4,5-Dihydroorotic acid (ECMDB00528) (M2MDB000147)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2012-05-31 10:27:15 -0600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2015-06-03 15:53:30 -0600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Accession Numbers |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid is a substrate of the enzyme orotate reductase [EC 1.3.1.14], which is part of the pyrimidine metabolism pathway. (KEGG) Dihydroorotate is oxidized by Dihydroorotate dehydrogenases (DHODs) to orotate. These dehydrogenases use their FMN (flavin mononucleotide) prosthetic group to abstract a hydride equivalent from C6 to deprotonate C5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
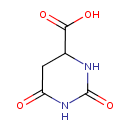
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C5H6N2O4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight: | Average: 158.1121 Monoisotopic: 158.03275669 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | UFIVEPVSAGBUSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C5H6N2O4/c8-3-1-2(4(9)10)6-5(11)7-3/h2H,1H2,(H,9,10)(H2,6,7,8,11) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 155-54-4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | 2,6-dioxo-1,3-diazinane-4-carboxylic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | dihydroorotic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | OC(=O)C1CC(=O)NC(=O)N1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alpha amino acids and derivatives. These are amino acids in which the amino group is attached to the carbon atom immediately adjacent to the carboxylate group (alpha carbon), or a derivative thereof. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Alpha amino acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | -1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid + Ubiquinone-8 > Orotic acid + Ubiquinol-8 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid + Menaquinone 8 > Menaquinol 8 + Orotic acid 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid + Water <> Ureidosuccinic acid + Hydrogen ion 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid + Fumaric acid <> Orotic acid + Succinic acid 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid + Water <> Ureidosuccinic acid 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid + a ubiquinone > Orotic acid + a ubiquinol 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid + a menaquinone > Orotic acid + a menaquinol 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid + Quinone <> Orotic acid + Hydroquinone N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate + Hydrogen ion > Water + 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid + 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid + Ubiquinone-1 + 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid > Ubiquinol-1 + Orotic acid 4 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid + Fumaric acid <> Orotic acid + Succinic acid 4 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid + Quinone <> Orotic acid + Hydroquinone 4 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid + Water <> Ureidosuccinic acid + Hydrogen ion 4 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid + Fumaric acid <> Orotic acid + Succinic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Pathways: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EcoCyc Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Find out more about how we convert literature concentrations. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Burger, Klaus; Neuhauser, Horst; Rudolph, Martin. A new, preparatively simple way to dihydroorotic acid, 1-methyl-4,5-dihydroorotic acid and their derivatives. Chemiker-Zeitung (1990), 114(7-8), 251-5. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-dihydroorotate + H(2)O = N-carbamoyl-L- aspartate
- Gene Name:
- pyrC
- Uniprot ID:
- P05020
- Molecular weight:
- 38827
Reactions
| (S)-dihydroorotate + H(2)O = N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-dihydroorotate + a quinone = orotate + a quinol
- Gene Name:
- pyrD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A7E1
- Molecular weight:
- 36774
Reactions
| (S)-dihydroorotate + a quinone = orotate + a quinol. |