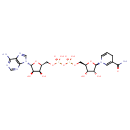
NADH (ECMDB01487) (M2MDB000398)
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- L-glutamate + H(2)O + NADP(+) = 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- gdhA
- Uniprot ID:
- P00370
- Molecular weight:
- 48581
Reactions
| L-glutamate + H(2)O + NADP(+) = 2-oxoglutarate + NH(3) + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- Transfer of electrons from NADH to the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme is believed to be ubiquinone. Does not couple the redox reaction to proton translocation
- Gene Name:
- ndh
- Uniprot ID:
- P00393
- Molecular weight:
- 47358
Reactions
| NADH + acceptor = NAD(+) + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid binding
- Specific function:
- L-homoserine + NAD(P)(+) = L-aspartate 4- semialdehyde + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- thrA
- Uniprot ID:
- P00561
- Molecular weight:
- 89119
Reactions
| L-homoserine + NAD(P)(+) = L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde + NAD(P)H. |
| ATP + L-aspartate = ADP + 4-phospho-L-aspartate. |
- General function:
- Involved in cellular amino acid biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- L-homoserine + NAD(P)(+) = L-aspartate 4- semialdehyde + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- metL
- Uniprot ID:
- P00562
- Molecular weight:
- 88887
Reactions
| L-homoserine + NAD(P)(+) = L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde + NAD(P)H. |
| ATP + L-aspartate = ADP + 4-phospho-L-aspartate. |
- General function:
- Involved in dihydrodipicolinate reductase activity
- Specific function:
- 2,3,4,5-tetrahydrodipicolinate + NAD(P)(+) = 2,3-dihydrodipicolinate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- dapB
- Uniprot ID:
- P04036
- Molecular weight:
- 28756
Reactions
| (S)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrodipicolinate + NAD(P)(+) = (S)-2,3-dihydrodipicolinate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidation of erythronate-4-phosphate to 3- hydroxy-2-oxo-4-phosphonooxybutanoate
- Gene Name:
- pdxB
- Uniprot ID:
- P05459
- Molecular weight:
- 41367
Reactions
| 4-phospho-D-erythronate + NAD(+) = (3R)-3-hydroxy-2-oxo-4-phosphonooxybutanoate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- D-sorbitol 6-phosphate + NAD(+) = D-fructose 6-phosphate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- srlD
- Uniprot ID:
- P05707
- Molecular weight:
- 27858
Reactions
| D-sorbitol 6-phosphate + NAD(+) = D-fructose 6-phosphate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in flavin adenine dinucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- First component of the membrane-bound D-lactate oxidase, which is believed to play an important role in the energization of the active transport of a variety of sugars and amino acids
- Gene Name:
- dld
- Uniprot ID:
- P06149
- Molecular weight:
- 64612
Reactions
| (R)-lactate + NAD(+) = pyruvate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Maintains high levels of reduced glutathione in the cytosol
- Gene Name:
- gor
- Uniprot ID:
- P06715
- Molecular weight:
- 48772
Reactions
| 2 glutathione + NADP(+) = glutathione disulfide + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring acyl groups
- Specific function:
- The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA and CO(2). It contains multiple copies of three enzymatic components:pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1), dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase (E2) and lipoamide dehydrogenase (E3)
- Gene Name:
- aceF
- Uniprot ID:
- P06959
- Molecular weight:
- 66096
Reactions
| Acetyl-CoA + enzyme N(6)-(dihydrolipoyl)lysine = CoA + enzyme N(6)-(S-acetyldihydrolipoyl)lysine. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the sequential NAD-dependent oxidations of L- histidinol to L-histidinaldehyde and then to L-histidine
- Gene Name:
- hisD
- Uniprot ID:
- P06988
- Molecular weight:
- 46110
Reactions
| L-histidinol + H(2)O + 2 NAD(+) = L-histidine + 2 NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- The transhydrogenation between NADH and NADP is coupled to respiration and ATP hydrolysis and functions as a proton pump across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- pntA
- Uniprot ID:
- P07001
- Molecular weight:
- 54623
Reactions
| NADPH + NAD(+) = NADP(+) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- Chorismate = prephenate
- Gene Name:
- tyrA
- Uniprot ID:
- P07023
- Molecular weight:
- 42042
Reactions
| Chorismate = prephenate. |
| Prephenate + NAD(+) = 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate + CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in formate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity
- Specific function:
- Decomposes formic acid to hydrogen and carbon dioxide under anaerobic conditions in the absence of exogenous electron acceptors
- Gene Name:
- fdhF
- Uniprot ID:
- P07658
- Molecular weight:
- 79373
Reactions
| Formate + NAD(+) = CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- L-threonine + NAD(+) = L-2-amino-3- oxobutanoate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- tdh
- Uniprot ID:
- P07913
- Molecular weight:
- 37239
Reactions
| L-threonine + NAD(+) = L-2-amino-3-oxobutanoate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- Ammonium hydroxide + 3 NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = nitrite + 3 NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- nirB
- Uniprot ID:
- P08201
- Molecular weight:
- 93121
Reactions
| Ammonium hydroxide + 3 NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = nitrite + 3 NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in flavin adenine dinucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Cell wall formation
- Gene Name:
- murB
- Uniprot ID:
- P08373
- Molecular weight:
- 37851
Reactions
| UDP-N-acetylmuramate + NADP(+) = UDP-N-acetyl-3-O-(1-carboxyvinyl)-D-glucosamine + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- D-mannitol 1-phosphate + NAD(+) = D-fructose 6-phosphate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- mtlD
- Uniprot ID:
- P09424
- Molecular weight:
- 41139
Reactions
| D-mannitol 1-phosphate + NAD(+) = D-fructose 6-phosphate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Oxidizes proline to glutamate for use as a carbon and nitrogen source and also function as a transcriptional repressor of the put operon
- Gene Name:
- putA
- Uniprot ID:
- P09546
- Molecular weight:
- 143814
Reactions
| L-proline + acceptor = (S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate + reduced acceptor. |
| (S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate + NAD(P)(+) + 2 H(2)O = L-glutamate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- 2 L-glutamate + NADP(+) = L-glutamine + 2- oxoglutarate + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- gltB
- Uniprot ID:
- P09831
- Molecular weight:
- 166708
Reactions
| 2 L-glutamate + NADP(+) = L-glutamine + 2-oxoglutarate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in iron-sulfur cluster binding
- Specific function:
- 2 L-glutamate + NADP(+) = L-glutamine + 2- oxoglutarate + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- gltD
- Uniprot ID:
- P09832
- Molecular weight:
- 52015
Reactions
| 2 L-glutamate + NADP(+) = L-glutamine + 2-oxoglutarate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the removal of elemental sulfur and selenium atoms from cysteine and selenocysteine to produce alanine. Functions as a sulfur delivery protein for NAD, biotin and Fe-S cluster synthesis. Transfers sulfur on 'Cys-456' of thiI in a transpersulfidation reaction. Transfers sulfur on 'Cys-19' of tusA in a transpersulfidation reaction. Functions also as a selenium delivery protein in the pathway for the biosynthesis of selenophosphate
- Gene Name:
- iscS
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6B7
- Molecular weight:
- 45089
Reactions
| L-cysteine + acceptor = L-alanine + S-sulfanyl-acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- The physiological substrate is not known
- Gene Name:
- ydiB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6D5
- Molecular weight:
- 31228
Reactions
| L-quinate + NAD(P)(+) = 3-dehydroquinate + NAD(P)H. |
| Shikimate + NAD(P)(+) = 3-dehydroshikimate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- D-altronate + NAD(+) = D-tagaturonate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- uxaB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6L7
- Molecular weight:
- 54808
Reactions
| D-altronate + NAD(+) = D-tagaturonate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- sn-glycerol 3-phosphate + NAD(P)(+) = glycerone phosphate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- gpsA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6S7
- Molecular weight:
- 36361
Reactions
| sn-glycerol 3-phosphate + NAD(P)(+) = glycerone phosphate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the complicated ring closure reaction between the two acyclic compounds 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate (DXP) and 3-amino-2-oxopropyl phosphate (1-amino-acetone-3-phosphate or AAP) to form pyridoxine 5'-phosphate (PNP) and inorganic phosphate
- Gene Name:
- pdxJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A794
- Molecular weight:
- 26384
Reactions
| 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate + 3-amino-2-oxopropyl phosphate = pyridoxine 5'-phosphate + phosphate + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the condensation reaction of fatty acid synthesis by the addition to an acyl acceptor of two carbons from malonyl-ACP. Specific for elongation from C-10 to unsaturated C-16 and C-18 fatty acids
- Gene Name:
- fabB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A953
- Molecular weight:
- 42613
Reactions
| Acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + malonyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] = 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + CO(2) + [acyl-carrier-protein]. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the aldehyde or oxo group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
- Specific function:
- D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + phosphate + NAD(+) = 3-phospho-D-glyceroyl phosphate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- gapA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9B2
- Molecular weight:
- 35532
Reactions
| D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + phosphate + NAD(+) = 3-phospho-D-glyceroyl phosphate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in erythrose-4-phosphate dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NAD-dependent conversion of D-erythrose 4- phosphate to 4-phosphoerythronate
- Gene Name:
- epd
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9B6
- Molecular weight:
- 37299
Reactions
| D-erythrose 4-phosphate + NAD(+) + H(2)O = 4-phosphoerythronate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in nitrite reductase [NAD(P)H] activity
- Specific function:
- Required for activity of the reductase
- Gene Name:
- nirD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9I8
- Molecular weight:
- 12284
Reactions
| Ammonium hydroxide + 3 NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = nitrite + 3 NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- L-proline + NAD(P)(+) = 1-pyrroline-5- carboxylate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- proC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9L8
- Molecular weight:
- 28145
Reactions
| L-proline + NAD(P)(+) = 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Lipoamide dehydrogenase is a component of the glycine cleavage system as well as of the alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complexes
- Gene Name:
- lpdA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9P0
- Molecular weight:
- 50688
Reactions
| Protein N(6)-(dihydrolipoyl)lysine + NAD(+) = protein N(6)-(lipoyl)lysine + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- This enzyme has three activities:ADH, ACDH, and PFL- deactivase. In aerobic conditions it acts as a hydrogen peroxide scavenger. The PFL deactivase activity catalyzes the quenching of the pyruvate-formate-lyase catalyst in an iron, NAD, and CoA dependent reaction
- Gene Name:
- adhE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9Q7
- Molecular weight:
- 96126
Reactions
| An alcohol + NAD(+) = an aldehyde or ketone + NADH. |
| Acetaldehyde + CoA + NAD(+) = acetyl-CoA + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- (R)-propane-1,2-diol + NAD(+) = (R)- lactaldehyde + NADH
- Gene Name:
- fucO
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9S1
- Molecular weight:
- 40644
Reactions
| (R)-propane-1,2-diol + NAD(+) = (R)-lactaldehyde + NADH. |
| (S)-propane-1,2-diol + NAD(+) = (S)-lactaldehyde + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Converts galactitol 1-phosphate to tagatose 6-phosphate
- Gene Name:
- gatD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9S3
- Molecular weight:
- 37390
Reactions
| Galactitol-1-phosphate + NAD(+) = L-tagatose 6-phosphate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NAD-dependent oxidation of glycerol to dihydroxyacetone (glycerone). Allows microorganisms to utilize glycerol as a source of carbon under anaerobic conditions. In E.coli, an important role of gldA is also likely to regulate the intracellular level of dihydroxyacetone by catalyzing the reverse reaction, i.e. the conversion of dihydroxyacetone into glycerol. Possesses a broad substrate specificity, since it is also able to oxidize 1,2-propanediol and to reduce glycolaldehyde, methylglyoxal and hydroxyacetone into ethylene glycol, lactaldehyde and 1,2-propanediol, respectively
- Gene Name:
- gldA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9S5
- Molecular weight:
- 38712
Reactions
| Glycerol + NAD(+) = glycerone + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid binding
- Specific function:
- 3-phospho-D-glycerate + NAD(+) = 3- phosphonooxypyruvate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- serA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9T0
- Molecular weight:
- 44175
Reactions
| 3-phospho-D-glycerate + NAD(+) = 3-phosphonooxypyruvate + NADH. |
| 2-hydroxyglutarate + NAD(+) = 2-oxoglutarate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Formate dehydrogenase allows E.coli to use formate as major electron donor during anaerobic respiration, when nitrate is used as electron acceptor. The beta chain is an electron transfer unit containing 4 cysteine clusters involved in the formation of iron-sulfur centers. Electrons are transferred from the gamma chain to the molybdenum cofactor of the alpha subunit
- Gene Name:
- fdnH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAJ3
- Molecular weight:
- 32239
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- Allows to use formate as major electron donor during aerobic respiration. The beta chain is an electron transfer unit containing 4 cysteine clusters involved in the formation of iron- sulfur centers. Electrons are transferred from the gamma chain to the molybdenum cofactor of the alpha subunit
- Gene Name:
- fdoH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAJ5
- Molecular weight:
- 33100
- General function:
- Involved in NAD(P)+ transhydrogenase (AB-specific) activity
- Specific function:
- The transhydrogenation between NADH and NADP is coupled to respiration and ATP hydrolysis and functions as a proton pump across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- pntB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AB67
- Molecular weight:
- 48723
Reactions
| NADPH + NAD(+) = NADP(+) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- (R)-glycerate + NAD(P)(+) = 2-hydroxy-3- oxopropanoate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- garR
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABQ2
- Molecular weight:
- 30427
Reactions
| D-glycerate + NAD(P)(+) = 2-hydroxy-3-oxopropanoate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in dihydrofolate reductase activity
- Specific function:
- Key enzyme in folate metabolism. Catalyzes an essential reaction for de novo glycine and purine synthesis, and for DNA precursor synthesis
- Gene Name:
- folA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABQ4
- Molecular weight:
- 17999
Reactions
| 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate + NADP(+) = 7,8-dihydrofolate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the multicomponent 3-phenylpropionate dioxygenase. Converts 3-phenylpropionic acid (PP) and cinnamic acid (CI) into 3-phenylpropionate-dihydrodiol (PP-dihydrodiol) and cinnamic acid-dihydrodiol (CI-dihydrodiol), respectively
- Gene Name:
- hcaE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABR5
- Molecular weight:
- 51109
Reactions
| 3-phenylpropanoate + NADH + O(2) = 3-(cis-5,6-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,3-dien-1-yl)propanoate + NAD(+). |
| (2E)-3-phenylprop-2-enoate + NADH + O(2) = (2E)-3-(2,3-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate + NAD(+). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the multicomponent 3-phenylpropionate dioxygenase, that converts 3-phenylpropionic acid (PP) and cinnamic acid (CI) into 3-phenylpropionate-dihydrodiol (PP- dihydrodiol) and cinnamic acid-dihydrodiol (CI-dihydrodiol), respectively. This protein seems to be a 2Fe-2S ferredoxin
- Gene Name:
- hcaC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABW0
- Molecular weight:
- 11329
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Inosine 5'-phosphate + NAD(+) + H(2)O = xanthosine 5'-phosphate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- guaB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ADG7
- Molecular weight:
- 52022
Reactions
| Inosine 5'-phosphate + NAD(+) + H(2)O = xanthosine 5'-phosphate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in methyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Multifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the SAM-dependent methylation of uroporphyrinogen III at position C-2 and C-7 to form precorrin-2 and then position C-12 or C-18 to form trimethylpyrrocorphin 2. It also catalyzes the conversion of precorrin-2 into siroheme. This reaction consists of the NAD- dependent oxidation of precorrin-2 into sirohydrochlorin and its subsequent ferrochelation into siroheme
- Gene Name:
- cysG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEA8
- Molecular weight:
- 49951
Reactions
| S-adenosyl-L-methionine + uroporphyrinogen III = S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + precorrin-1. |
| S-adenosyl-L-methionine + precorrin-1 = S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + precorrin-2. |
| Precorrin-2 + NAD(+) = sirohydrochlorin + NADH. |
| Siroheme + 2 H(+) = sirohydrochlorin + Fe(2+). |
- General function:
- Involved in enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADH) activity
- Specific function:
- Acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NAD(+) = trans- 2,3-dehydroacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NADH
- Gene Name:
- fabI
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEK4
- Molecular weight:
- 27864
Reactions
| Acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NAD(+) = trans-2,3-dehydroacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in respiratory electron transport chain
- Specific function:
- Formate dehydrogenase allows E.coli to use formate as major electron donor during anaerobic respiration, when nitrate is used as electron acceptor. Subunit gamma is the cytochrome b556(FDN) component of the formate dehydrogenase
- Gene Name:
- fdnI
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEK7
- Molecular weight:
- 25368
- General function:
- Involved in respiratory electron transport chain
- Specific function:
- Allows to use formate as major electron donor during aerobic respiration. Subunit gamma is probably the cytochrome b556(FDO) component of the formate dehydrogenase
- Gene Name:
- fdoI
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEL0
- Molecular weight:
- 24606
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reduction of soluble flavins by reduced pyridine nucleotides. Seems to reduces the complexed Fe(3+) iron of siderophores to Fe(2+), thus releasing it from the chelator
- Gene Name:
- fre
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEN1
- Molecular weight:
- 26242
Reactions
| Reduced riboflavin + NAD(P)(+) = riboflavin + NAD(P)H. |
| 2 cob(II)alamin + NAD(+) = 2 aquacob(III)alamin + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- 7-alpha-dehydroxylation of cholic acid, yielding deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid, respectively. Highest affinity with taurochenodeoxycholic acid
- Gene Name:
- hdhA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AET8
- Molecular weight:
- 26778
Reactions
| 3-alpha,7-alpha,12-alpha-trihydroxy-5-beta-cholanate + NAD(+) = 3-alpha,12-alpha-dihydroxy-7-oxo-5-beta-cholanate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (NADPH) activity
- Specific function:
- 5-methyltetrahydrofolate + NAD(P)(+) = 5,10- methylenetetrahydrofolate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- metF
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEZ1
- Molecular weight:
- 33102
Reactions
| 5-methyltetrahydrofolate + NAD(P)(+) = 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on NADH or NADPH
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFC3
- Molecular weight:
- 16457
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFC7
- Molecular weight:
- 25056
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFD1
- Molecular weight:
- 18590
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient. This subunit may bind ubiquinone
- Gene Name:
- nuoH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFD4
- Molecular weight:
- 36219
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoI
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFD6
- Molecular weight:
- 20538
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFE0
- Molecular weight:
- 19874
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on NADH or NADPH
- Specific function:
- There are 2 NADH dehydrogenases in E.coli, however only this complex is able to use dNADH (reduced nicotinamide hypoxanthine dinucleotide, deamino-NADH) and dNADH-DB (dimethoxy- 5-methyl-6-decyl-1,4-benzoquinone) as substrates
- Gene Name:
- nuoK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFE4
- Molecular weight:
- 10845
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoM
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFE8
- Molecular weight:
- 56524
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoN
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFF0
- Molecular weight:
- 52044
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (succinyl-transferring) activity
- Specific function:
- The 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of 2-oxoglutarate to succinyl-CoA and CO(2). It contains multiple copies of three enzymatic components:2- oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (E1), dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase (E2) and lipoamide dehydrogenase (E3)
- Gene Name:
- sucA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFG3
- Molecular weight:
- 105061
Reactions
| 2-oxoglutarate + [dihydrolipoyllysine-residue succinyltransferase] lipoyllysine = [dihydrolipoyllysine-residue succinyltransferase] S-succinyldihydrolipoyllysine + CO(2). |
63. Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue succinyltransferase component of 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring acyl groups
- Specific function:
- The 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of 2-oxoglutarate to succinyl-CoA and CO(2). It contains multiple copies of three enzymatic components:2- oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (E1), dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase (E2) and lipoamide dehydrogenase (E3)
- Gene Name:
- sucB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFG6
- Molecular weight:
- 44011
Reactions
| Succinyl-CoA + enzyme N(6)-(dihydrolipoyl)lysine = CoA + enzyme N(6)-(S-succinyldihydrolipoyl)lysine. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA and CO(2). It contains multiple copies of three enzymatic components:pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1), dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase (E2) and lipoamide dehydrogenase (E3)
- Gene Name:
- aceE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFG8
- Molecular weight:
- 99668
Reactions
| Pyruvate + [dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase] lipoyllysine = [dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase] S-acetyldihydrolipoyllysine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reduction of dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate
- Gene Name:
- folM
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFS3
- Molecular weight:
- 26348
Reactions
| 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate + NADP(+) = 7,8-dihydrofolate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- 2,3-dihydro-2,3-dihydroxybenzoate + NAD(+) = 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- entA
- Uniprot ID:
- P15047
- Molecular weight:
- 26250
Reactions
| 2,3-dihydro-2,3-dihydroxybenzoate + NAD(+) = 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in choline dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Can catalyze the oxidation of choline to betaine aldehyde and betaine aldehyde to glycine betaine at the same rate
- Gene Name:
- betA
- Uniprot ID:
- P17444
- Molecular weight:
- 61877
Reactions
| Choline + acceptor = betaine aldehyde + reduced acceptor. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Betaine aldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O = betaine + NADH
- Gene Name:
- betB
- Uniprot ID:
- P17445
- Molecular weight:
- 52911
Reactions
| Betaine aldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O = betaine + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in 4-hydroxythreonine-4-phosphate dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NAD(P)-dependent oxidation of 4- (phosphohydroxy)-L-threonine (HTP) into 2-amino-3-oxo-4- (phosphohydroxy)butyric acid which spontaneously decarboxylates to form 3-amino-2-oxopropyl phosphate (AHAP)
- Gene Name:
- pdxA
- Uniprot ID:
- P19624
- Molecular weight:
- 35114
Reactions
| 4-(phosphonooxy)-L-threonine + NAD(+) = (2S)-2-amino-3-oxo-4-phosphonooxybutanoate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- This enzyme may serve as a scavenger, allowing the cell to utilize biotin sulfoxide as a biotin source. It reduces a spontaneous oxidation product of biotin, D-biotin D-sulfoxide (BSO or BDS), back to biotin
- Gene Name:
- bisC
- Uniprot ID:
- P20099
- Molecular weight:
- 85850
- General function:
- Involved in 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the formation of an hydroxyacyl-CoA by addition of water on enoyl-CoA. Also exhibits 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA epimerase and 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase activities. Involved in the aerobic and anaerobic degradation of long-chain fatty acids
- Gene Name:
- fadB
- Uniprot ID:
- P21177
- Molecular weight:
- 79593
Reactions
| (S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA + NAD(+) = 3-oxoacyl-CoA + NADH. |
| (3S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA = trans-2(or 3)-enoyl-CoA + H(2)O. |
| (S)-3-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA = (R)-3-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA. |
| (3Z)-dodec-3-enoyl-CoA = (2E)-dodec-2-enoyl-CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the breakdown of putrescine. Was previously shown to have a weak but measurable ALDH enzyme activity that prefers NADP over NAD as coenzyme
- Gene Name:
- puuC
- Uniprot ID:
- P23883
- Molecular weight:
- 53418
Reactions
| Gamma-glutamyl-gamma-aminobutyraldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O = gamma-glutamyl-gamma-aminobutyrate + NADH. |
| An aldehyde + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = a carboxylate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in formate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity
- Specific function:
- Formate dehydrogenase allows E.coli to use formate as major electron donor during anaerobic respiration, when nitrate is used as electron acceptor. The alpha subunit forms the active site
- Gene Name:
- fdnG
- Uniprot ID:
- P24183
- Molecular weight:
- 112963
Reactions
| Formate + NAD(+) = CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Various electron acceptors are also reduced by HMP in vitro, including dihydropterine, ferrisiderophores, ferric citrate, cytochrome c, nitrite, S-nitrosoglutathione, and alkylhydroperoxides. However, it is unknown if these reactions are of any biological significance in vivo
- Gene Name:
- hmp
- Uniprot ID:
- P24232
- Molecular weight:
- 43867
Reactions
| 2 NO + 2 O(2) + NAD(P)H = 2 NO(3)(-) + NAD(P)(+). |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Has high formaldehyde dehydrogenase activity in the presence of glutathione and catalyzes the oxidation of normal alcohols in a reaction that is not GSH-dependent. In addition, hemithiolacetals other than those formed from GSH, including omega-thiol fatty acids, also are substrates
- Gene Name:
- frmA
- Uniprot ID:
- P25437
- Molecular weight:
- 39359
Reactions
| S-(hydroxymethyl)glutathione + NAD(P)(+) = S-formylglutathione + NAD(P)H. |
| An alcohol + NAD(+) = an aldehyde or ketone + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Succinate semialdehyde + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = succinate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- gabD
- Uniprot ID:
- P25526
- Molecular weight:
- 51720
Reactions
| Succinate semialdehyde + NADP(+) + H(2)O = succinate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Acts on lactaldehyde as well as other aldehydes
- Gene Name:
- aldA
- Uniprot ID:
- P25553
- Molecular weight:
- 52272
Reactions
| (S)-lactaldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O = (S)-lactate + NADH. |
| Glycolaldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O = glycolate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-malate + NAD(+) = pyruvate + CO(2) + NADH
- Gene Name:
- sfcA
- Uniprot ID:
- P26616
- Molecular weight:
- 63197
Reactions
| (S)-malate + NAD(+) = pyruvate + CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in aminomethyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- The glycine cleavage system catalyzes the degradation of glycine
- Gene Name:
- gcvT
- Uniprot ID:
- P27248
- Molecular weight:
- 40146
Reactions
| [Protein]-S(8)-aminomethyldihydrolipoyllysine + tetrahydrofolate = [protein]-dihydrolipoyllysine + 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Conversion of NADPH, generated by peripheral catabolic pathways, to NADH, which can enter the respiratory chain for energy generation
- Gene Name:
- sthA
- Uniprot ID:
- P27306
- Molecular weight:
- 51560
Reactions
| NADPH + NAD(+) = NADP(+) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the four-electron oxidation of UDP-N-acetyl-D- mannosamine (UDP-ManNAc), reducing NAD(+) and releasing UDP-N- acetylmannosaminuronic acid (UDP-ManNAcA)
- Gene Name:
- wecC
- Uniprot ID:
- P27829
- Molecular weight:
- 45838
Reactions
| UDP-N-acetyl-D-mannosamine + 2 NAD(+) + H(2)O = UDP-N-acetyl-D-mannosaminuronate + 2 NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidation of 3-carboxy-2-hydroxy-4- methylpentanoate (3-isopropylmalate) to 3-carboxy-4-methyl-2- oxopentanoate. The product decarboxylates to 4-methyl-2 oxopentanoate
- Gene Name:
- leuB
- Uniprot ID:
- P30125
- Molecular weight:
- 39517
Reactions
| (2R,3S)-3-isopropylmalate + NAD(+) = 4-methyl-2-oxopentanoate + CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in Mo-molybdopterin cofactor biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Involved in sulfur transfer in the conversion of molybdopterin precursor Z to molybdopterin
- Gene Name:
- moaD
- Uniprot ID:
- P30748
- Molecular weight:
- 8758
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoF
- Uniprot ID:
- P31979
- Molecular weight:
- 49292
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in formate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity
- Specific function:
- Allows to use formate as major electron donor during aerobic respiration. Subunit alpha possibly forms the active site
- Gene Name:
- fdoG
- Uniprot ID:
- P32176
- Molecular weight:
- 112549
Reactions
| Formate + NAD(+) = CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- NAD(+) + H(2)O = AMP + NMN
- Gene Name:
- nudC
- Uniprot ID:
- P32664
- Molecular weight:
- 29689
Reactions
| NAD(+) + H(2)O = AMP + NMN. |
- General function:
- Involved in glycine dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) activity
- Specific function:
- The glycine cleavage system catalyzes the degradation of glycine. The P protein binds the alpha-amino group of glycine through its pyridoxal phosphate cofactor; CO(2) is released and the remaining methylamine moiety is then transferred to the lipoamide cofactor of the H protein
- Gene Name:
- gcvP
- Uniprot ID:
- P33195
- Molecular weight:
- 104376
Reactions
| Glycine + H-protein-lipoyllysine = H-protein-S-aminomethyldihydrolipoyllysine + CO(2). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on NADH or NADPH
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoC
- Uniprot ID:
- P33599
- Molecular weight:
- 68236
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in electron carrier activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoG
- Uniprot ID:
- P33602
- Molecular weight:
- 100298
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity
- Specific function:
- NDH-1 shuttles electrons from NADH, via FMN and iron- sulfur (Fe-S) centers, to quinones in the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme in this species is believed to be ubiquinone. Couples the redox reaction to proton translocation (for every two electrons transferred, four hydrogen ions are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane), and thus conserves the redox energy in a proton gradient
- Gene Name:
- nuoL
- Uniprot ID:
- P33607
- Molecular weight:
- 66438
Reactions
| NADH + quinone = NAD(+) + quinol. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of glyoxylate and hydroxypyruvate into glycolate and glycerate, respectively. Can also reduce 2,5-diketo-D-gluconate (25DKG) to 5-keto-D- gluconate (5KDG), 2-keto-D-gluconate (2KDG) to D-gluconate, and 2- keto-L-gulonate (2KLG) to L-idonate (IA), but it is not its physiological function. Inactive towards 2-oxoglutarate, oxaloacetate, pyruvate, 5-keto-D-gluconate, D-fructose and L- sorbose. Activity with NAD is very low
- Gene Name:
- ghrB
- Uniprot ID:
- P37666
- Molecular weight:
- 35395
Reactions
| Glycolate + NADP(+) = glyoxylate + NADPH. |
| D-glycerate + NAD(P)(+) = hydroxypyruvate + NAD(P)H. |
| D-gluconate + NADP(+) = 2-dehydro-D-gluconate + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reduction of 2,3-diketo-L-gulonate in the presence of NADH, to form 3-keto-L-gulonate
- Gene Name:
- dlgD
- Uniprot ID:
- P37672
- Molecular weight:
- 36572
Reactions
| 3-dehydro-L-gulonate + NAD(P)(+) = (4R,5S)-4,5,6-trihydroxy-2,3-dioxohexanoate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in dTDP-4-dehydrorhamnose reductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reduction of dTDP-6-deoxy-L-lyxo-4- hexulose to yield dTDP-L-rhamnose. RmlD uses NADH and NADPH nearly equally well
- Gene Name:
- rfbD
- Uniprot ID:
- P37760
- Molecular weight:
- 32694
Reactions
| dTDP-6-deoxy-L-mannose + NADP(+) = dTDP-4-dehydro-6-deoxy-L-mannose + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in 2-deoxy-D-gluconate 3-dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reduction of 2,5-diketo-3-deoxygluconate (DKII or 4,6-dihydroxy-2,5-dioxohexanoate) into 2-keto-3- deoxygluconate (KDG or 2-dehydro-3-deoxygluconate) with a concomitant oxidation of NADH
- Gene Name:
- kduD
- Uniprot ID:
- P37769
- Molecular weight:
- 27070
Reactions
| 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-gluconate + NAD(+) = (4S)-4,6-dihydroxy-2,5-dioxohexanoate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Reduction of a variety of nitroaromatic compounds using NADH (and to lesser extent NADPH) as source of reducing equivalents; two electrons are transferred. Capable of reducing nitrofurazone, quinones and the anti-tumor agent CB1954 (5- (aziridin-1-yl)-2,4-dinitrobenzamide). The reduction of CB1954 results in the generation of cytotoxic species
- Gene Name:
- nfnB
- Uniprot ID:
- P38489
- Molecular weight:
- 23905
Reactions
| A 5,6,7,8-tetrahydropteridine + NAD(P)(+) = a 6,7-dihydropteridine + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- D-mannonate + NAD(+) = D-fructuronate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- uxuB
- Uniprot ID:
- P39160
- Molecular weight:
- 53580
Reactions
| D-mannonate + NAD(+) = D-fructuronate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NADH/NADPH-dependent oxidation of L- idonate to 5-ketogluconate (5KG)
- Gene Name:
- idnD
- Uniprot ID:
- P39346
- Molecular weight:
- 37146
Reactions
| L-idonate + NAD(P)(+) = 5-dehydrogluconate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Preferred specificity is towards 1-propanol
- Gene Name:
- adhP
- Uniprot ID:
- P39451
- Molecular weight:
- 35379
Reactions
| An alcohol + NAD(+) = an aldehyde or ketone + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Fermentative lactate dehydrogenase
- Gene Name:
- ldhA
- Uniprot ID:
- P52643
- Molecular weight:
- 36535
Reactions
| (R)-lactate + NAD(+) = pyruvate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the radical-mediated insertion of two sulfur atoms into the C-6 and C-8 positions of the octanoyl moiety bound to the lipoyl domains of lipoate-dependent enzymes, thereby converting the octanoylated domains into lipoylated derivatives. Free octanoate is not a substrate for lipA
- Gene Name:
- lipA
- Uniprot ID:
- P60716
- Molecular weight:
- 36071
Reactions
| Protein N(6)-(octanoyl)lysine + 2 sulfur + 2 S-adenosyl-L-methionine = protein N(6)-(lipoyl)lysine + 2 L-methionine + 2 5'-deoxyadenosine. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reversible oxidation of malate to oxaloacetate
- Gene Name:
- mdh
- Uniprot ID:
- P61889
- Molecular weight:
- 32337
Reactions
| (S)-malate + NAD(+) = oxaloacetate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in isopentenyl diphosphate biosynthetic process, mevalonate-independent pathway
- Specific function:
- Converts 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate into isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP). Is also involved in penicillin tolerance and control of the stringent response. Seems to directly or indirectly interact with relA to maintain it in an inactive form during normal growth
- Gene Name:
- ispH
- Uniprot ID:
- P62623
- Molecular weight:
- 34774
Reactions
| Isopentenyl diphosphate + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate + NAD(P)H. |
| Dimethylallyl diphosphate + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on other nitrogenous compounds as donors
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reduction of hydroxylamine to form NH(3) and H(2)O. Is also able to reduce hydroxylamine analogs such as methylhydroxylamine and hydroxyquinone. Might have a role as a scavenger of potentially toxic by-products of nitrate metabolism
- Gene Name:
- hcp
- Uniprot ID:
- P75825
- Molecular weight:
- 60063
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of glyoxylate and hydroxypyruvate into glycolate and glycerate, respectively. Inactive towards 2-oxo-D-gluconate, 2-oxoglutarate, oxaloacetate and pyruvate. Only D- and L-glycerate are involved in the oxidative activity with NADP. Activity with NAD is very low
- Gene Name:
- ghrA
- Uniprot ID:
- P75913
- Molecular weight:
- 35343
Reactions
| Glycolate + NADP(+) = glyoxylate + NADPH. |
| D-glycerate + NAD(P)(+) = hydroxypyruvate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Could possibly oxidize fatty acids using specific components
- Gene Name:
- paaF
- Uniprot ID:
- P76082
- Molecular weight:
- 27237
Reactions
| (3S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA = trans-2(or 3)-enoyl-CoA + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-3-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA + NADP(+) = 3- acetoacetyl-CoA + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- paaH
- Uniprot ID:
- P76083
- Molecular weight:
- 51732
Reactions
| (S)-3-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA + NADP(+) = 3-acetoacetyl-CoA + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NAD-dependent reduction of succinylglutamate semialdehyde into succinylglutamate. Also shows activity with decanal or succinic semialdehyde as the electron donor and NAD as the electron acceptor. No activity is detected with NADP as the electron acceptor. Therefore, is an aldehyde dehydrogenase with broad substrate specificity
- Gene Name:
- astD
- Uniprot ID:
- P76217
- Molecular weight:
- 53026
Reactions
| N-succinyl-L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O = N-succinyl-L-glutamate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in magnesium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NAD(+)-dependent oxidative decarboxylation of D-malate into pyruvate. Is essential for aerobic growth on D- malate as the sole carbon source. But is not required for anaerobic D-malate utilization, although DmlA is expressed and active in those conditions. Appears to be not able to use L- tartrate as a substrate for dehydrogenation instead of D-malate
- Gene Name:
- dmlA
- Uniprot ID:
- P76251
- Molecular weight:
- 40315
Reactions
| (R)-malate + NAD(+) = pyruvate + CO(2) + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- UDP-glucose + 2 NAD(+) + H(2)O = UDP- glucuronate + 2 NADH
- Gene Name:
- ugd
- Uniprot ID:
- P76373
- Molecular weight:
- 43656
Reactions
| UDP-glucose + 2 NAD(+) + H(2)O = UDP-glucuronate + 2 NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- (R)-glycerate + NAD(P)(+) = 2-hydroxy-3- oxopropanoate + NAD(P)H
- Gene Name:
- glxR
- Uniprot ID:
- P77161
- Molecular weight:
- 30800
Reactions
| D-glycerate + NAD(P)(+) = 2-hydroxy-3-oxopropanoate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in flavin adenine dinucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Xanthine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = urate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- yagS
- Uniprot ID:
- P77324
- Molecular weight:
- 33858
Reactions
| Xanthine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = urate + NADH. |
| Hypoxanthine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = xanthine + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydroxymethyl-, formyl- and related transferase activity
- Specific function:
- Bifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of UDP-glucuronic acid (UDP-GlcUA) to UDP-4-keto- arabinose (UDP-Ara4O) and the addition of a formyl group to UDP-4- amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinose (UDP-L-Ara4N) to form UDP-L-4-formamido- arabinose (UDP-L-Ara4FN). The modified arabinose is attached to lipid A and is required for resistance to polymyxin and cationic antimicrobial peptides
- Gene Name:
- arnA
- Uniprot ID:
- P77398
- Molecular weight:
- 74288
Reactions
| UDP-alpha-D-glucuronate + NAD(+) = UDP-beta-L-threo-pentapyranos-4-ulose + CO(2) + NADH. |
| 10-formyltetrahydrofolate + UDP-4-amino-4-deoxy-beta-L-arabinose = 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate + UDP-4-deoxy-4-formamido-beta-L-arabinose. |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the formation of an hydroxyacyl-CoA by addition of water on enoyl-CoA. Also exhibits 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA epimerase and 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase activities. Strongly involved in the anaerobic degradation of long and medium-chain fatty acids in the presence of nitrate and weakly involved in the aerobic degradation of long-chain fatty acids
- Gene Name:
- fadJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P77399
- Molecular weight:
- 77072
Reactions
| (3S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA = trans-2(or 3)-enoyl-CoA + H(2)O. |
| (S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA + NAD(+) = 3-oxoacyl-CoA + NADH. |
| (S)-3-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA = (R)-3-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Xanthine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = urate + NADH
- Gene Name:
- yagR
- Uniprot ID:
- P77489
- Molecular weight:
- 78088
Reactions
| Xanthine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = urate + NADH. |
| Hypoxanthine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = xanthine + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the anaerobic utilization of allantoin
- Gene Name:
- allD
- Uniprot ID:
- P77555
- Molecular weight:
- 37967
Reactions
| (S)-ureidoglycolate + NAD(P)(+) = oxalureate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (acetylating) activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the conversion of acetaldehyde to acetyl-CoA, using NAD(+) and coenzyme A. Is the final enzyme in the meta- cleavage pathway for the degradation of 3-phenylpropanoate. Functions as a chaperone protein for folding of mhpE
- Gene Name:
- mhpF
- Uniprot ID:
- P77580
- Molecular weight:
- 33442
Reactions
| Acetaldehyde + CoA + NAD(+) = acetyl-CoA + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the multicomponent 3-phenylpropionate dioxygenase, that converts 3-phenylpropionic acid (PP) and cinnamic acid (CI) into 3-phenylpropionate-dihydrodiol (PP- dihydrodiol) and cinnamic acid-dihydrodiol (CI-dihydrodiol), respectively
- Gene Name:
- hcaD
- Uniprot ID:
- P77650
- Molecular weight:
- 43978
Reactions
| Reduced ferredoxin + NAD(+) = oxidized ferredoxin + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in aminobutyraldehyde dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidation of 1-pyrroline, which is spontaneously formed from 4-aminobutanal, leading to 4- aminobutanoate (GABA). Can also oxidize n-alkyl medium-chain aldehydes, but with a lower catalytic efficiency
- Gene Name:
- ydcW
- Uniprot ID:
- P77674
- Molecular weight:
- 50830
Reactions
| 4-aminobutanal + NAD(+) + H(2)O = 4-aminobutanoate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in FMN reductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes an NAD(P)H-dependent reduction of FMN, but is also able to reduce FAD or riboflavin
- Gene Name:
- ssuE
- Uniprot ID:
- P80644
- Molecular weight:
- 21253
Reactions
| FMNH(2) + NADP(+) = FMN + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Acts almost equally well on phenylacetaldehyde, 4- hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde
- Gene Name:
- feaB
- Uniprot ID:
- P80668
- Molecular weight:
- 53699
Reactions
| Phenylacetaldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O = phenylacetate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Presumed to be a dehydrogenase, but possibly an oxidase. Participates in limited purine salvage (requires aspartate) but does not support aerobic growth on purines as the sole carbon source (purine catabolism). Deletion results in increased adenine sensitivity, suggesting that this protein contributes to the conversion of adenine to guanine nucleotides during purine salvage
- Gene Name:
- xdhA
- Uniprot ID:
- Q46799
- Molecular weight:
- 81320
Reactions
| Xanthine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = urate + NADH. |
| Hypoxanthine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = xanthine + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in flavin adenine dinucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Presumed to be a dehydrogenase, but possibly an oxidase. Participates in limited purine salvage (requires aspartate) but does not support aerobic growth on purines as the sole carbon source (purine catabolism)
- Gene Name:
- xdhB
- Uniprot ID:
- Q46800
- Molecular weight:
- 31557
Reactions
| Xanthine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = urate + NADH. |
| Hypoxanthine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = xanthine + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Iron-sulfur subunit of the xanthine dehydrogenase complex
- Gene Name:
- xdhC
- Uniprot ID:
- Q46801
- Molecular weight:
- 16922
- General function:
- Involved in 3-phenylpropionate dioxygenase activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the multicomponent 3-phenylpropionate dioxygenase. Converts 3-phenylpropionic acid (PP) and cinnamic acid (CI) into 3-phenylpropionate-dihydrodiol (PP-dihydrodiol) and cinnamic acid-dihydrodiol (CI-dihydrodiol), respectively
- Gene Name:
- hcaF
- Uniprot ID:
- Q47140
- Molecular weight:
- 20579
Reactions
| 3-phenylpropanoate + NADH + O(2) = 3-(cis-5,6-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,3-dien-1-yl)propanoate + NAD(+). |
| (2E)-3-phenylprop-2-enoate + NADH + O(2) = (2E)-3-(2,3-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate + NAD(+). |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- yneI
- Uniprot ID:
- P76149
- Molecular weight:
- 49717
Reactions
| Succinate semialdehyde + NAD(P)(+) + H(2)O = succinate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis
- Specific function:
- Makes part of the rut operon, which is required for the utilization of pyrimidines as sole nitrogen source
- Gene Name:
- rutC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFQ5
- Molecular weight:
- 13763
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Converts 3-phenylpropionate-dihydrodiol (PP-dihydrodiol) and cinnamic acid-dihydrodiol (CI-dihydrodiol) into 3-(2,3-dihydroxylphenyl)propanoic acid (DHPP) and 2,3-dihydroxicinnamic acid (DHCI), respectively (By similarity). Converts 3-phenylpropionate-dihydrodiol (PP-dihydrodiol) and cinnamic acid-dihydrodiol (CI-dihydrodiol) into 3-(2,3-dihydroxylphenyl)propanoic acid (DHPP) and 2,3-dihydroxicinnamic acid (DHCI), respectively (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- hcaB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0CI31
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
Reactions
| 3-(cis-5,6-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,3-dien-1-yl)propanoate + NAD(+) = 3-(2,3-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoate + NADH. |
| 3-(cis-5,6-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,3-dien-1-yl)propanoate + NAD(+) = 3-(2,3-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoate + NADH. |
| (2E)-3-(cis-5,6-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,3-dien-1-yl)prop-2-enoate + NAD(+) = (2E)-3-(2,3-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- yihU
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9V8
- Molecular weight:
- 31158
- General function:
- Involved in FMN binding
- Specific function:
- Makes part of the rut operon, which is required for the utilization of pyrimidines as sole nitrogen source
- Gene Name:
- rutF
- Uniprot ID:
- P75893
- Molecular weight:
- 17749
Reactions
| FMNH(2) + NAD(+) = FMN + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in iron-sulfur cluster binding
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- yeiA
- Uniprot ID:
- P25889
- Molecular weight:
- 45069
Reactions
| 5,6-dihydrouracil + NAD(+) = uracil + NADH. |
| 5,6-dihydrothymine + NAD(+) = thymine + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on paired donors, with incorporation or reduction of molecular oxygen
- Specific function:
- Part of the rut operon, which is required for the utilization of pyrimidines as sole nitrogen source
- Gene Name:
- rutA
- Uniprot ID:
- P75898
- Molecular weight:
- 42219
Reactions
| Uracil + FMNH(2) + O(2) = (Z)-3-ureidoacrylate peracid + FMN + H(2)O. |
| Thymine + FMNH(2) + O(2) = (Z)-2-methylureidoacrylate peracid + FMN + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- yeiT
- Uniprot ID:
- P76440
- Molecular weight:
- 44329
Reactions
| 5,6-dihydrouracil + NAD(+) = uracil + NADH. |
| 5,6-dihydrothymine + NAD(+) = thymine + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Putative L-galactonate oxidoreductase that is required for growth on L-galactonate as the sole carbon source
- Gene Name:
- yjjN
- Uniprot ID:
- P39400
- Molecular weight:
- 36448
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Reduces trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) into trimethylamine; an anaerobic reaction coupled to energy-yielding reactions
- Gene Name:
- torA
- Uniprot ID:
- P33225
- Molecular weight:
- 94455
Reactions
| Trimethylamine + 2 (ferricytochrome c)-subunit + H(2)O = trimethylamine N-oxide + 2 (ferrocytochrome c)-subunit + 2 H(+). |
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the anaerobic respiratory chain of trimethylamine-N-oxide reductase torA. Acts by transferring electrons from the membranous menaquinones to torA. This transfer probably involves an electron transfer pathway from menaquinones to the N-terminal domain of torC, then from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, and finally to torA. TorC apocytochrome negatively autoregulates the torCAD operon probably by inhibiting the torS kinase activity
- Gene Name:
- torC
- Uniprot ID:
- P33226
- Molecular weight:
- 43606
- General function:
- Involved in thiamine biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the synthesis of the hydroxymethylpyrimidine phosphate (HMP-P) moiety of thiamine from aminoimidazole ribotide (AIR) in a radical S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM)-dependent reaction
- Gene Name:
- thiC
- Uniprot ID:
- P30136
- Molecular weight:
- 70850
Reactions
| 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole + S-adenosyl-L-methionine = 4-amino-2-methyl-5-phosphomethylpyrimidine + 5'-deoxyadenosine + L-methionine + formate + CO. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidation-reduction process
- Specific function:
- One of at least two accessory proteins for anaerobic nitric oxide (NO) reductase. Reduces the rubredoxin moiety of NO reductase
- Gene Name:
- norW
- Uniprot ID:
- P37596
- Molecular weight:
- 41403
Reactions
| Reduced NO reductase rubredoxin + NAD(+) = oxidized NO reductase rubredoxin + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)propionate hydroxylase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the insertion of one atom of molecular oxygen into position 2 of the phenyl ring of 3-(3- hydroxyphenyl)propionate (3-HPP) and hydroxycinnamic acid (3HCI)
- Gene Name:
- mhpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P77397
- Molecular weight:
- 62185
Reactions
| 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate + NADH + O(2) = 3-(2,3-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoate + H(2)O + NAD(+). |
| (2E)-3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate + NADH + O(2) = (2E)-3-(2,3-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate + H(2)O + NAD(+). |
- General function:
- Amino acid transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- The glycine cleavage system catalyzes the degradation of glycine. The H protein shuttles the methylamine group of glycine from the P protein to the T protein
- Gene Name:
- gcvH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6T9
- Molecular weight:
- 13811
- General function:
- Involved in iron ion binding
- Specific function:
- Anaerobic nitric oxide reductase; uses NADH to detoxify nitric oxide (NO), protecting several 4Fe-4S NO-sensitive enzymes. Has at least 2 reductase partners, only one of which (NorW, flavorubredoxin reductase) has been identified. NO probably binds to the di-iron center; electrons enter from the reductase at rubredoxin and are transferred sequentially to the FMN center and the di-iron center. Also able to function as an aerobic oxygen reductase
- Gene Name:
- norV
- Uniprot ID:
- Q46877
- Molecular weight:
- 54234
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- eutE
- Uniprot ID:
- P77445
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- yiaY
- Uniprot ID:
- P37686
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- eutG
- Uniprot ID:
- P76553
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- paoA
- Uniprot ID:
- P77165
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- yeaW
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABR7
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- nfsA
- Uniprot ID:
- P17117
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- nemA
- Uniprot ID:
- P77258
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- yjeF
- Uniprot ID:
- P31806
- Molecular weight:
- 54650
Reactions
| ADP + (6S)-6-beta-hydroxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydronicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide = AMP + phosphate + NADH. |
| (R)-NADHX = (S)-NADHX. |
- General function:
- zinc ion binding
- Specific function:
- Not known; probable catabolic enzyme.
- Gene Name:
- rspB
- Uniprot ID:
- P38105
- Molecular weight:
- 36563
Reactions
| = |
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the formation of an hydroxyacyl-CoA by addition of water on enoyl-CoA. Also exhibits 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA epimerase and 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase activities. Involved in the aerobic and anaerobic degradation of long-chain fatty acids
- Gene Name:
- fadB
- Uniprot ID:
- P21177
- Molecular weight:
- 79593
Reactions
| (S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA + NAD(+) = 3-oxoacyl-CoA + NADH. |
| (3S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA = trans-2(or 3)-enoyl-CoA + H(2)O. |
| (S)-3-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA = (R)-3-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA. |
| (3Z)-dodec-3-enoyl-CoA = (2E)-dodec-2-enoyl-CoA. |