L-Valine (ECMDB00883) (M2MDB000196)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2012-05-31 13:01:47 -0600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2015-09-13 12:56:09 -0600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Accession Numbers |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
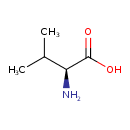
| Name: | L-Valine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Valine is an alpha-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH(NH2)CH(CH3)2. L-Valine is one of 20 proteinogenic amino acids. Its codons are GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG. This amino acid is classified as nonpolar. Along with leucine and isoleucine, valine is a branched-chain amino acid. It is named after the plant valerian. (Wikipedia) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C5H11NO2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight: | Average: 117.1463 Monoisotopic: 117.078978601 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | KZSNJWFQEVHDMF-BYPYZUCNSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C5H11NO2/c1-3(2)4(6)5(7)8/h3-4H,6H2,1-2H3,(H,7,8)/t4-/m0/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 72-18-4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | (2S)-2-amino-3-methylbutanoic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | L-valine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | CC(C)[C@H](N)C(O)=O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as valine and derivatives. Valine and derivatives are compounds containing valine or a derivative thereof resulting from reaction of valine at the amino group or the carboxy group, or from the replacement of any hydrogen of glycine by a heteroatom. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Valine and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | 295-300 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | Adenosine triphosphate + Water + L-Valine > ADP + Hydrogen ion + Phosphate + L-Valine Adenosine triphosphate + Water + L-Valine > ADP + Hydrogen ion + Phosphate + L-Valine alpha-Ketoisovaleric acid + L-Alanine <> Pyruvic acid + L-Valine + a-Ketoisovaleric acid alpha-Ketoglutarate + L-Valine <> alpha-Ketoisovaleric acid + L-Glutamate Adenosine triphosphate + tRNA(Val) + L-Valine + tRNA(Val) <> Adenosine monophosphate + Pyrophosphate + L-Valyl-tRNA(Val) + L-Valyl-tRNA(Val) L-Valine + Pyruvic acid <> alpha-Ketoisovaleric acid + L-Alanine Adenosine triphosphate + L-Valine + tRNA(Val) <> Adenosine monophosphate + Pyrophosphate + L-Valyl-tRNA(Val) Adenosine triphosphate + L-Valine + Water > ADP + Phosphate + L-Valine + Hydrogen ion Adenosine triphosphate + L-Valine + Water > ADP + Phosphate + L-Valine + Hydrogen ion L-Valine + Oxoglutaric acid <> alpha-Ketoisovaleric acid + L-Glutamate L-Valine + Pyruvic acid > a-Ketoisovaleric acid + L-Alanine L-Valine + Oxoglutaric acid > a-Ketoisovaleric acid + L-Glutamate Adenosine triphosphate + L-Valine + tRNA(Val) > Adenosine monophosphate + Pyrophosphate + L-valyl-tRNA(Val) L-Valine + Pyruvic acid + L-Valine > L-Alanine + a-Ketoisovaleric acid + L-Alanine a-Ketoisovaleric acid + L-Glutamic acid + L-Glutamate > Oxoglutaric acid + L-Valine + L-Valine Isovaleric acid + L-Glutamic acid + L-Glutamate > Oxoglutaric acid + L-Valine + L-Valine 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid + L-Glutamic acid + 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid + L-Glutamate > Oxoglutaric acid + L-Valine + L-Valine L-Valine + Adenosine triphosphate + Hydrogen ion + tRNA(Val) + L-Valine > Adenosine monophosphate + Pyrophosphate + L-Valyl-tRNA(Val) L-Valine + Adenosine triphosphate + Water + L-Valine > L-Valine + Adenosine diphosphate + Pyrophosphate + Hydrogen ion + ADP Adenosine triphosphate + tRNA(Val) + L-Valine <> Adenosine monophosphate + Pyrophosphate + L-Valyl-tRNA(Val) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EcoCyc Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Find out more about how we convert literature concentrations. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Kinoshita, Shukuo; Udaka, Shigezo. L-Valine production by fermentation. (1962), 2 pp. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the attachment of valine to tRNA(Val). As ValRS can inadvertently accommodate and process structurally similar amino acids such as threonine, to avoid such errors, it has a "posttransfer" editing activity that hydrolyzes mischarged Thr-tRNA(Val) in a tRNA-dependent manner
- Gene Name:
- valS
- Uniprot ID:
- P07118
- Molecular weight:
- 108192
Reactions
| ATP + L-valine + tRNA(Val) = AMP + diphosphate + L-valyl-tRNA(Val). |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity
- Specific function:
- L-valine + pyruvate = 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate + L-alanine
- Gene Name:
- avtA
- Uniprot ID:
- P09053
- Molecular weight:
- 46711
Reactions
| L-valine + pyruvate = 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate + L-alanine. |
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for branched-chain amino acids. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrates across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- livH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEX7
- Molecular weight:
- 32982
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for branched-chain amino acids. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrates across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- livM
- Uniprot ID:
- P22729
- Molecular weight:
- 46269
- General function:
- Involved in 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- yfbQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A959
- Molecular weight:
- 45517
Reactions
| L-alanine + 2-oxoglutarate = pyruvate + L-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Acts on leucine, isoleucine and valine
- Gene Name:
- ilvE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AB80
- Molecular weight:
- 34093
Reactions
| L-leucine + 2-oxoglutarate = 4-methyl-2-oxopentanoate + L-glutamate. |
| L-isoleucine + 2-oxoglutarate = (S)-3-methyl-2-oxopentanoate + L-glutamate. |
| L-valine + 2-oxoglutarate = 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate + L-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Component of the leucine-specific transport system
- Gene Name:
- livG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9S7
- Molecular weight:
- 28427
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid transport
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of the leucine, isoleucine, valine, (threonine) transport system, which is one of the two periplasmic binding protein-dependent transport systems of the high-affinity transport of the branched-chain amino acids
- Gene Name:
- livJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AD96
- Molecular weight:
- 39076
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Component of the leucine-specific transport system
- Gene Name:
- livF
- Uniprot ID:
- P22731
- Molecular weight:
- 26310
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Probably part of a binding-protein-dependent transport system yecCS for an amino acid. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- yecC
- Uniprot ID:
- P37774
- Molecular weight:
- 27677
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probably part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system yecCS for an amino acid; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- yecS
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFT2
- Molecular weight:
- 24801
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for branched-chain amino acids. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrates across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- livH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEX7
- Molecular weight:
- 32982
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for branched-chain amino acids. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrates across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- livM
- Uniprot ID:
- P22729
- Molecular weight:
- 46269
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Non-specific porin
- Gene Name:
- ompN
- Uniprot ID:
- P77747
- Molecular weight:
- 41220
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Uptake of inorganic phosphate, phosphorylated compounds, and some other negatively charged solutes
- Gene Name:
- phoE
- Uniprot ID:
- P02932
- Molecular weight:
- 38922
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Component of the leucine-specific transport system
- Gene Name:
- livG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A9S7
- Molecular weight:
- 28427
- General function:
- Involved in amino acid transport
- Specific function:
- This protein is a component of the leucine, isoleucine, valine, (threonine) transport system, which is one of the two periplasmic binding protein-dependent transport systems of the high-affinity transport of the branched-chain amino acids
- Gene Name:
- livJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AD96
- Molecular weight:
- 39076
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Component of the leucine-specific transport system
- Gene Name:
- livF
- Uniprot ID:
- P22731
- Molecular weight:
- 26310
- General function:
- Involved in efflux transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- ygaH
- Uniprot ID:
- P43667
- Molecular weight:
- 12023
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- OmpF is a porin that forms passive diffusion pores which allow small molecular weight hydrophilic materials across the outer membrane. It is also a receptor for the bacteriophage T2
- Gene Name:
- ompF
- Uniprot ID:
- P02931
- Molecular weight:
- 39333
- General function:
- Involved in branched-chain aliphatic amino acid transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the LIV-II transport system for branched- chain amino acids. This LIV-II transport system may be H(+)- coupled
- Gene Name:
- brnQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AD99
- Molecular weight:
- 46208
- General function:
- Amino acid transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- ygaZ
- Uniprot ID:
- P76630
- Molecular weight:
- 26107
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Forms passive diffusion pores which allow small molecular weight hydrophilic materials across the outer membrane
- Gene Name:
- ompC
- Uniprot ID:
- P06996
- Molecular weight:
- 40368