Deoxyadenosine (ECMDB00101) (M2MDB000039)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2012-05-31 09:57:24 -0600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2015-09-13 15:15:17 -0600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Accession Numbers |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
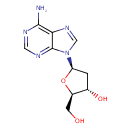
| Name: | Deoxyadenosine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Deoxyadenosine is a member of the chemical class known as Purine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides and Analogues. These are compounds consisting of a purine linked to a ribose which lacks an hydroxyl group at position 2. Deoxyadenosine is a deoxyribonucleoside. It is a derivative of the nucleoside adenosine, differing from the latter by the replacement of a hydroxyl group (-OH) by hydrogen (-H) at the 2' position of its ribose sugar moiety. Deoxyadenosine is the DNA nucleoside A, which pairs with deoxythymidine (T) in double-stranded DNA. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C10H13N5O3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight: | Average: 251.2419 Monoisotopic: 251.101839307 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | OLXZPDWKRNYJJZ-RRKCRQDMSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C10H13N5O3/c11-9-8-10(13-3-12-9)15(4-14-8)7-1-5(17)6(2-16)18-7/h3-7,16-17H,1-2H2,(H2,11,12,13)/t5-,6+,7+/m0/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 958-09-8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | (2R,3S,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-3-ol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | 2-deoxyadenosine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@H]1C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as purine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides. Purine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides are compounds consisting of a purine linked to a ribose which lacks a hydroxyl group at position 2. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Nucleosides, nucleotides, and analogues | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Purine nucleosides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Purine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Purine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | 189 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | Deoxyadenosine monophosphate + Water > Deoxyadenosine + Phosphate Deoxyadenosine + Hydrogen ion + Water > Deoxyinosine + Ammonium Deoxyadenosine + Phosphate <> Deoxyribose 1-phosphate + Adenine Deoxyadenosine monophosphate + Water <> Deoxyadenosine + Phosphate Deoxyadenosine + Water <> Deoxyinosine + Ammonia Water + Deoxyadenosine > Ammonia + Deoxyinosine Deoxyadenosine + Phosphate <> Adenine + deoxyribose-1-phosphate Deoxyadenosine + Phosphate > Adenine + Deoxyribose 1-phosphate Deoxyinosine + Ammonium < Water + Hydrogen ion + Deoxyadenosine Deoxyadenosine monophosphate + Water > Deoxyadenosine + Phosphate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EcoCyc Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Find out more about how we convert literature concentrations. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Anderson, Charles D.; Goodman, Leon; Baker, B. R. Potential anticancer agents. XIX. Synthesis of 2-deoxyadenosine. Journal of the American Chemical Society (1959), 81 3967-74. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Degradation of external UDP-glucose to uridine monophosphate and glucose-1-phosphate, which can then be used by the cell
- Gene Name:
- ushA
- Uniprot ID:
- P07024
- Molecular weight:
- 60824
Reactions
| UDP-sugar + H(2)O = UMP + alpha-D-aldose 1-phosphate. |
| A 5'-ribonucleotide + H(2)O = a ribonucleoside + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Nucleotidase with a broad substrate specificity as it can dephosphorylate various ribo- and deoxyribonucleoside 5'- monophosphates and ribonucleoside 3'-monophosphates with highest affinity to 3'-AMP. Also hydrolyzes polyphosphate (exopolyphosphatase activity) with the preference for short-chain- length substrates (P20-25). Might be involved in the regulation of dNTP and NTP pools, and in the turnover of 3'-mononucleotides produced by numerous intracellular RNases (T1, T2, and F) during the degradation of various RNAs. Also plays a significant physiological role in stress-response and is required for the survival of E.coli in stationary growth phase
- Gene Name:
- surE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A840
- Molecular weight:
- 26900
Reactions
| A 5'-ribonucleotide + H(2)O = a ribonucleoside + phosphate. |
| A 3'-ribonucleotide + H(2)O = a ribonucleoside + phosphate. |
| (Polyphosphate)(n) + H(2)O = (polyphosphate)(n-1) + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Nucleotidase that shows high phosphatase activity toward three nucleoside 5'-monophosphates, UMP, dUMP, and dTMP, and very low activity against TDP, IMP, UDP, GMP, dGMP, AMP, dAMP, and 6- phosphogluconate. Is strictly specific to substrates with 5'- phosphates and shows no activity against nucleoside 2'- or 3'- monophosphates. Might be involved in the pyrimidine nucleotide substrate cycles
- Gene Name:
- yjjG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A8Y1
- Molecular weight:
- 25300
Reactions
| A 5'-ribonucleotide + H(2)O = a ribonucleoside + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in purine-nucleoside phosphorylase activity
- Specific function:
- Cleavage of guanosine or inosine to respective bases and sugar-1-phosphate molecules
- Gene Name:
- deoD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABP8
- Molecular weight:
- 25950
Reactions
| Purine nucleoside + phosphate = purine + alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in acid phosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- Dephosphorylates several organic phosphomonoesters and catalyzes the transfer of low-energy phosphate groups from phosphomonoesters to hydroxyl groups of various organic compounds. Preferentially acts on aryl phosphoesters. Might function as a broad-spectrum dephosphorylating enzyme able to scavenge both 3'- and 5'-nucleotides and also additional organic phosphomonoesters
- Gene Name:
- aphA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE22
- Molecular weight:
- 26103
Reactions
| A phosphate monoester + H(2)O = an alcohol + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in deaminase activity
- Specific function:
- Adenosine + H(2)O = inosine + NH(3)
- Gene Name:
- add
- Uniprot ID:
- P22333
- Molecular weight:
- 36397
Reactions
| Adenosine + H(2)O = inosine + NH(3). |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Nucleotidase that shows strict specificity toward deoxyribonucleoside 5'-monophosphates and does not dephosphorylate 5'-ribonucleotides or ribonucleoside 3'-monophosphates. Might be involved in the regulation of all dNTP pools in E.coli
- Gene Name:
- yfbR
- Uniprot ID:
- P76491
- Molecular weight:
- 22708
Reactions
| A 5'-ribonucleotide + H(2)O = a ribonucleoside + phosphate. |
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in nucleoside:sodium symporter activity
- Specific function:
- Transports nucleosides with a high affinity except guanosine and deoxyguanosine. Driven by a proton motive force
- Gene Name:
- nupC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFF2
- Molecular weight:
- 43475
- General function:
- Involved in nucleoside transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Transports nucleosides with a high affinity. Driven by a proton motive force
- Gene Name:
- nupG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFF4
- Molecular weight:
- 46389
- General function:
- Involved in nucleoside:sodium symporter activity
- Specific function:
- Nucleoside transporter
- Gene Name:
- nupX
- Uniprot ID:
- P33021
- Molecular weight:
- 43409
- General function:
- Involved in nucleoside transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Constitutes the receptor for colicin K and phage T6, and functions as substrate-specific channel for nucleosides and deoxynucleosides
- Gene Name:
- tsx
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A927
- Molecular weight:
- 33589