylates B6 vitamers; functions in a salvage pathway. Uses pyridoxal, pyridoxine, and pyridoxamine as substrates
- Gene Name:
- pdxK
- Uniprot ID:
- P40191
- Molecular weight:
- 30847
Reactions
| ATP + pyridoxal = ADP + pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc) to ManNAc-6-P. Has also low level glucokinase activity in vitro
- Gene Name:
- nanK
- Uniprot ID:
- P45425
- Molecular weight:
- 29644
Reactions
| ATP + N-acyl-D-mannosamine = ADP + N-acyl-D-mannosamine 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Phosphorylates fructoselysine to yield fructoselysine 6- phosphate
- Gene Name:
- frlD
- Uniprot ID:
- P45543
- Molecular weight:
- 28332
Reactions
| ATP + fructoselysine = ADP + fructoselysine 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in shikimate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + D-gluconate = ADP + 6-phospho-D- gluconate
- Gene Name:
- gntK
- Uniprot ID:
- P46859
- Molecular weight:
- 19543
Reactions
| ATP + D-gluconate = ADP + 6-phospho-D-gluconate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Probable catalytic subunit of a protein translocase for flagellum-specific export, or a proton translocase involved in local circuits at the flagellum. May be involved in a specialized protein export pathway that proceeds without signal peptide cleavage
- Gene Name:
- fliI
- Uniprot ID:
- P52612
- Molecular weight:
- 49315
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + H(+)(In) = ADP + phosphate + H(+)(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in protein binding
- Specific function:
- Essential for recycling GMP and indirectly, cGMP
- Gene Name:
- gmk
- Uniprot ID:
- P60546
- Molecular weight:
- 23593
Reactions
| ATP + GMP = ADP + GDP. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of the position 2 hydroxy group of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-D-erythritol. Phosphorylates isopentenyl phosphate at low rates. Also acts on isopentenol, and, much less efficiently, dimethylallyl alcohol. Dimethylallyl monophosphate does not serve as a substrate
- Gene Name:
- ispE
- Uniprot ID:
- P62615
- Molecular weight:
- 30925
Reactions
| ATP + 4-(cytidine 5'-diphospho)-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol = ADP + 2-phospho-4-(cytidine 5'-diphospho)-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex MalEFGK involved in maltose/maltodextrin import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- malK
- Uniprot ID:
- P68187
- Molecular weight:
- 40990
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + maltose(Out) = ADP + phosphate + maltose(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Key component of the F(0) channel; it plays a direct role in translocation across the membrane. A homomeric c-ring of 10 subunits forms the central stalk rotor element with the F(1) delta and epsilon subunits
- Gene Name:
- atpE
- Uniprot ID:
- P68699
- Molecular weight:
- 8256
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reversible transfer of the terminal phosphate group between ATP and AMP. This small ubiquitous enzyme involved in the energy metabolism and nucleotide synthesis, is essential for maintenance and cell growth
- Gene Name:
- adk
- Uniprot ID:
- P69441
- Molecular weight:
- 23586
Reactions
| ATP + AMP = 2 ADP. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex PotABCD involved in spermidine/putrescine import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- potA
- Uniprot ID:
- P69874
- Molecular weight:
- 43028
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + polyamine(Out) = ADP + phosphate + polyamine(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Provides the precursors necessary for DNA synthesis. Catalyzes the biosynthesis of deoxyribonucleotides from the corresponding ribonucleotides. R2 contains the tyrosyl radical required for catalysis
- Gene Name:
- nrdB
- Uniprot ID:
- P69924
- Molecular weight:
- 43517
Reactions
| 2'-deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate + thioredoxin disulfide + H(2)O = ribonucleoside diphosphate + thioredoxin. |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of thiamine to thiamine phosphate
- Gene Name:
- thiK
- Uniprot ID:
- P75948
- Molecular weight:
- 32397
Reactions
| ATP + thiamine = ADP + thiamine phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in N-acetylglucosamine kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc) derived from cell-wall degradation, yielding GlcNAc-6-P. Has also low level glucokinase activity in vitro
- Gene Name:
- nagK
- Uniprot ID:
- P75959
- Molecular weight:
- 33042
Reactions
| ATP + N-acetyl-D-glucosamine = ADP + N-acetyl-D-glucosamine 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in diacylglycerol kinase activity
- Specific function:
- In vitro phosphorylates phosphatidylglycerol but not diacylglycerol; the in vivo substrate is unknown
- Gene Name:
- yegS
- Uniprot ID:
- P76407
- Molecular weight:
- 32038
- General function:
- Involved in phosphomethylpyrimidine kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of hydroxymethylpyrimidine phosphate (HMP-P) to HMP-PP, and of HMP to HMP-P. Shows no activity with pyridoxal, pyridoxamine or pyridoxine
- Gene Name:
- thiD
- Uniprot ID:
- P76422
- Molecular weight:
- 28633
Reactions
| ATP + 4-amino-5-hydroxymethyl-2-methylpyrimidine = ADP + 4-amino-5-phosphonooxymethyl-2-methylpyrimidine. |
| ATP + 4-amino-2-methyl-5-phosphomethylpyrimidine = ADP + 4-amino-2-methyl-5-diphosphomethylpyrimidine. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydroxyethylthiazole kinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + 4-methyl-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)thiazole = ADP + 4-methyl-5-(2-phosphonooxyethyl)thiazole
- Gene Name:
- thiM
- Uniprot ID:
- P76423
- Molecular weight:
- 27339
Reactions
| ATP + 4-methyl-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)thiazole = ADP + 4-methyl-5-(2-phosphonooxyethyl)thiazole. |
- General function:
- Involved in pyridoxal kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Phosphorylates B6 vitamers; functions in a salvage pathway. Uses pyridoxamine, but has negligible activity toward pyridoxal and pyridoxine as substrates
- Gene Name:
- pdxY
- Uniprot ID:
- P77150
- Molecular weight:
- 31322
Reactions
| ATP + pyridoxal = ADP + pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in glycerate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + (R)-glycerate = ADP + 3-phospho-(R)- glycerate
- Gene Name:
- glxK
- Uniprot ID:
- P77364
- Molecular weight:
- 38734
Reactions
| ATP + (R)-glycerate = ADP + 3-phospho-(R)-glycerate. |
- General function:
- Involved in metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Cysteine desulfurases mobilize the sulfur from L- cysteine to yield L-alanine, an essential step in sulfur metabolism for biosynthesis of a variety of sulfur-containing biomolecules. Component of the suf operon, which is activated and required under specific conditions such as oxidative stress and iron limitation. Acts as a potent selenocysteine lyase in vitro, that mobilizes selenium from L-selenocysteine. Selenocysteine lyase activity is however unsure in vivo
- Gene Name:
- sufS
- Uniprot ID:
- P77444
- Molecular weight:
- 44433
Reactions
| L-cysteine + acceptor = L-alanine + S-sulfanyl-acceptor. |
| L-selenocysteine + reduced acceptor = selenide + L-alanine + acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Member of the two-component regulatory system cusS/cusR. Copper ion sensor. Could also be a silver ion sensor. Probably activates cusR by phosphorylation
- Gene Name:
- cusS
- Uniprot ID:
- P77485
- Molecular weight:
- 53738
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the specific phosphorylation of 1,6-anhydro-N- acetylmuramic acid (anhMurNAc) with the simultaneous cleavage of the 1,6-anhydro ring, generating MurNAc-6-P. Is required for the utilization of anhMurNAc either imported from the medium or derived from its own cell wall murein, and thus plays a role in cell wall recycling
- Gene Name:
- anmK
- Uniprot ID:
- P77570
- Molecular weight:
- 39496
Reactions
| ATP + 1,6-anhydro-N-acetyl-beta-muramate + H(2)O = ADP + N-acetylmuramate 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in cellular amino acid biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- yahI
- Uniprot ID:
- P77624
- Molecular weight:
- 33931
- General function:
- Involved in glutamate-ammonia ligase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the breakdown of putrescine via the biosynthesis of gamma-L-glutamylputrescine
- Gene Name:
- puuA
- Uniprot ID:
- P78061
- Molecular weight:
- 53177
Reactions
| ATP + L-glutamate + putrescine = ADP + phosphate + gamma-L-glutamylputrescine. |
- General function:
- Involved in cellular amino acid biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- yqeA
- Uniprot ID:
- Q46807
- Molecular weight:
- 33071
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in copper export. May also be involved in silver export
- Gene Name:
- copA
- Uniprot ID:
- Q59385
- Molecular weight:
- 87872
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Cu(+)(In) = ADP + phosphate + Cu(+)(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- ytfR
- Uniprot ID:
- Q6BEX0
- Molecular weight:
- 55259
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring glycosyl groups
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes heptose transfer to the lipopolysaccharide core. It transfers a heptose, called heptose(III), to the heptose(II) of the inner core
- Gene Name:
- rfaQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P25742
- Molecular weight:
- 38730
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of heptose(II) of the outer membrane lipopolysaccharide core
- Gene Name:
- rfaY
- Uniprot ID:
- P27240
- Molecular weight:
- 27461
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring glycosyl groups
- Specific function:
- Adds the terminal N-acetyl-D-glucosamine group on the glucose(II) group of LPS
- Gene Name:
- waaU
- Uniprot ID:
- P27242
- Molecular weight:
- 41729
Reactions
| UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine + lipopolysaccharide = UDP + N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyllipopolysaccharide. |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring glycosyl groups
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- rfaF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37692
- Molecular weight:
- 39042
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of heptose(I) of the outer membrane lipopolysaccharide core
- Gene Name:
- rfaP
- Uniprot ID:
- P25741
- Molecular weight:
- 30872
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring glycosyl groups
- Specific function:
- Heptose transfer to the lipopolysaccharide core. It transfers the innnermost heptose to [4'-P](3-deoxy-D-manno- octulosonic acid)2-IVA
- Gene Name:
- rfaC
- Uniprot ID:
- P24173
- Molecular weight:
- 35544
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport
- Gene Name:
- artI
- Uniprot ID:
- P30859
- Molecular weight:
- 26929
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport. Binds L-arginine with high affinity
- Gene Name:
- artJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P30860
- Molecular weight:
- 26829
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- artQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE34
- Molecular weight:
- 26217
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Has low ATPase activity. The sufBCD complex acts synergistically with sufE to stimulate the cysteine desulfurase activity of sufS. The sufBCD complex contributes to the assembly or repair of oxygen-labile iron-sulfur clusters under oxidative stress. May facilitate iron uptake from extracellular iron chelators under iron limitation
- Gene Name:
- sufC
- Uniprot ID:
- P77499
- Molecular weight:
- 27582
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system ydcSTUV
- Gene Name:
- ydcS
- Uniprot ID:
- P76108
- Molecular weight:
- 42295
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Probably part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system ydcSTUV. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- ydcT
- Uniprot ID:
- P77795
- Molecular weight:
- 37040
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system ydcSTUV; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ydcU
- Uniprot ID:
- P77156
- Molecular weight:
- 34360
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system ydcSTUV; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ydcV
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFR9
- Molecular weight:
- 28722
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- yjfF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37772
- Molecular weight:
- 34977
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- ytfQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P39325
- Molecular weight:
- 34344
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ytfT
- Uniprot ID:
- P39328
- Molecular weight:
- 35659
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for maltose; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- malF
- Uniprot ID:
- P02916
- Molecular weight:
- 57013
- General function:
- Involved in cobalamin transport
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex BtuCDF involved in vitamin B12 import. Involved in the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- btuC
- Uniprot ID:
- P06609
- Molecular weight:
- 34949
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex fhuCDB involved in iron(3+)-hydroxamate import. Responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fhuB
- Uniprot ID:
- P06972
- Molecular weight:
- 70422
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for phosphate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- pstA
- Uniprot ID:
- P07654
- Molecular weight:
- 32321
- General function:
- Involved in lipopolysaccharide transport
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex lptBFG involved in the translocation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from the inner membrane to the outer membrane
- Gene Name:
- lptG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ADC6
- Molecular weight:
- 39618
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for L-arabinose. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- araH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE26
- Molecular weight:
- 34211
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- artM
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE30
- Molecular weight:
- 24914
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP (TC 3.A.1.6.1) involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- cysW
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEB0
- Molecular weight:
- 32537
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- dppB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEF8
- Molecular weight:
- 37497
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- dppC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEG1
- Molecular weight:
- 32308
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for glutamine; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- glnP
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEQ6
- Molecular weight:
- 24364
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for aspartate/glutamate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- gltJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AER3
- Molecular weight:
- 27502
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for aspartate/glutamate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- gltK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AER5
- Molecular weight:
- 24914
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for histidine; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- hisM
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEU3
- Molecular weight:
- 26870
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for branched-chain amino acids. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrates across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- livH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEX7
- Molecular weight:
- 32982
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for molybdenum; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- modB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AF01
- Molecular weight:
- 24939
- General function:
- Involved in lipopolysaccharide-transporting ATPase acti
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex lptBFG involved in the translocation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from the inner membrane to the outer membrane
- Gene Name:
- lptF
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AF98
- Molecular weight:
- 40357
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a nickel transport system, probably translocates nickel through the bacterial inner membrane
- Gene Name:
- nikC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFA9
- Molecular weight:
- 30362
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for oligopeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- oppB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFH2
- Molecular weight:
- 33443
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for oligopeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- oppC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFH6
- Molecular weight:
- 33022
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine and spermidine
- Gene Name:
- potB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFK4
- Molecular weight:
- 31062
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine and spermidine
- Gene Name:
- potC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFK6
- Molecular weight:
- 29111
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine
- Gene Name:
- potI
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFL1
- Molecular weight:
- 30540
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for phosphate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- pstC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGH8
- Molecular weight:
- 34121
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ribose. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- rbsC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGI1
- Molecular weight:
- 33452
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for D-xylose. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- xylH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGI4
- Molecular weight:
- 41030
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for sn-glycerol-3-phosphate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ugpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P10905
- Molecular weight:
- 33264
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for sn-glycerol-3-phosphate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ugpE
- Uniprot ID:
- P10906
- Molecular weight:
- 31499
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a multicomponent binding-protein-dependent transport system for glycine betaine/L-proline
- Gene Name:
- proW
- Uniprot ID:
- P14176
- Molecular weight:
- 37619
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for citrate-dependent Fe(3+). Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fecD
- Uniprot ID:
- P15029
- Molecular weight:
- 34131
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for citrate-dependent Fe(3+). Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fecC
- Uniprot ID:
- P15030
- Molecular weight:
- 34892
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP (TC 3.A.1.6.1) involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- cysU
- Uniprot ID:
- P16701
- Molecular weight:
- 30292
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for branched-chain amino acids. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrates across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- livM
- Uniprot ID:
- P22729
- Molecular weight:
- 46269
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for galactoside. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- mglC
- Uniprot ID:
- P23200
- Molecular weight:
- 35550
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ferric enterobactin. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fepD
- Uniprot ID:
- P23876
- Molecular weight:
- 33871
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ferric enterobactin. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fepG
- Uniprot ID:
- P23877
- Molecular weight:
- 34910
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Somehow involved in the cytochrome D branch of aerobic respiration. Seems to be a component of a transport system
- Gene Name:
- cydC
- Uniprot ID:
- P23886
- Molecular weight:
- 62920
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Somehow involved in the cytochrome D branch of aerobic respiration. Seems to be a component of a transport system
- Gene Name:
- cydD
- Uniprot ID:
- P29018
- Molecular weight:
- 65055
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine
- Gene Name:
- potH
- Uniprot ID:
- P31135
- Molecular weight:
- 35489
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex thiBPQ involved in thiamine import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- thiP
- Uniprot ID:
- P31549
- Molecular weight:
- 59532
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system AlsBAC for D-allose; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- alsC
- Uniprot ID:
- P32720
- Molecular weight:
- 34315
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- yehW
- Uniprot ID:
- P33359
- Molecular weight:
- 25514
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- yehY
- Uniprot ID:
- P33361
- Molecular weight:
- 41138
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a nickel transport system, probably translocates nickel through the bacterial inner membrane
- Gene Name:
- nikB
- Uniprot ID:
- P33591
- Molecular weight:
- 35248
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for histidine; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- hisQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P52094
- Molecular weight:
- 24649
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in lipid A export and possibly also in glycerophospholipid export and for biogenesis of the outer membrane. Transmembrane domains (TMD) form a pore in the inner membrane and the ATP-binding domain (NBD) is responsible for energy generation
- Gene Name:
- msbA
- Uniprot ID:
- P60752
- Molecular weight:
- 64460
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for maltose; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- malG
- Uniprot ID:
- P68183
- Molecular weight:
- 32225
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex gsiABCD involved in glutathione import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- gsiC
- Uniprot ID:
- P75798
- Molecular weight:
- 34066
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex gsiABCD involved in glutathione import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- gsiD
- Uniprot ID:
- P75799
- Molecular weight:
- 33238
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system for aliphatic sulfonates. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ssuC
- Uniprot ID:
- P75851
- Molecular weight:
- 28925
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ddpABCDF, which is probably involved in D,D-dipeptide transport. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ddpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P77308
- Molecular weight:
- 37345
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ddpABCDF, which is probably involved in D,D-dipeptide transport. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ddpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P77463
- Molecular weight:
- 31971
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system for taurine. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- tauC
- Uniprot ID:
- Q47539
- Molecular weight:
- 29812
- General function:
- Involved in phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the ADP transfer to D-glycero-D-manno-heptose 1-phosphate, yielding ADP-D,D-heptose
- Gene Name:
- hldE
- Uniprot ID:
- P76658
- Molecular weight:
- 51050
Reactions
| ATP + D-glycero-beta-D-manno-heptose 7-phosphate = ADP + D-glycero-beta-D-manno-heptose 1,7-bisphosphate. |
| ATP + D-glycero-beta-D-manno-heptose 1-phosphate = diphosphate + ADP-D-glycero-beta-D-manno-heptose. |
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a nickel transport system, probably represents the nickel binder
- Gene Name:
- nikA
- Uniprot ID:
- P33590
- Molecular weight:
- 58718
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- This protein specifically binds sulfate and is involved in its transmembrane transport
- Gene Name:
- sbp
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG78
- Molecular weight:
- 36659
- General function:
- Involved in GTP binding
- Specific function:
- GTP-driven Fe(2+) uptake system
- Gene Name:
- feoB
- Uniprot ID:
- P33650
- Molecular weight:
- 84473
- General function:
- Involved in intramolecular lyase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the interconversion of beta-pyran and beta- furan forms of D-ribose. It also catalyzes the conversion between beta-allofuranose and beta-allopyranose
- Gene Name:
- rbsD
- Uniprot ID:
- P04982
- Molecular weight:
- 15292
Reactions
| Beta-D-ribopyranose = beta-D-ribofuranose. |
| Beta-D-allopyranose = beta-D-allofuranose. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex MetNIQ involved in methionine import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable). It has also been shown to be involved in formyl-L-methionine transport
- Gene Name:
- metN
- Uniprot ID:
- P30750
- Molecular weight:
- 37788
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ddpABCDF, which is probably involved in D,D-dipeptide transport. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- ddpD
- Uniprot ID:
- P77268
- Molecular weight:
- 36100
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for glutamine. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- glnQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P10346
- Molecular weight:
- 26731
- General function:
- Involved in sulfur compound metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system for aliphatic sulfonates. Putative binding protein
- Gene Name:
- ssuA
- Uniprot ID:
- P75853
- Molecular weight:
- 34557
- General function:
- Involved in maltose transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity maltose membrane transport system malEFGK. Initial receptor for the active transport of and chemotaxis toward maltooligosaccharides
- Gene Name:
- malE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEX9
- Molecular weight:
- 43387
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Binds ferrienterobactin; part of the binding-protein- dependent transport system for uptake of ferrienterobactin
- Gene Name:
- fepB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEL6
- Molecular weight:
- 34283
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for oligopeptides. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- oppF
- Uniprot ID:
- P77737
- Molecular weight:
- 37197
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- ygfA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AC28
- Molecular weight:
- 21105
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity D-xylose membrane transport system. Binds with high affinity to xylose
- Gene Name:
- xylF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37387
- Molecular weight:
- 35734
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ZnuABC involved in zinc import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- znuC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9X1
- Molecular weight:
- 27867
- General function:
- Involved in iron-sulfur cluster assembly
- Specific function:
- The sufBCD complex acts synergistically with sufE to stimulate the cysteine desulfurase activity of sufS. The sufBCD complex contributes to the assembly or repair of oxygen-labile iron-sulfur clusters under oxidative stress. May facilitate iron uptake from extracellular iron chelators under iron limitation
- Gene Name:
- sufB
- Uniprot ID:
- P77522
- Molecular weight:
- 54745
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- dppD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAG0
- Molecular weight:
- 35844
- General function:
- Inorganic ion transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- cyaY
- Uniprot ID:
- P27838
- Molecular weight:
- 12231
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Essential for the uptake of the murein peptide L-alanyl- gamma-D-glutamyl-meso-diaminopimelate. Also transports some alpha- linked peptides such as Pro-Phe-Lys with low affinity. The transport is effected by the oligopeptide permease system
- Gene Name:
- mppA
- Uniprot ID:
- P77348
- Molecular weight:
- 59900
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- wcaK
- Uniprot ID:
- P71242
- Molecular weight:
- 47343
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Could catalyze the transfer of CoA to carnitine, generating the initial carnitinyl-CoA needed for the CaiB reaction cycle
- Gene Name:
- caiC
- Uniprot ID:
- P31552
- Molecular weight:
- 58559
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- This periplasmic binding protein is involved in an arginine transport system. ArgT and histidine-binding protein J (hisJ) interact with a common membrane-bound receptor, hisP
- Gene Name:
- argT
- Uniprot ID:
- P09551
- Molecular weight:
- 27991
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex BtuCDF involved in vitamin B12 import. Binds vitamin B12 and delivers it to the periplasmic surface of BtuC
- Gene Name:
- btuF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37028
- Molecular weight:
- 29367
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system AlsBAC for D-allose
- Gene Name:
- alsB
- Uniprot ID:
- P39265
- Molecular weight:
- 32910
- General function:
- Involved in FMN binding
- Specific function:
- Low-potential electron donor to a number of redox enzymes (Potential). Involved in the reactivation of inactive cob(II)alamin in methionine synthase
- Gene Name:
- fldA
- Uniprot ID:
- P61949
- Molecular weight:
- 19737
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex gsiABCD involved in glutathione import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- gsiA
- Uniprot ID:
- P75796
- Molecular weight:
- 69113
- General function:
- Involved in protein complex assembly
- Specific function:
- Required for the export of heme to the periplasm for the biogenesis of c-type cytochromes
- Gene Name:
- ccmC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABM1
- Molecular weight:
- 27885
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP (TC 3.A.1.6.1) involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. This protein specifically binds thiosulfate and is involved in its transmembrane transport
- Gene Name:
- cysP
- Uniprot ID:
- P16700
- Molecular weight:
- 37614
- General function:
- Involved in glycerone kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Dihydroxyacetone binding subunit of the dihydroxyacetone kinase, which is responsible for phosphorylating dihydroxyacetone. Binds covalently dihydroxyacetone in hemiaminal linkage. Acts also as a corepressor of dhaR by binding to its sensor domain, in the absence of dihydroxyacetone
- Gene Name:
- dhaK
- Uniprot ID:
- P76015
- Molecular weight:
- 38215
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- yehX
- Uniprot ID:
- P33360
- Molecular weight:
- 34424
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of the oligopeptide permease, a binding protein-dependent transport system, it binds peptides up to five amino acids long with high affinity
- Gene Name:
- oppA
- Uniprot ID:
- P23843
- Molecular weight:
- 60899
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex lptBFG involved in the translocation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from the inner membrane to the outer membrane. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- lptB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9V1
- Molecular weight:
- 26800
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- dppF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37313
- Molecular weight:
- 37560
- General function:
- Involved in phosphate ion binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex pstSACB involved in phosphate import
- Gene Name:
- pstS
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG82
- Molecular weight:
- 37024
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Participates in cysteine desulfuration mediated by sufS. Cysteine desulfuration mobilizes sulfur from L-cysteine to yield L-alanine and constitutes an essential step in sulfur metabolism for biosynthesis of a variety of sulfur-containing biomolecules. Functions as a sulfur acceptor for sufS, by mediating the direct transfer of the sulfur atom from the S-sulfanylcysteine of sufS, an intermediate product of cysteine desulfuration process. Together with the sufBCD complex, it thereby enhances up to 50- fold, the cysteine desulfurase activity of sufS. Component of the suf operon, which is activated and required under specific conditions such as oxidative stress and iron limitation. Does not affect the selenocysteine lyase activity of sufS
- Gene Name:
- sufE
- Uniprot ID:
- P76194
- Molecular weight:
- 15800
- General function:
- Involved in heme transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the export of heme to the periplasm for the biogenesis of c-type cytochromes
- Gene Name:
- ccmB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABL8
- Molecular weight:
- 23618
- General function:
- Involved in lipopolysaccharide transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the translocation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from the inner membrane to the outer membrane
- Gene Name:
- lptC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ADV9
- Molecular weight:
- 21703
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Monothiol glutaredoxin involved in the biogenesis of iron-sulfur clusters (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- grxD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AC69
- Molecular weight:
- 12879
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity L-arabinose membrane transport system. Binds with high affinity to arabinose, but can also bind D-galactose (approximately 2-fold reduction) and D- fucose (approximately 40-fold reduction)
- Gene Name:
- araF
- Uniprot ID:
- P02924
- Molecular weight:
- 35541
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ThiBPQ involved in thiamine import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- thiQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P31548
- Molecular weight:
- 24999
- General function:
- Involved in transport
- Specific function:
- Required for the export of heme to the periplasm for the biogenesis of c-type cytochromes (Potential)
- Gene Name:
- ccmD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABM5
- Molecular weight:
- 7745
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- artP
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAF6
- Molecular weight:
- 27022
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Member of a multicomponent binding-protein-dependent transport system (the proU transporter) which serves as the glycine betaine/L-proline transporter
- Gene Name:
- proX
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFM2
- Molecular weight:
- 36022
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for glutamate and aspartate. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- gltL
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAG3
- Molecular weight:
- 26661
- General function:
- Involved in lipopolysaccharide binding
- Specific function:
- Required for the translocation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from the inner membrane to the outer membrane. May act as a chaperone that facilitates LPS transfer across the aquaeous environment of the periplasm. Interacts specifically with the lipid A domain of LPS
- Gene Name:
- lptA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ADV1
- Molecular weight:
- 20127
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity D-ribose membrane transport system and also serves as the primary chemoreceptor for chemotaxis
- Gene Name:
- rbsB
- Uniprot ID:
- P02925
- Molecular weight:
- 30950
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Component of the leucine-specific transport system
- Gene Name:
- livG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9S7
- Molecular weight:
- 28427
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the high-affinity histidine permease, a binding-protein-dependent transport system. The other components are proteins hisQ, hisM, and hisP
- Gene Name:
- hisJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEU0
- Molecular weight:
- 28483
- General function:
- Energy production and conversion
- Specific function:
- A possible function for this protein is to guide the assembly of the membrane sector of the ATPase enzyme complex
- Gene Name:
- atpI
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABC0
- Molecular weight:
- 13632
- General function:
- Involved in arsenite transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in arsenical resistance. Thought to form the channel of an arsenite pump
- Gene Name:
- arsB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AB93
- Molecular weight:
- 45497
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid transport
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of the leucine, isoleucine, valine, (threonine) transport system, which is one of the two periplasmic binding protein-dependent transport systems of the high-affinity transport of the branched-chain amino acids
- Gene Name:
- livJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AD96
- Molecular weight:
- 39076
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity zinc uptake transport system
- Gene Name:
- znuB
- Uniprot ID:
- P39832
- Molecular weight:
- 27728
- General function:
- Involved in protein-heme linkage
- Specific function:
- Heme chaperone required for the biogenesis of c-type cytochromes. Transiently binds heme delivered by CcmC and transfers the heme to apo-cytochromes in a process facilitated by CcmF and CcmH
- Gene Name:
- ccmE
- Uniprot ID:
- P69490
- Molecular weight:
- 17698
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex NikABCDE involved in nickel import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- nikD
- Uniprot ID:
- P33593
- Molecular weight:
- 26820
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Ni(2+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + Ni(2+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Component of the leucine-specific transport system
- Gene Name:
- livF
- Uniprot ID:
- P22731
- Molecular weight:
- 26310
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ddpABCDF, which is probably involved in D,D-dipeptide transport. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- ddpF
- Uniprot ID:
- P77622
- Molecular weight:
- 34621
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- The disulfide bond functions as an electron carrier in the glutathione-dependent synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides by the enzyme ribonucleotide reductase. In addition, it is also involved in reducing some disulfides in a coupled system with glutathione reductase
- Gene Name:
- grxC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AC62
- Molecular weight:
- 9137
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Binds citrate-dependent Fe(3+); part of the binding- protein-dependent transport system for uptake of citrate-dependent Fe(3+)
- Gene Name:
- fecB
- Uniprot ID:
- P15028
- Molecular weight:
- 33146
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Dipeptide-binding protein of a transport system that can be subject to osmotic shock. DppA is also required for peptide chemotaxis
- Gene Name:
- dppA
- Uniprot ID:
- P23847
- Molecular weight:
- 60293
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- This protein is involved in the active transport of galactose and glucose. It plays a role in the chemotaxis towards the two sugars by interacting with the trg chemoreceptor
- Gene Name:
- mglB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEE5
- Molecular weight:
- 35712
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex NikABCDE involved in nickel import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- nikE
- Uniprot ID:
- P33594
- Molecular weight:
- 29721
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Ni(2+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + Ni(2+)(In). |
- General function:
- Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones
- Specific function:
- Probable chaperone. Has ATPase activity. Not stimulated by dnaJ
- Gene Name:
- hscC
- Uniprot ID:
- P77319
- Molecular weight:
- 61986
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- kdpF
- Uniprot ID:
- P36937
- Molecular weight:
- 3072
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- sn-glycerol-3-phosphate and glycerophosphoryl diester- binding protein interacts with the binding protein-dependent transport system ugpACE
- Gene Name:
- ugpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG80
- Molecular weight:
- 48448
- General function:
- Involved in glycerone kinase activity
- Specific function:
- ADP-binding subunit of the dihydroxyacetone kinase, which is responsible for phosphorylating dihydroxyacetone. DhaL- ADP receives a phosphoryl group from dhaM and transmits it to dihydroxyacetone. DhaL-ADP acts also as a coactivator by binding to the sensor domain of dhaR. DhaL-ATP is inactive
- Gene Name:
- dhaL
- Uniprot ID:
- P76014
- Molecular weight:
- 22632
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex TauABC involved in taurine import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- tauB
- Uniprot ID:
- Q47538
- Molecular weight:
- 28297
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + taurine(Out) = ADP + phosphate + taurine(In). |
- General function:
- Inorganic ion transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of a D-methionine permease, a binding protein-dependent, ATP-driven transport system
- Gene Name:
- metQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P28635
- Molecular weight:
- 29432
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ModABC involved in molybdenum import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- modC
- Uniprot ID:
- P09833
- Molecular weight:
- 39102
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + molybdate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + molybdate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules
- Gene Name:
- osmF
- Uniprot ID:
- P33362
- Molecular weight:
- 32609
- General function:
- Involved in argininosuccinate synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the ATP-dependent conversion of 7-carboxy-7- deazaguanine (CDG) to 7-cyano-7-deazaguanine (preQ(0))
- Gene Name:
- queC
- Uniprot ID:
- P77756
- Molecular weight:
- 25514
Reactions
| 7-carboxy-7-carbaguanine + NH(3) + ATP = 7-cyano-7-carbaguanine + ADP + phosphate + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for oligopeptides. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- oppD
- Uniprot ID:
- P76027
- Molecular weight:
- 37188
- General function:
- Involved in metal ion binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity zinc uptake transport system
- Gene Name:
- znuA
- Uniprot ID:
- P39172
- Molecular weight:
- 33777
- General function:
- Involved in iron-sulfur cluster assembly
- Specific function:
- The sufBCD complex acts synergistically with sufE to stimulate the cysteine desulfurase activity of sufS. The sufBCD complex contributes to the assembly or repair of oxygen-labile iron-sulfur clusters under oxidative stress. May facilitate iron uptake from extracellular iron chelators under iron limitation. Required for the stability of the fhuF protein
- Gene Name:
- sufD
- Uniprot ID:
- P77689
- Molecular weight:
- 46822
- General function:
- Amino acid transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for putrescine. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- potG
- Uniprot ID:
- P31134
- Molecular weight:
- 41930
- General function:
- Involved in protein binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in reducing some disulfides in a coupled system with glutathione reductase. Does not act as hydrogen donor for ribonucleotide reductase
- Gene Name:
- grxB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AC59
- Molecular weight:
- 24350
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex gsiABCD involved in glutathione import
- Gene Name:
- gsiB
- Uniprot ID:
- P75797
- Molecular weight:
- 56470
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system for taurine
- Gene Name:
- tauA
- Uniprot ID:
- Q47537
- Molecular weight:
- 34266
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex SsuABC involved in aliphatic sulfonates import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- ssuB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAI1
- Molecular weight:
- 27738
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- The disulfide bond functions as an electron carrier in the glutathione-dependent synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides by the enzyme ribonucleotide reductase. In addition, it is also involved in reducing some disulfides in a coupled system with glutathione reductase
- Gene Name:
- grxA
- Uniprot ID:
- P68688
- Molecular weight:
- 9685
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Participates in various redox reactions through the reversible oxidation of its active center dithiol to a disulfide and catalyzes dithiol-disulfide exchange reactions
- Gene Name:
- trxA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AA25
- Molecular weight:
- 11807
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for glutamate and aspartate. Binds to both aspartate and glutamate
- Gene Name:
- gltI
- Uniprot ID:
- P37902
- Molecular weight:
- 33420
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid transport
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of the leucine-specific transport system, which is one of the two periplasmic binding protein-dependent transport systems of the high-affinity transport of the branched-chain amino acids in E.coli
- Gene Name:
- livK
- Uniprot ID:
- P04816
- Molecular weight:
- 39378
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a glutamine-transport system glnHPQ
- Gene Name:
- glnH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEQ3
- Molecular weight:
- 27190
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Reutilizes the intact tripeptide L-alanyl-gamma-D- glutamyl-meso-diaminopimelate by linking it to UDP-N-acetylmuramic acid
- Gene Name:
- mpl
- Uniprot ID:
- P37773
- Molecular weight:
- 49874
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine. Polyamine binding protein
- Gene Name:
- potF
- Uniprot ID:
- P31133
- Molecular weight:
- 40839
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ddpABCDF, which is probably involved in D,D-dipeptide transport
- Gene Name:
- ddpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P76128
- Molecular weight:
- 57641
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine and spermidine. Polyamine binding protein
- Gene Name:
- potD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFK9
- Molecular weight:
- 38867
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex fhuCDB involved in iron(3+)-hydroxamate import. Binds the iron(3+)-hydroxamate complex and transfers it to the membrane-bound permease. Required for the transport of all iron(3+)-hydroxamate siderophores such as ferrichrome, gallichrome, desferrioxamine, coprogen, aerobactin, shizokinen, rhodotorulic acid and the antibiotic albomycin
- Gene Name:
- fhuD
- Uniprot ID:
- P07822
- Molecular weight:
- 32998
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex thiBPQ involved in thiamine import
- Gene Name:
- thiB
- Uniprot ID:
- P31550
- Molecular weight:
- 36163
- General function:
- Involved in molybdate transmembrane-transporting ATPase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the transport of molybdenum into the cell. Binds molybdate with high specificity and affinity
- Gene Name:
- modA
- Uniprot ID:
- P37329
- Molecular weight:
- 27364
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- Member of the two-component regulatory system ArcB/ArcA. Sensor-regulator protein for anaerobic repression of the arc modulon. Activates ArcA via a four-step phosphorelay. ArcB can also dephosphorylate ArcA by a reverse phosphorelay involving His- 717 and Asp-576
- Gene Name:
- arcB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEC3
- Molecular weight:
- 87982
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- Member of the two-component regulatory system AtoS/AtoC; may activate AtoC by phosphorylation
- Gene Name:
- atoS
- Uniprot ID:
- Q06067
- Molecular weight:
- 67789
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- Member of the two-component regulatory system BaeS/BaeR. May activate BaeR by phosphorylation
- Gene Name:
- baeS
- Uniprot ID:
- P30847
- Molecular weight:
- 51991
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- Member of the two-component regulatory system UvrY/BarA involved in the regulation of carbon metabolism via the CsrA/CsrB regulatory system. Phosphorylates UvrY, probably via a four-step phosphorelay
- Gene Name:
- barA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEC5
- Molecular weight:
- 102452
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- Member of the two-component regulatory system BasS/BasR Autophosphorylates and activates BasR by phosphorylation
- Gene Name:
- basS
- Uniprot ID:
- P30844
- Molecular weight:
- 41029
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Cell motility
- Specific function:
- Involved in the transmission of sensory signals from the chemoreceptors to the flagellar motors. CheA is autophosphorylated; it can transfer its phosphate group to either CheB or CheY
- Gene Name:
- cheA
- Uniprot ID:
- P07363
- Molecular weight:
- 71382
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- This protein is involved in several diverse cellular processes, such as the functioning of acetohydroxyacid synthetase I, in the biosynthesis of isoleucine and valine, the traJ protein activation activity for tra gene expression in F plasmid, and the synthesis, translocation, or stability of cell envelope proteins. Activates cpxR by phosphorylation
- Gene Name:
- cpxA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE82
- Molecular weight:
- 51624
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- Member of the two-component regulatory system creC/creB involved in catabolic regulation. CreC may function as a membrane- associated protein kinase that phosphorylates creB in response to environmental signals. CreC can also phosphorylate phoB
- Gene Name:
- creC
- Uniprot ID:
- P08401
- Molecular weight:
- 52176
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Replication, recombination and repair
- Specific function:
- Has a helix-destabilizing activity, which is not coupled to the ATPase activity. Can unwind the 23S rRNA as well as 16S rRNA. Exhibits an RNA-dependent ATPase activity, specifically stimulated by bacterial 23S rRNA. Could play a major role in ribosome assembly, specifically in the assembly process of the active center of 50S ribosomal subunits
- Gene Name:
- dbpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P21693
- Molecular weight:
- 49187
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- Member of the two-component regulatory system dcuR/dcuS. Involved in the C4-dicarboxylate-stimulated regulation of the genes encoding the anaerobic fumarate respiratory system (frdABCD; nuoAN; dcuB; dcuC; sdhCDAB; etc.). Weakly regulates the aerobic C4-dicarboxylate transporter dctA. Activates dcuR by phosphorylation
- Gene Name:
- dcuS
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEC8
- Molecular weight:
- 60550
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Replication, recombination and repair
- Specific function:
- Acts in 50S ribosomal subunit biogenesis at low temperatures, acting after srmB. Has a helix-destabilizing activity; however it is unclear whether it requires ATP:according to PubMed:8552679, it does not require ATP, while according to PubMed:15196029 and PubMed:15554978, it requires ATP. Requires a helicase substrate with a single-stranded overhang. Plays a key role in optimal cell growth at low temperature and is required for normal cell division. When overexpressed suppresses cold-sensitive mutants of the rpsB gene (ribosomal protein S2) and of the smbA2 cold-sensitive mutant (pyrH, uridylate kinase). Can replace rhlB, another ATP-dependent RNA helicase, in the RNA degradosome in vitro. Stimulates translation, probably at the level of initiation, of some mRNAs
- Gene Name:
- deaD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9P6
- Molecular weight:
- 70546
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Transcription
- Specific function:
- Probable helicase involved in DNA repair and perhaps also replication
- Gene Name:
- dinG
- Uniprot ID:
- P27296
- Molecular weight:
- 81439
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Replication, recombination and repair
- Specific function:
- Participates in initiation and elongation during chromosome replication; it exhibits DNA-dependent ATPase activity and contains distinct active sites for ATP binding, DNA binding, and interaction with dnaC protein, primase, and other prepriming proteins
- Gene Name:
- dnaB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ACB0
- Molecular weight:
- 52390
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- Member of the two-component regulatory system DpiA/DpiB, which is essential for expression of citrate-specific fermentation genes and genes involved in plasmid inheritance. Could be involved in response to both the presence of citrate and external redox conditions. Functions as a sensor kinase that phosphorylates DpiA in the presence of citrate
- Gene Name:
- dpiB
- Uniprot ID:
- P77510
- Molecular weight:
- 61684
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- Member of the two-component regulatory system envZ/ompR involved in the regulation of osmoregulation (genes ompF and ompC). EnvZ functions as a membrane-associated protein kinase that phosphorylates ompR in response to environmental signals
- Gene Name:
- envZ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEJ4
- Molecular weight:
- 50334
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Amino acid transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Member of the two-component regulatory system evgS/evgA. Phosphorylates evgA via a four-step phosphorelay in response to environmental signals
- Gene Name:
- evgS
- Uniprot ID:
- P30855
- Molecular weight:
- 134742
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- Probable member of a two-component regulatory system yfhA/yfhK. May activate yfhA by phosphorylation
- Gene Name:
- yfhK
- Uniprot ID:
- P52101
- Molecular weight:
- 53330
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Replication, recombination and repair
- Specific function:
- Helicase IV catalyzes the unwinding of duplex DNA in the 3' to 5' direction with respect to the bound single strand in a reaction that is dependent upon the hydrolysis of ATP
- Gene Name:
- helD
- Uniprot ID:
- P15038
- Molecular weight:
- 77976
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Unbalanced or excessive expression of hipA is toxic to the cell
- Gene Name:
- hipA
- Uniprot ID:
- P23874
- Molecular weight:
- 49275
Reactions
| ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein. |
- General function:
- Replication, recombination and repair
- Specific function:
- Not yet known
- Gene Name:
- hrpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P43329
- Molecular weight:
- 149027
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Replication, recombination and repair
- Specific function:
- ATP + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate
- Gene Name:
- hrpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P37024
- Molecular weight:
- 89147
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- Member of the two-component regulatory system kdpD/kdpE involved in the regulation of the kdp operon. KdpD may function as a membrane-associated protein kinase that phosphorylates kdpE in response to environmental signals
- Gene Name:
- kdpD
- Uniprot ID:
- P21865
- Molecular weight:
- 98717
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- Acts as a sensor for nitrate/nitrite and transduces signal of nitrate/nitrite availability to the narL/narP proteins. NarQ probably activates narL and narP by phosphorylation. NarQ probably negatively regulates the narL protein by dephosphorylation
- Gene Name:
- narQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P27896
- Molecular weight:
- 63696
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- Acts as a sensor for nitrate/nitrite and transduces signal of nitrate availability to the narL protein and of both nitrate/nitrite to the narP protein. NarX probably activates narL and narP by phosphorylation in the presence of nitrate. NarX also plays a negative role in controlling narL activity, probably through dephosphorylation in the absence of nitrate
- Gene Name:
- narX
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFA2
- Molecular weight:
- 67083
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- yjeF
- Uniprot ID:
- P31806
- Molecular weight:
- 54650
Reactions
| ADP + (6S)-6-beta-hydroxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydronicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide = AMP + phosphate + NADH. |
| (R)-NADHX = (S)-NADHX. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- NtrB acts as a signal transducer which responds to the nitrogen level of cell and modulates the activity of ntrC. In nitrogen limitation ntrB activates ntrC by phosphorylating it, while in nitrogen excess ntrC is dephosphorylated and consequently inactivated by ntrB
- Gene Name:
- glnL
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFB5
- Molecular weight:
- 38556
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Inorganic ion transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex PhnCDE involved in phosphonates, phosphate esters, phosphite and phosphate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- phnC
- Uniprot ID:
- P16677
- Molecular weight:
- 29430
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + phosphonate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + phosphonate(In). |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- Member of the two-component regulatory system phoR/phoB involved in the phosphate regulon genes expression. PhoR may function as a membrane-associated protein kinase that phosphorylates phoB in response to environmental signals
- Gene Name:
- phoR
- Uniprot ID:
- P08400
- Molecular weight:
- 49629
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the phosphorylation of pseudouridine to pseudouridine 5'-phosphate (PsiMP)
- Gene Name:
- psuK
- Uniprot ID:
- P30235
- Molecular weight:
- 33573
Reactions
| ATP + pseudouridine = ADP + pseudouridine 5'-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- Member of a two-component regulatory system qseB/qseC. Activates the flagella regulon by activating transcription of flhDC. May activate qseB by phosphorylation
- Gene Name:
- qseC
- Uniprot ID:
- P40719
- Molecular weight:
- 50281
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- May serves as a phosphotransfer intermediate between RcsC and RcsB. It may acquire a phosphoryl group at His-842 from RcsC 'Asp-866' and transmit it to 'Asp-56' of RcsB
- Gene Name:
- rcsD
- Uniprot ID:
- P39838
- Molecular weight:
- 100371
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Replication, recombination and repair
- Specific function:
- Critical role in recombination and DNA repair. Help process Holliday junction intermediates to mature products by catalyzing branch migration. Has a DNA unwinding activity characteristic of a DNA helicase with a 3' to 5' polarity. recG unwind branched duplex DNA (Y-DNA). Has a role in constitutive stable DNA replication (csdR) and R-loop formation
- Gene Name:
- recG
- Uniprot ID:
- P24230
- Molecular weight:
- 76430
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Replication, recombination and repair
- Specific function:
- Involved in the recF recombination pathway; its gene expression is under the regulation of the SOS system. It is a DNA helicase
- Gene Name:
- recQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P15043
- Molecular weight:
- 68363
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Replication, recombination and repair
- Specific function:
- Rep helicase is a single-stranded DNA-dependent ATPase involved in DNA replication; it can initiate unwinding at a nick in the DNA. It binds to the single-stranded DNA and acts in a progressive fashion along the DNA in the 3' to 5' direction
- Gene Name:
- rep
- Uniprot ID:
- P09980
- Molecular weight:
- 77024
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Replication, recombination and repair
- Specific function:
- Can carry out ATP-dependent unwinding of double stranded RNA. Has a role in RNA decay. Involved in the RNA degradosome, a multi-enzyme complex important in RNA processing and messenger RNA degradation
- Gene Name:
- rhlB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A8J8
- Molecular weight:
- 47125
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Replication, recombination and repair
- Specific function:
- Acts as an ATP-dependent RNA helicase, able to unwind ds-RNA
- Gene Name:
- rhlE
- Uniprot ID:
- P25888
- Molecular weight:
- 49989
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- Member of the two-component regulatory system rstB/rstA. RstB functions as a membrane-associated protein kinase that phosphorylates rstA (Potential)
- Gene Name:
- rstB
- Uniprot ID:
- P18392
- Molecular weight:
- 49282
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Replication, recombination and repair
- Specific function:
- The ruvA-ruvB complex in the presence of ATP renatures cruciform structure in supercoiled DNA with palindromic sequence, indicating that it may promote strand exchange reactions in homologous recombination. RuvAB is an helicase that mediates the Holliday junction migration by localized denaturation and reannealing. RuvA stimulates, in the presence of DNA, the weak ATPase activity of ruvB. Binds both single- and double-stranded DNA (dsDNA). Binds preferentially to supercoiled rather than to relaxed dsDNA
- Gene Name:
- ruvA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A809
- Molecular weight:
- 22086
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Replication, recombination and repair
- Specific function:
- The ruvA-ruvB complex in the presence of ATP renatures cruciform structure in supercoiled DNA with palindromic sequence, indicating that it may promote strand exchange reactions in homologous recombination. RuvAB is an helicase that mediates the Holliday junction migration by localized denaturation and reannealing
- Gene Name:
- ruvB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A812
- Molecular weight:
- 37173
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Replication, recombination and repair
- Specific function:
- RNA-dependent ATPase activity. Acts in 50S ribosomal subunit biogenesis at low temperatures, acting before deaD/csdA. Suppressor of a mutant defective in 50S ribosomal subunit assembly. Probably interacts with 23S ribosomal RNA
- Gene Name:
- srmB
- Uniprot ID:
- P21507
- Molecular weight:
- 49914
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in tRNA binding
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- ypfI
- Uniprot ID:
- P76562
- Molecular weight:
- 74892
Reactions
| (Elongator tRNA(Met))-cytidine(34) + ATP + acetyl-CoA = (elongator tRNA(Met))-N(4)-acetylcytidine(34) + ADP + phosphate + CoA. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- Member of the two-component regulatory system torS/torR involved in the anaerobic utilization of trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO). Detects the presence of TMAO in the medium and, in response, activates torR via a four-step phosphorelay. When TMAO is removed, torS can dephosphorylate torR, probably by a reverse phosphorelay involving His-860 and Asp-733
- Gene Name:
- torS
- Uniprot ID:
- P39453
- Molecular weight:
- 101023
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- Member of the two-component regulatory system uhpB/uhpA involved in the regulation of the uptake of hexose phosphates. UhpB functions as a membrane-associated protein kinase that phosphorylates uhpA in response to environmental signals
- Gene Name:
- uhpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P09835
- Molecular weight:
- 56305
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Replication, recombination and repair
- Specific function:
- Has both ATPase and helicase activities. Unwinds DNA duplexes with 3' to 5' polarity with respect to the bound strand and initiates unwinding most effectively when a single-stranded region is present. Involved in the post-incision events of nucleotide excision repair and methyl-directed mismatch repair
- Gene Name:
- uvrD
- Uniprot ID:
- P03018
- Molecular weight:
- 81989
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- Probable member of a two-component regulatory system yedW/yedV. May activate yedW by phosphorylation
- Gene Name:
- yedV
- Uniprot ID:
- P76339
- Molecular weight:
- 50849
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Signal transduction mechanisms
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- yehU
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AD14
- Molecular weight:
- 62092
Reactions
| ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis
- Specific function:
- ATP + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate
- Gene Name:
- yoaA
- Uniprot ID:
- P76257
- Molecular weight:
- 70377
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O = ADP + phosphate. |
- General function:
- protein phosphorylation
- Specific function:
- A protein kinase that (auto)phosphorylates on Ser and Thr residues (PubMed:17302814). Probably acts to suppress the effects of stress linked to accumulation of reactive oxygen species. Protects cells from stress by antagonizing the MazE-MazF TA module, probably indirectly as it has not been seen to phosphorylate MazE, MazF or MazG (PubMed:23416055). Probably involved in the extracytoplasmic stress response (PubMed:9159398).
- Gene Name:
- srkA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0C0K3
- Molecular weight:
- 38120
Reactions
| ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein |
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in potassium-transporting ATPase activity
- Specific function:
- One of the components of the high-affinity ATP-driven potassium transport (or KDP) system, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of hydrogen and potassium ions
- Gene Name:
- kdpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P03959
- Molecular weight:
- 59189
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + K(+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + K(+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- One of the components of the high-affinity ATP-driven potassium transport (or KDP) system, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of hydrogen and potassium ions
- Gene Name:
- kdpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P03960
- Molecular weight:
- 72198
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + K(+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + K(+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in potassium-transporting ATPase activity
- Specific function:
- One of the components of the high-affinity ATP-driven potassium transport (or KDP) system, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of hydrogen and potassium ions. The C subunit may be involved in assembly of the KDP complex
- Gene Name:
- kdpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P03961
- Molecular weight:
- 20267
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + K(+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + K(+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex RbsABCD involved in ribose import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- rbsA
- Uniprot ID:
- P04983
- Molecular weight:
- 55041
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + monosaccharide(Out) = ADP + phosphate + monosaccharide(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex BtuCDF involved in vitamin B12 import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- btuD
- Uniprot ID:
- P06611
- Molecular weight:
- 27081
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + vitamin B12(Out) = ADP + phosphate + vitamin B12(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for histidine. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- hisP
- Uniprot ID:
- P07109
- Molecular weight:
- 28653
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex fhuCDB involved in iron(3+)-hydroxamate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- fhuC
- Uniprot ID:
- P07821
- Molecular weight:
- 28886
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + iron chelate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + iron chelate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism
- Specific function:
- Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- atpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6E6
- Molecular weight:
- 15068
- General function:
- Involved in nucleoside diphosphate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Major role in the synthesis of nucleoside triphosphates other than ATP. The ATP gamma phosphate is transferred to the NDP beta phosphate via a ping-pong mechanism, using a phosphorylated active-site intermediate
- Gene Name:
- ndk
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A763
- Molecular weight:
- 15463
Reactions
| ATP + nucleoside diphosphate = ADP + nucleoside triphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex AraFGH involved in arabinose import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- araG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAF3
- Molecular weight:
- 55018
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + monosaccharide(Out) = ADP + phosphate + monosaccharide(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex MglABC involved in galactose/methyl galactoside import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- mglA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAG8
- Molecular weight:
- 56415
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + monosaccharide(Out) = ADP + phosphate + monosaccharide(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex pstSACB involved in phosphate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- pstB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAH0
- Molecular weight:
- 29027
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + phosphate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + phosphate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Key component of the proton channel; it plays a direct role in the translocation of protons across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- atpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AB98
- Molecular weight:
- 30303
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the F(0) channel, it forms part of the peripheral stalk, linking F(1) to F(0)
- Gene Name:
- atpF
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABA0
- Molecular weight:
- 17264
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism
- Specific function:
- This protein is part of the stalk that links CF(0) to CF(1). It either transmits conformational changes from CF(0) to CF(1) or is implicated in proton conduction
- Gene Name:
- atpH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABA4
- Molecular weight:
- 19332
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism
- Specific function:
- Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane. The gamma chain is believed to be important in regulating ATPase activity and the flow of protons through the CF(0) complex
- Gene Name:
- atpG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABA6
- Molecular weight:
- 31577
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane. The alpha chain is a regulatory subunit
- Gene Name:
- atpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABB0
- Molecular weight:
- 55222
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + H(+)(In) = ADP + phosphate + H(+)(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane. The catalytic sites are hosted primarily by the beta subunits
- Gene Name:
- atpD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABB4
- Molecular weight:
- 50325
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + H(+)(In) = ADP + phosphate + H(+)(Out). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex UgpABCE involved in sn-glycerol-3-phosphate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable). Can also transport glycerophosphoryl diesters
- Gene Name:
- ugpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P10907
- Molecular weight:
- 39524
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + glycerol-3-phosphate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + glycerol-3-phosphate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for citrate-dependent Fe(3+). Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- fecE
- Uniprot ID:
- P15031
- Molecular weight:
- 28191
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- cysA
- Uniprot ID:
- P16676
- Molecular weight:
- 41059
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + sulfate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + sulfate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ferric enterobactin. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- fepC
- Uniprot ID:
- P23878
- Molecular weight:
- 29784
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for D-methionine and the toxic methionine analog alpha-methyl- methionine. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- metI
- Uniprot ID:
- P31547
- Molecular weight:
- 23256
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex AlsBAC involved in D-allose import. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- alsA
- Uniprot ID:
- P32721
- Molecular weight:
- 56744
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + monosaccharide(Out) = ADP + phosphate + monosaccharide(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex FbpABC involved in Fe(3+) ions import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- fbpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P37009
- Molecular weight:
- 39059
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Fe(3+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + Fe(3+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex XylFGH involved in xylose import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable). The XylFGH system can also transport ribose in absence of xylose
- Gene Name:
- xylG
- Uniprot ID:
- P37388
- Molecular weight:
- 56470
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + monosaccharide(Out) = ADP + phosphate + monosaccharide(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex MalEFGK involved in maltose/maltodextrin import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- malK
- Uniprot ID:
- P68187
- Molecular weight:
- 40990
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + maltose(Out) = ADP + phosphate + maltose(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrogen ion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Key component of the F(0) channel; it plays a direct role in translocation across the membrane. A homomeric c-ring of 10 subunits forms the central stalk rotor element with the F(1) delta and epsilon subunits
- Gene Name:
- atpE
- Uniprot ID:
- P68699
- Molecular weight:
- 8256
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex PotABCD involved in spermidine/putrescine import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- potA
- Uniprot ID:
- P69874
- Molecular weight:
- 43028
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + polyamine(Out) = ADP + phosphate + polyamine(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- ytfR
- Uniprot ID:
- Q6BEX0
- Molecular weight:
- 55259
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport
- Gene Name:
- artI
- Uniprot ID:
- P30859
- Molecular weight:
- 26929
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport. Binds L-arginine with high affinity
- Gene Name:
- artJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P30860
- Molecular weight:
- 26829
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- artM
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE32
- Molecular weight:
- 24914
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- artQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE34
- Molecular weight:
- 26217
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Has low ATPase activity. The sufBCD complex acts synergistically with sufE to stimulate the cysteine desulfurase activity of sufS. The sufBCD complex contributes to the assembly or repair of oxygen-labile iron-sulfur clusters under oxidative stress. May facilitate iron uptake from extracellular iron chelators under iron limitation
- Gene Name:
- sufC
- Uniprot ID:
- P77499
- Molecular weight:
- 27582
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system ydcSTUV
- Gene Name:
- ydcS
- Uniprot ID:
- P76108
- Molecular weight:
- 42295
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Probably part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system ydcSTUV. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- ydcT
- Uniprot ID:
- P77795
- Molecular weight:
- 37040
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system ydcSTUV; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ydcU
- Uniprot ID:
- P77156
- Molecular weight:
- 34360
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system ydcSTUV; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ydcV
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFR9
- Molecular weight:
- 28722
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Probably part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system yecCS for an amino acid. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- yecC
- Uniprot ID:
- P37774
- Molecular weight:
- 27677
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system yecCS for an amino acid; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- yecS
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFT2
- Molecular weight:
- 24801
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- yjfF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37772
- Molecular weight:
- 34977
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- ytfQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P39325
- Molecular weight:
- 34344
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ytfT
- Uniprot ID:
- P39328
- Molecular weight:
- 35659
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex lsrABCD involved in autoinducer 2 (AI-2) import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- lsrC
- Uniprot ID:
- B1XEA2
- Molecular weight:
- 36394
- General function:
- Involved in cobalamin transport
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex BtuCDF involved in vitamin B12 import. Involved in the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- btuC
- Uniprot ID:
- B1XG18
- Molecular weight:
- 34949
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for maltose; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- malF
- Uniprot ID:
- P02916
- Molecular weight:
- 57013
- General function:
- Involved in cobalamin transport
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex BtuCDF involved in vitamin B12 import. Involved in the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- btuC
- Uniprot ID:
- P06609
- Molecular weight:
- 34949
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex fhuCDB involved in iron(3+)-hydroxamate import. Responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fhuB
- Uniprot ID:
- P06972
- Molecular weight:
- 70422
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for phosphate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- pstA
- Uniprot ID:
- P07654
- Molecular weight:
- 32321
- General function:
- Involved in lipopolysaccharide transport
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex lptBFG involved in the translocation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from the inner membrane to the outer membrane
- Gene Name:
- lptG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ADC6
- Molecular weight:
- 39618
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for L-arabinose. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- araH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE26
- Molecular weight:
- 34211
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- artM
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE30
- Molecular weight:
- 24914
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP (TC 3.A.1.6.1) involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- cysW
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEB0
- Molecular weight:
- 32537
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- dppB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEF8
- Molecular weight:
- 37497
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- dppC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEG1
- Molecular weight:
- 32308
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for glutamine; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- glnP
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEQ6
- Molecular weight:
- 24364
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for aspartate/glutamate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- gltJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AER3
- Molecular weight:
- 27502
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for aspartate/glutamate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- gltK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AER5
- Molecular weight:
- 24914
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for histidine; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- hisM
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEU3
- Molecular weight:
- 26870
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for branched-chain amino acids. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrates across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- livH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEX7
- Molecular weight:
- 32982
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for molybdenum; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- modB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AF01
- Molecular weight:
- 24939
- General function:
- Involved in lipopolysaccharide-transporting ATPase acti
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex lptBFG involved in the translocation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from the inner membrane to the outer membrane
- Gene Name:
- lptF
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AF98
- Molecular weight:
- 40357
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a nickel transport system, probably translocates nickel through the bacterial inner membrane
- Gene Name:
- nikC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFA9
- Molecular weight:
- 30362
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for oligopeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- oppB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFH2
- Molecular weight:
- 33443
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for oligopeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- oppC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFH6
- Molecular weight:
- 33022
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine and spermidine
- Gene Name:
- potB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFK4
- Molecular weight:
- 31062
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine and spermidine
- Gene Name:
- potC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFK6
- Molecular weight:
- 29111
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine
- Gene Name:
- potI
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFL1
- Molecular weight:
- 30540
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex lsrABCD involved in autoinducer 2 (AI-2) import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- lsrD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFS1
- Molecular weight:
- 34456
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for phosphate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- pstC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGH8
- Molecular weight:
- 34121
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ribose. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- rbsC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGI1
- Molecular weight:
- 33452
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for D-xylose. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- xylH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGI4
- Molecular weight:
- 41030
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for sn-glycerol-3-phosphate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ugpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P10905
- Molecular weight:
- 33264
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for sn-glycerol-3-phosphate; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ugpE
- Uniprot ID:
- P10906
- Molecular weight:
- 31499
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a multicomponent binding-protein-dependent transport system for glycine betaine/L-proline
- Gene Name:
- proW
- Uniprot ID:
- P14176
- Molecular weight:
- 37619
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for citrate-dependent Fe(3+). Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fecD
- Uniprot ID:
- P15029
- Molecular weight:
- 34131
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for citrate-dependent Fe(3+). Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fecC
- Uniprot ID:
- P15030
- Molecular weight:
- 34892
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for phosphonates; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- phnE
- Uniprot ID:
- P16683
- Molecular weight:
- 28383
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP (TC 3.A.1.6.1) involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- cysU
- Uniprot ID:
- P16701
- Molecular weight:
- 30292
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for branched-chain amino acids. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrates across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- livM
- Uniprot ID:
- P22729
- Molecular weight:
- 46269
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for galactoside. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- mglC
- Uniprot ID:
- P23200
- Molecular weight:
- 35550
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ferric enterobactin. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fepD
- Uniprot ID:
- P23876
- Molecular weight:
- 33871
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for ferric enterobactin. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- fepG
- Uniprot ID:
- P23877
- Molecular weight:
- 34910
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine
- Gene Name:
- potH
- Uniprot ID:
- P31135
- Molecular weight:
- 35489
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex thiBPQ involved in thiamine import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- thiP
- Uniprot ID:
- P31549
- Molecular weight:
- 59532
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system AlsBAC for D-allose; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- alsC
- Uniprot ID:
- P32720
- Molecular weight:
- 34315
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- yehW
- Uniprot ID:
- P33359
- Molecular weight:
- 25514
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- yehY
- Uniprot ID:
- P33361
- Molecular weight:
- 41138
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a nickel transport system, probably translocates nickel through the bacterial inner membrane
- Gene Name:
- nikB
- Uniprot ID:
- P33591
- Molecular weight:
- 35248
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for histidine; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- hisQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P52094
- Molecular weight:
- 24649
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in lipid A export and possibly also in glycerophospholipid export and for biogenesis of the outer membrane. Transmembrane domains (TMD) form a pore in the inner membrane and the ATP-binding domain (NBD) is responsible for energy generation
- Gene Name:
- msbA
- Uniprot ID:
- P60752
- Molecular weight:
- 64460
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for maltose; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- malG
- Uniprot ID:
- P68183
- Molecular weight:
- 32225
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex gsiABCD involved in glutathione import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- gsiC
- Uniprot ID:
- P75798
- Molecular weight:
- 34066
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex gsiABCD involved in glutathione import. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- gsiD
- Uniprot ID:
- P75799
- Molecular weight:
- 33238
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system for aliphatic sulfonates. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ssuC
- Uniprot ID:
- P75851
- Molecular weight:
- 28925
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ddpABCDF, which is probably involved in D,D-dipeptide transport. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ddpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P77308
- Molecular weight:
- 37345
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ddpABCDF, which is probably involved in D,D-dipeptide transport. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- ddpC
- Uniprot ID:
- P77463
- Molecular weight:
- 31971
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system for taurine. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- tauC
- Uniprot ID:
- Q47539
- Molecular weight:
- 29812
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a nickel transport system, probably represents the nickel binder
- Gene Name:
- nikA
- Uniprot ID:
- P33590
- Molecular weight:
- 58718
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- This protein specifically binds sulfate and is involved in its transmembrane transport
- Gene Name:
- sbp
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG78
- Molecular weight:
- 36659
- General function:
- Involved in GTP binding
- Specific function:
- GTP-driven Fe(2+) uptake system
- Gene Name:
- feoB
- Uniprot ID:
- P33650
- Molecular weight:
- 84473
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex MetNIQ involved in methionine import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable). It has also been shown to be involved in formyl-L-methionine transport
- Gene Name:
- metN
- Uniprot ID:
- P30750
- Molecular weight:
- 37788
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ddpABCDF, which is probably involved in D,D-dipeptide transport. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- ddpD
- Uniprot ID:
- P77268
- Molecular weight:
- 36100
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for glutamine. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- glnQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P10346
- Molecular weight:
- 26731
- General function:
- Involved in sulfur compound metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system for aliphatic sulfonates. Putative binding protein
- Gene Name:
- ssuA
- Uniprot ID:
- P75853
- Molecular weight:
- 34557
- General function:
- Involved in maltose transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity maltose membrane transport system malEFGK. Initial receptor for the active transport of and chemotaxis toward maltooligosaccharides
- Gene Name:
- malE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEX9
- Molecular weight:
- 43387
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Binds ferrienterobactin; part of the binding-protein- dependent transport system for uptake of ferrienterobactin
- Gene Name:
- fepB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEL6
- Molecular weight:
- 34283
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for oligopeptides. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- oppF
- Uniprot ID:
- P77737
- Molecular weight:
- 37197
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity D-xylose membrane transport system. Binds with high affinity to xylose
- Gene Name:
- xylF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37387
- Molecular weight:
- 35734
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ZnuABC involved in zinc import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- znuC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9X1
- Molecular weight:
- 27867
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- dppD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAG0
- Molecular weight:
- 35844
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Essential for the uptake of the murein peptide L-alanyl- gamma-D-glutamyl-meso-diaminopimelate. Also transports some alpha- linked peptides such as Pro-Phe-Lys with low affinity. The transport is effected by the oligopeptide permease system
- Gene Name:
- mppA
- Uniprot ID:
- P77348
- Molecular weight:
- 59900
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- This periplasmic binding protein is involved in an arginine transport system. ArgT and histidine-binding protein J (hisJ) interact with a common membrane-bound receptor, hisP
- Gene Name:
- argT
- Uniprot ID:
- P09551
- Molecular weight:
- 27991
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex BtuCDF involved in vitamin B12 import. Binds vitamin B12 and delivers it to the periplasmic surface of BtuC
- Gene Name:
- btuF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37028
- Molecular weight:
- 29367
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system AlsBAC for D-allose
- Gene Name:
- alsB
- Uniprot ID:
- P39265
- Molecular weight:
- 32910
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex gsiABCD involved in glutathione import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- gsiA
- Uniprot ID:
- P75796
- Molecular weight:
- 69113
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex cysAWTP (TC 3.A.1.6.1) involved in sulfate/thiosulfate import. This protein specifically binds thiosulfate and is involved in its transmembrane transport
- Gene Name:
- cysP
- Uniprot ID:
- P16700
- Molecular weight:
- 37614
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- yehX
- Uniprot ID:
- P33360
- Molecular weight:
- 34424
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of the oligopeptide permease, a binding protein-dependent transport system, it binds peptides up to five amino acids long with high affinity
- Gene Name:
- oppA
- Uniprot ID:
- P23843
- Molecular weight:
- 60899
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- dppF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37313
- Molecular weight:
- 37560
- General function:
- Involved in phosphate ion binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex pstSACB involved in phosphate import
- Gene Name:
- pstS
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG82
- Molecular weight:
- 37024
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity L-arabinose membrane transport system. Binds with high affinity to arabinose, but can also bind D-galactose (approximately 2-fold reduction) and D- fucose (approximately 40-fold reduction)
- Gene Name:
- araF
- Uniprot ID:
- P02924
- Molecular weight:
- 35541
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ThiBPQ involved in thiamine import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- thiQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P31548
- Molecular weight:
- 24999
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ArtPIQMJ involved in arginine transport. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- artP
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAF6
- Molecular weight:
- 27022
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for glutamate and aspartate. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- gltL
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAG3
- Molecular weight:
- 26661
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity D-ribose membrane transport system and also serves as the primary chemoreceptor for chemotaxis
- Gene Name:
- rbsB
- Uniprot ID:
- P02925
- Molecular weight:
- 30950
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Component of the leucine-specific transport system
- Gene Name:
- livG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9S7
- Molecular weight:
- 28427
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the high-affinity histidine permease, a binding-protein-dependent transport system. The other components are proteins hisQ, hisM, and hisP
- Gene Name:
- hisJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEU0
- Molecular weight:
- 28483
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid transport
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of the leucine, isoleucine, valine, (threonine) transport system, which is one of the two periplasmic binding protein-dependent transport systems of the high-affinity transport of the branched-chain amino acids
- Gene Name:
- livJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AD96
- Molecular weight:
- 39076
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity zinc uptake transport system
- Gene Name:
- znuB
- Uniprot ID:
- P39832
- Molecular weight:
- 27728
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex NikABCDE involved in nickel import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- nikD
- Uniprot ID:
- P33593
- Molecular weight:
- 26820
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Ni(2+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + Ni(2+)(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Component of the leucine-specific transport system
- Gene Name:
- livF
- Uniprot ID:
- P22731
- Molecular weight:
- 26310
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ddpABCDF, which is probably involved in D,D-dipeptide transport. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- ddpF
- Uniprot ID:
- P77622
- Molecular weight:
- 34621
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Binds citrate-dependent Fe(3+); part of the binding- protein-dependent transport system for uptake of citrate-dependent Fe(3+)
- Gene Name:
- fecB
- Uniprot ID:
- P15028
- Molecular weight:
- 33146
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Dipeptide-binding protein of a transport system that can be subject to osmotic shock. DppA is also required for peptide chemotaxis
- Gene Name:
- dppA
- Uniprot ID:
- P23847
- Molecular weight:
- 60293
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- This protein is involved in the active transport of galactose and glucose. It plays a role in the chemotaxis towards the two sugars by interacting with the trg chemoreceptor
- Gene Name:
- mglB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEE5
- Molecular weight:
- 35712
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex NikABCDE involved in nickel import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- nikE
- Uniprot ID:
- P33594
- Molecular weight:
- 29721
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + Ni(2+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + Ni(2+)(In). |
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- kdpF
- Uniprot ID:
- P36937
- Molecular weight:
- 3072
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- sn-glycerol-3-phosphate and glycerophosphoryl diester- binding protein interacts with the binding protein-dependent transport system ugpACE
- Gene Name:
- ugpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG80
- Molecular weight:
- 48448
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex TauABC involved in taurine import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- tauB
- Uniprot ID:
- Q47538
- Molecular weight:
- 28297
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + taurine(Out) = ADP + phosphate + taurine(In). |
- General function:
- Inorganic ion transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of a D-methionine permease, a binding protein-dependent, ATP-driven transport system
- Gene Name:
- metQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P28635
- Molecular weight:
- 29432
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ModABC involved in molybdenum import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- modC
- Uniprot ID:
- P09833
- Molecular weight:
- 39102
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + molybdate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + molybdate(In). |
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules
- Gene Name:
- osmF
- Uniprot ID:
- P33362
- Molecular weight:
- 32609
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for oligopeptides. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- oppD
- Uniprot ID:
- P76027
- Molecular weight:
- 37188
- General function:
- Involved in metal ion binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in the high-affinity zinc uptake transport system
- Gene Name:
- znuA
- Uniprot ID:
- P39172
- Molecular weight:
- 33777
- General function:
- Amino acid transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for putrescine. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- potG
- Uniprot ID:
- P31134
- Molecular weight:
- 41930
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex gsiABCD involved in glutathione import
- Gene Name:
- gsiB
- Uniprot ID:
- P75797
- Molecular weight:
- 56470
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system for taurine
- Gene Name:
- tauA
- Uniprot ID:
- Q47537
- Molecular weight:
- 34266
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex SsuABC involved in aliphatic sulfonates import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable)
- Gene Name:
- ssuB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAI1
- Molecular weight:
- 27738
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for glutamate and aspartate. Binds to both aspartate and glutamate
- Gene Name:
- gltI
- Uniprot ID:
- P37902
- Molecular weight:
- 33420
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid transport
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of the leucine-specific transport system, which is one of the two periplasmic binding protein-dependent transport systems of the high-affinity transport of the branched-chain amino acids in E.coli
- Gene Name:
- livK
- Uniprot ID:
- P04816
- Molecular weight:
- 39378
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a glutamine-transport system glnHPQ
- Gene Name:
- glnH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEQ3
- Molecular weight:
- 27190
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine. Polyamine binding protein
- Gene Name:
- potF
- Uniprot ID:
- P31133
- Molecular weight:
- 40839
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex ddpABCDF, which is probably involved in D,D-dipeptide transport
- Gene Name:
- ddpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P76128
- Molecular weight:
- 57641
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Required for the activity of the bacterial periplasmic transport system of putrescine and spermidine. Polyamine binding protein
- Gene Name:
- potD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFK9
- Molecular weight:
- 38867
- General function:
- Involved in binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex fhuCDB involved in iron(3+)-hydroxamate import. Binds the iron(3+)-hydroxamate complex and transfers it to the membrane-bound permease. Required for the transport of all iron(3+)-hydroxamate siderophores such as ferrichrome, gallichrome, desferrioxamine, coprogen, aerobactin, shizokinen, rhodotorulic acid and the antibiotic albomycin
- Gene Name:
- fhuD
- Uniprot ID:
- P07822
- Molecular weight:
- 32998
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex thiBPQ involved in thiamine import
- Gene Name:
- thiB
- Uniprot ID:
- P31550
- Molecular weight:
- 36163
- General function:
- Involved in molybdate transmembrane-transporting ATPase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the transport of molybdenum into the cell. Binds molybdate with high specificity and affinity
- Gene Name:
- modA
- Uniprot ID:
- P37329
- Molecular weight:
- 27364
- General function:
- Inorganic ion transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex PhnCDE involved in phosphonates, phosphate esters, phosphite and phosphate import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- phnC
- Uniprot ID:
- P16677
- Molecular weight:
- 29430
Reactions
| ATP + H(2)O + phosphonate(Out) = ADP + phosphate + phosphonate(In). |
- General function:
- ATPase activity, coupled to transmembrane movement of substances
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex LsrABCD involved in autoinducer 2 (AI-2) import. Responsible for energy coupling to the transport system (Probable). This protein is essential for aerobic growth.
- Gene Name:
- lsrA
- Uniprot ID:
- P77257
- Molecular weight:
- 55820
- General function:
- periplasmic space
- Specific function:
- Part of the ABC transporter complex LsrABCD involved in autoinducer 2 (AI-2) import. Binds AI-2 and delivers it to the LsrC and LsrD permeases (Probable).
- Gene Name:
- lsrB
- Uniprot ID:
- P76142
- Molecular weight:
- 36684
- General function:
- transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system for cystine.
- Gene Name:
- fliY
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEM9
- Molecular weight:
- 29038
- General function:
- alkylphosphonate transport
- Specific function:
- Phosphonate binding protein that is part of the phosphonate uptake system. Exhibits high affinity for 2-aminoethylphosphonate, and somewhat less affinity to ethylphosphonate, methylphosphonate, phosphonoacetate and phenylphosphonate.
- Gene Name:
- phnD
- Uniprot ID:
- P16682
- Molecular weight:
- 37370